93% of doctors believe digital tools lead to better patient outcomes.
80% now offer virtual consultations. The healthcare experience has changed (for doctors and for patients) and there’s no going back.
Top players like BCG predict a more than 80% compound annual growth rate for AI and GenAI use in healthcare over the next five years.
These numbers are just a glimpse of what’s possible with digital transformation in healthcare. So, how does this work out across the healthcare workforce every day?
Sometimes, it’s as simple as a nurse being able to pull up patient records in seconds instead of spending 40 minutes digging through paper files. This is a small example, but behind the scenes, even more powerful changes are underway (and we can't wait to unpack them).
If you work in L&D, IT, clinical operations, or public health, and you're helping roll out systems like EHRs, AI tools, remote patient monitoring, etc., this blog is for you. We’ll break down what digital transformation in healthcare really means and how to make sure the technology actually works for the people using it.
Scan the Sections:
- What is Digital Transformation in Healthcare?
- Examples of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
- Importance of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
- Benefits of Digital transformation in Healthcare
- Challenges of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
- Best Practices for Implementing Digital Transformation in Healthcare
- Digital Transformation in Healthcare Case Studies
What is Digital Transformation in Healthcare?
DEFINITION:
Digital transformation in healthcare is the purposeful adoption of digital technologies across clinical, administrative, and operational functions to enhance patient experiences, boost care efficiency, and deliver better care outcomes.
1. Digitization
- The first step involves converting paper-based records and analog workflows into digital formats.
- Goal: Preserve or store information digitally.
- Example: Scanning paper medical records and storing them as PDFs or entering handwritten prescriptions into a digital file.
2. Digitalization
- This stage focuses on using digital tools to optimize existing healthcare processes.
- Goal: Increase efficiency, accuracy, and speed.
- Example: Using Electronic Health Records (EHRs) to access patient history instantly, or automating appointment reminders through SMS.
3. Digital Transformation
- The most advanced stage, where entire systems, workflows, and care models are reimagined and redesigned around digital capabilities.
- Goal: Deliver connected, personalized, and proactive care at scale.
- Example: Implementing AI-powered diagnostics, remote patient monitoring, and integrated platforms that track patient outcomes across care settings.
Each layer builds upon the previous one, moving healthcare organizations closer to a fully connected, data-driven, and patient-centered future.
Examples of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
Let’s take a closer look at some of the key ways healthcare technology is being applied today:
1. Telemedicine
Bringing Care to Your Doorstep
- Telemedicine has made it easier for people to access care without leaving their homes, which is especially beneficial for those in rural or underserved areas.
- Platforms like Teladoc and Amwell allow patients to consult with doctors via video calls, phone calls, or even messaging. This is especially important for people with mobility issues, chronic illnesses, or those who live in areas far from healthcare facilities.
- For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine proved essential in ensuring that people could still receive medical advice while minimizing the risk of exposure.
2. Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Simplifying Patient Data
- Imagine being a doctor who has to track down a patient’s health records from different departments – that sounds like a nightmare, right?
- Well, EHR systems like Epic and Cerner solve this issue by providing a centralized, easily accessible record of a patient’s medical history.
- These systems allow different healthcare providers – from specialists to nurses – to access the same data in real time, ensuring that every member of the care team has a complete picture of the patient’s health.

3. AI in Diagnostics
Smarter, Faster Diagnoses
- AI is transforming the way doctors diagnose and treat illnesses. Tools like IBM Watson Health and PathAI analyze massive amounts of data, including medical images, to help doctors spot patterns and make quicker, more accurate diagnoses.
- Whether it’s detecting cancer earlier through imaging or analyzing medical histories to predict heart disease risk, AI is speeding up the diagnostic process and helping doctors make better decisions.
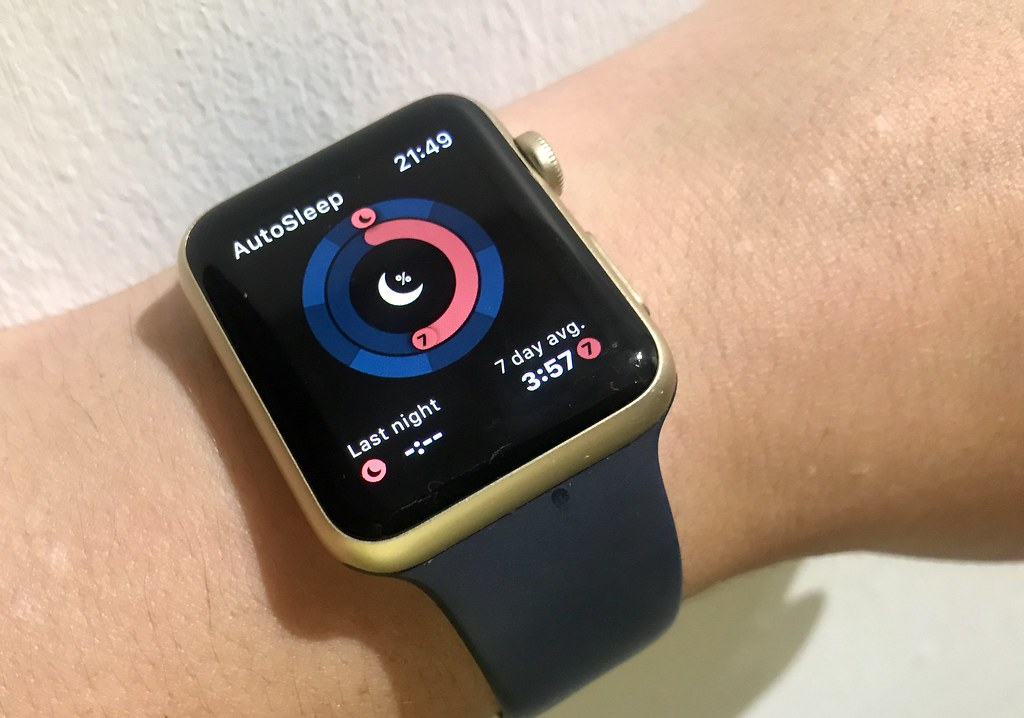
4. Wearables and Remote Monitoring
Keeping Health in Check 24/7
- IoT Devices like the Apple Watch or Fitbit aren’t just fitness trackers – they’re also healthcare tools. These wearables monitor things like heart rate, activity levels, and even sleep patterns.
- Some are even capable of tracking things like blood oxygen levels, ECGs, or detecting falls. With the data collected, healthcare providers can monitor their patients’ health remotely, identifying issues before they become emergencies.

5. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Reducing Admin Work and Improving Efficiency
- A lot of time in healthcare is spent on repetitive administrative tasks like scheduling appointments, processing billing, and handling paperwork.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tools like UiPath or Blue Prism automate these routine tasks, freeing up healthcare staff to focus more on patient care.
- Instead of spending hours on admin work, staff can devote their time to more meaningful, patient-focused activities.
6. Patient Portals and Mobile Apps
Giving Patients Control
- Apps like MyChart and other patient portals give patients easy access to their own medical records, allowing them to track appointments, lab results, and prescriptions.
- These tools empower patients to be more involved in their own care, allowing them to book appointments, communicate with doctors, and access their health information without needing to call the office.
- This is particularly useful for managing chronic conditions or keeping up with ongoing treatments.
7. Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
Supporting Better Decisions
- When doctors are faced with complex cases, Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) like UpToDate and Zynx Health provide evidence-based recommendations to help them make informed decisions.
- These systems tap into vast libraries of clinical guidelines, research, and patient data to give healthcare providers the most relevant and up-to-date information, helping them choose the best treatment plans for their patients.
It may sound like this is all technology of the future, but it’s already changing lives today. As it grows, it brings better and more affordable care to more people.
Importance of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
Each group within the healthcare ecosystem experiences digital transformation in its own way, based on its roles, needs, and priorities. Let’s look in more detail:
1. For Hospital Leaders / Administrators:
- Digital transformation matters to hospital leaders and administrators because it supports smarter decision-making, improves patient throughput, and reduces administrative overhead.
- With technologies like AI-powered diagnostic tools and automated billing, they can manage resources, reduce human error, and improve the bottom line.
- Take: Narayana Health, one of India's largest hospital networks, implemented AI-backed analytics to optimize OT schedules and reduce patient wait times.
- As a result, they saw better bed management, faster admissions, and reduction in idle resources. Digitized billing & claims processing reduced insurance settlement delays by 40%.
2. For Clinicians / Healthcare Professionals:
- Doctors and healthcare workers benefit from easier access to patient histories, decision-support systems, and diagnostic tools—all of which reduce cognitive burden and improve care delivery.
- In India, the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) is a scheme that focuses on building a unified health record system. With patient consent, a doctor in one part of the country can access a patient’s health history, even if that patient received care in a different city or state.
- Similar efforts are taking shape globally. The NHS in the UK is expanding shared care records, Australia’s My Health Record enables nationwide access to patient data, and in the U.S., interoperability laws under the 21st Century Cures Act are connecting systems across providers.
3. For Patients:
- For care seekers, digital transformation brings faster appointments, virtual consultations, easier access to medical records, and more personalized care.
- It puts patients at the center of healthcare experience, making care more accessible, efficient, and responsive.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, platforms like Practo and Tata Health made it possible for millions of Indians to consult doctors online.
- For example: A diabetic patient in a remote village could now follow up with a specialist in Mumbai, without the burden of travel, wait times, or paperwork.
4. For Government or Public Health Officials:
- Going digital helps public health organizations collect better data, respond to emergencies faster, and plan public health efforts better. These should be top priorities for any government.
- CoWIN became a global case study for digital vaccination management during COVID. It allowed real-time tracking of vaccine stock, appointments, & coverage at scale, helping India administer over 2 billion doses.
- Now, platforms like the National Health Stack are laying the groundwork for universal health coverage and proactive disease surveillance.
5. For Tech or Innovation Teams in Healthcare:
- Digital transformation opens up new possibilities like predictive analytics, IoT-based monitoring, and AI-powered diagnostics. This paves the way for new markets and products that can evolve over time and reshape how care is delivered.
- Startups like Niramai (which uses thermal imaging and AI to detect breast cancer) and HealthPlix (an EMR tool for doctors) are reshaping how diagnostics and practice management are delivered.
- These tools are built to serve doctors in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities where traditional healthcare infrastructure is still developing.
Benefits of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
Here’s a quick look at how going digital improves care, outcomes, and operations:
1. Care for All, Anywhere
Virtual consultations, mobile apps, and telehealth remove geographic and physical barriers, bringing timely care to remote and underserved populations.
2. Smarter Diagnoses, Faster Decisions
AI and predictive analytics detect risks early, analyze scans, and personalize treatment — improving accuracy and outcomes.
3. One Patient, One Record
EHRs and interoperable systems give providers complete, real-time data, cutting down on errors, duplicate tests, and fragmented care.
4. Patients in Control
Wearables, health apps, and portals help people track vitals, meds, and appointments, making them active partners in their care.
5. Faster Workflows, Lower Costs
Digital tools automate admin tasks, reduce burnout, increase efficiency, and cut costs through better resource use and fewer readmissions.
6. Ready for Any Crisis
From COVID-19 to natural disasters, digital systems support outbreak tracking, remote care, vaccine delivery, and real-time coordination.
Challenges in Digital Transformation in Healthcare
1. Technological Challenges
These relate to the systems, tools, and infrastructure required for digital transformation.
- Data Interoperability Issues
Legacy systems and non-standardized data formats hinder seamless integration across platforms and providers. - Cybersecurity Risks
Increased digital footprints make healthcare systems prime targets for ransomware, phishing, and data breaches. - Digital Divide and Infrastructure Gaps
Rural areas and underserved populations often lack access to high-speed internet and connected health tools. - Unclear ROI on Technology Investments
Difficulty measuring tangible outcomes from tools like AI and analytics leads to funding hesitations.
2. Regulatory and Ethical Challenges
These involve compliance with legal frameworks and the responsible use of emerging technologies.
- Regulatory Compliance Complexity
Navigating HIPAA, GDPR, and local laws adds administrative burden and legal risk. - Ethical Concerns in AI and Automation
Black-box algorithms and bias in machine learning raise accountability and trust issues in clinical decision-making.
3. Organizational and Human-Centric Challenges
These cover workforce readiness, change management, and internal resistance.
- Resistance to Change Among Staff
Healthcare workers may resist digital adoption due to fear, unfamiliarity, or past tech failures. - Physician Burnout and Alert Fatigue
Repetitive alerts and heavy documentation demands impact employee productivity and increase emotional exhaustion. - Lack of Training on Digital Tools
Insufficient onboarding and upskilling leave staff ill-equipped to use digital systems effectively.
Friendly Note: To curb organizational challenges, healthcare organizations can add a Digital Adoption Platform like Gyde to their existing tech stack. It sits on top of your EHR, ERPs, or any software system and provides personalized in-app self-help support through audio-visual walkthroughs, contextual help articles, bite-sized videos and more.
Best Practices for Implementing Digital Transformation in Healthcare
To successfully implement digital transformation in healthcare, here are some best practices and strategies that can guide you on this journey.
1/ Promote Healthcare Technology Acceptance
Healthcare Technology Acceptance refers to how healthcare professionals and organizations adopt and effectively use new digital tools. It involves the perceptions, attitudes, and behaviors of users (clinicians, administrators, or staff) toward the technology, which significantly impacts the success of digital transformation.
Why It’s a Best Practice: When healthcare staff feel confident using new technologies, they adopt them more fully, improving efficiency, patient care, and outcomes.
How Healthcare Organizations Promote it:
- Involve users early. Engage clinicians and staff in the decision-making process to ensure the technology meets their needs and gains buy-in.
- Choose user-centered design tools that integrate seamlessly into existing workflows to minimize disruption.
- Clearly explain how the technology will improve workflows, save time, and enhance patient care.
2/ Evaluate Trends, But Implement What Adds Real Value
The healthcare industry is filled with trends like AI, telemedicine, and IoT. AI, for example, is hailed for revolutionizing diagnostics and patient care. However, not every organization needs to adopt every trend.
Why it’s a Best Practice: This approach helps healthcare organizations avoid "shiny object syndrome," where they chase every new trend without assessing its actual value.
How Healthcare Organizations Can Do It:
- Stay informed about industry trends, but assess if they align with your organization’s strategic goals and infrastructure.
- Consider factors like budget, staff training, and technology infrastructure before pursuing new trends like AI.
- Prioritize technologies that will address current challenges and bring measurable improvements in patient care and operational efficiency.
3/ Leverage Proven Frameworks to Guide Healthcare Digital Transformation
Why It’s a Best Practice: Healthcare digital transformation is complex, but using proven frameworks can provide structure and measurable outcomes.
Below are key frameworks to guide your digital transformation:
1. Digital Maturity Model
What It Is: A framework used to assess the current digital capabilities of an organization, identifying strengths and areas for improvement.
Purpose: Helps healthcare organizations evaluate their digital maturity to prioritize investments, scale infrastructure, and set achievable goals.
Organizations that regularly assess their digital maturity adopt technologies faster and improve patient outcomes (Deloitte study).
2. The Kirkpatrick Model (for Training)
What It Is: A model for evaluating training programs, measuring four levels of effectiveness: reaction, learning, behavior, and results.
Purpose: Ensures that new digital skills are not only learned but also applied effectively to improve patient care.
Healthcare organizations using the Kirkpatrick Model see 15-20% improvement in training outcomes, leading to better patient care (Journal of Healthcare Management).
3. Triple Aim Framework
What It Is: A framework focused on improving three key healthcare objectives: patient experience, population health, and cost reduction.
Purpose: Ensures digital transformation initiatives address these three critical goals simultaneously.
Organizations adopting the Triple Aim framework saw improvements in patient outcomes, care delivery efficiency, and cost management (Health Affairs).
4/ Unify Your Systems with a Digital Thread
One of the most powerful (and often overlooked) best practices in healthcare digital transformation is implementing a digital thread.
Think of it as a red line that connects every part of your healthcare ecosystem, from clinical workflows and patient data to medical devices and administrative processes.

Why It’s a Best Practice: A digital thread is more than just data integration. It’s a best practice that ensures end-to-end connectivity, enabling real-time insights, contextual decision-making, and complete traceability across a patient’s journey.
By adopting a digital thread approach, healthcare organizations can:
- Break down data silos across departments and systems
- Improve care coordination and patient safety with real-time updates
- Enable predictive care by connecting historical and real-time data
- Make sure compliance and audit readiness through seamless traceability
- Enhance patient experiences through personalized, connected care
In essence, the digital thread becomes the backbone of transformation, quietly powering smarter decisions, smoother workflows, and better outcomes across the board.
Digital Transformation in Healthcare Case Studies
Case Study 1: Empowering Non-Tech Users at South County Health with Gyde
South County Health is an independent, non-profit acute care hospital serving southern Rhode Island. With a mission to deliver exceptional care to its community, the organization continuously invests in digital technologies and systems.
The Challenge: Despite adopting a modern HRMS (Human Resource Management System), South County Health faced a common hurdle:
Many employees were unfamiliar with how to effectively use the system.
- Tasks like setting performance objectives or scheduling meetings with managers required guidance.
- Staff often had to leave the system to search SharePoint, browse user manuals, or request support.
This slowed down processes, created frustration, and reduced system adoption.
As a solution, South County Health partnered with Gyde's In-App Guidance Platform to bridge the digital skill gap by embedding intuitive, contextual support directly within their HRMS. They provided:
- Step-by-step in-app walkthroughs for key workflows like creating objectives or scheduling check-ins.
- Contextual help articles surfaced right when and where users needed them.
- Just-in-time process videos could be accessed on demand, eliminating the need to switch between tools or refer to static documentation.
Since implementing Gyde, South County Health has seen significant improvements:
- 50 %+ increase in process completion speed
- Higher engagement and reduced dependency on external support or manuals
- Improved user confidence and system adoption among non-tech employees and achieved maximum ROI on software investment.
Case Study 2: How a Leading Healthcare System Went Mobile with PWC
One of the largest academic and global healthcare systems in the U.S., with $5.2B in revenue, 4,000+ physicians, and 30,000 employees, wanted to move beyond its traditional strengths to become a digital leader in patient experience.
The Challenge: Discovering that 40% of their website traffic was coming from mobile—a clear sign that patients wanted healthcare access on the go. However, their existing app was outdated and underwhelming: disconnected systems, clunky UI, and limited integration with clinical and billing systems.
Patients expected appointment scheduling, e-check-in, provider search, wayfinding, and mobile billing. Internally, the organization also lacked a structured mobile app development capability to sustain innovation.
As a solution, they collaborated with PwC, which partnered closely with the client’s Chief Innovation Officer to co-create a next-gen mobile experience platform.
- Starting with customer journey mapping workshops at the PwC Experience Center, stakeholders from across departments co-developed a unified vision for the patient journey.
- A new native mobile app was built using agile sprints with capabilities like provider search, scheduling, clinical support, and mobile payments.
- A governance model spanning IT, legal, marketing, clinical ops, and revenue cycle ensured alignment and ownership.
Within six months, the healthcare system went from concept to launch. The results?
- 64% monthly adoption across 500,000+ patients in the first 3 months
- $5M in anticipated savings from efficiency gains in physician offices
- $10M in revenue uplift from improved billing and collections via the app
- A powerful “traceability matrix” was established to measure ROI from each feature.
Case Study 3: VitalCare Network’s approach to digital transformation
VitalCare Network, based in Australia, operates 40 hospitals and 250+ specialized care centers. Since 2007, the organization has focused on leveraging technology to deliver high-quality, efficient, and accessible healthcare across diverse populations.
The Challenge: Rising patient demand coupled with limited rural accessibility. This led to:
- Manual processes and disconnected systems led to delayed diagnostics, inconsistent treatment protocols, and underutilized resources.
- Lack of scalable digital infrastructure hinders remote healthcare delivery.
As a solution: VitalCare launched a network-wide digital transformation strategy:
- Rolled out a unified digital health platform for real-time data access
- Deployed a telehealth program powered by AI-based diagnostic tools and IoT-enabled health monitoring devices
- Simplified system-wide integration for better coordination and resource utilization
As a result, they saw:
- 40% reduction in administrative overhead
- 60% increase in patient reach, especially in rural areas
- 30% improvement in treatment outcomes
- Boosted data accuracy, patient tracking, and overall satisfaction
Help Healthcare Teams Learn and Use Digital Tools Faster with DAPs
As discussed in the blog, from EHRs to HRMS tools, Digital adoption platforms are built for in-app guidance that makes sure the knowledge sticks, whether you're a super-specialty hospital or a district health office.
For example, Gyde is an AI-powered digital adoption platform that offers just what your clinical and admin teams need — real-time, contextual guidance that shows exactly where to click, what to enter, and how to finish a task.
Gyde equips your healthcare teams with on-the-job support built right into your applications:
- Step-by-step audio-visual walkthroughs so staff can follow procedures with confidence
- Contextual help that appears only when and where it’s needed
- Short, focused videos to visually demonstrate key workflows
- In-app assessments to verify process understanding in real time
- Assist Mode that provides support only when users request it

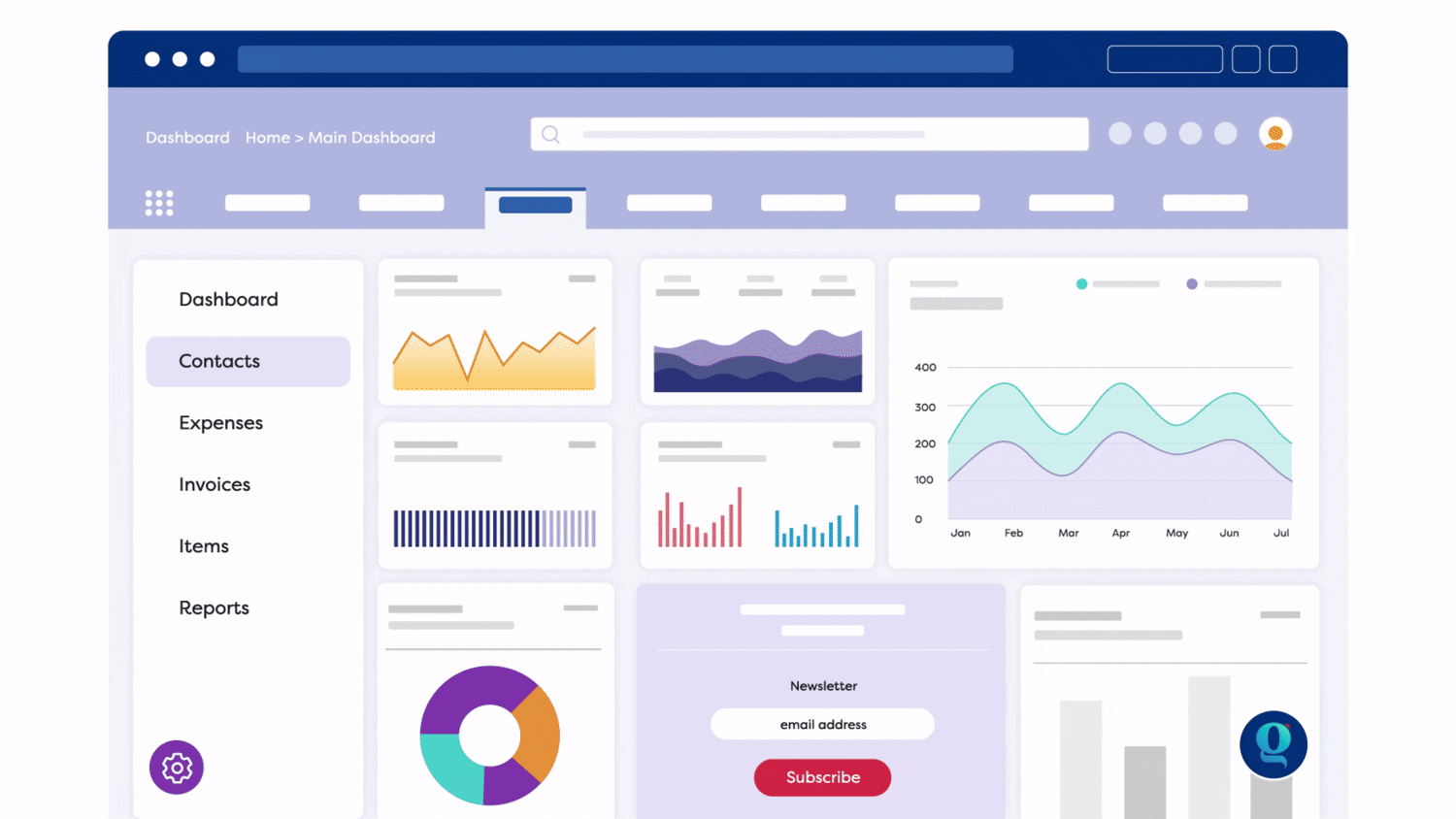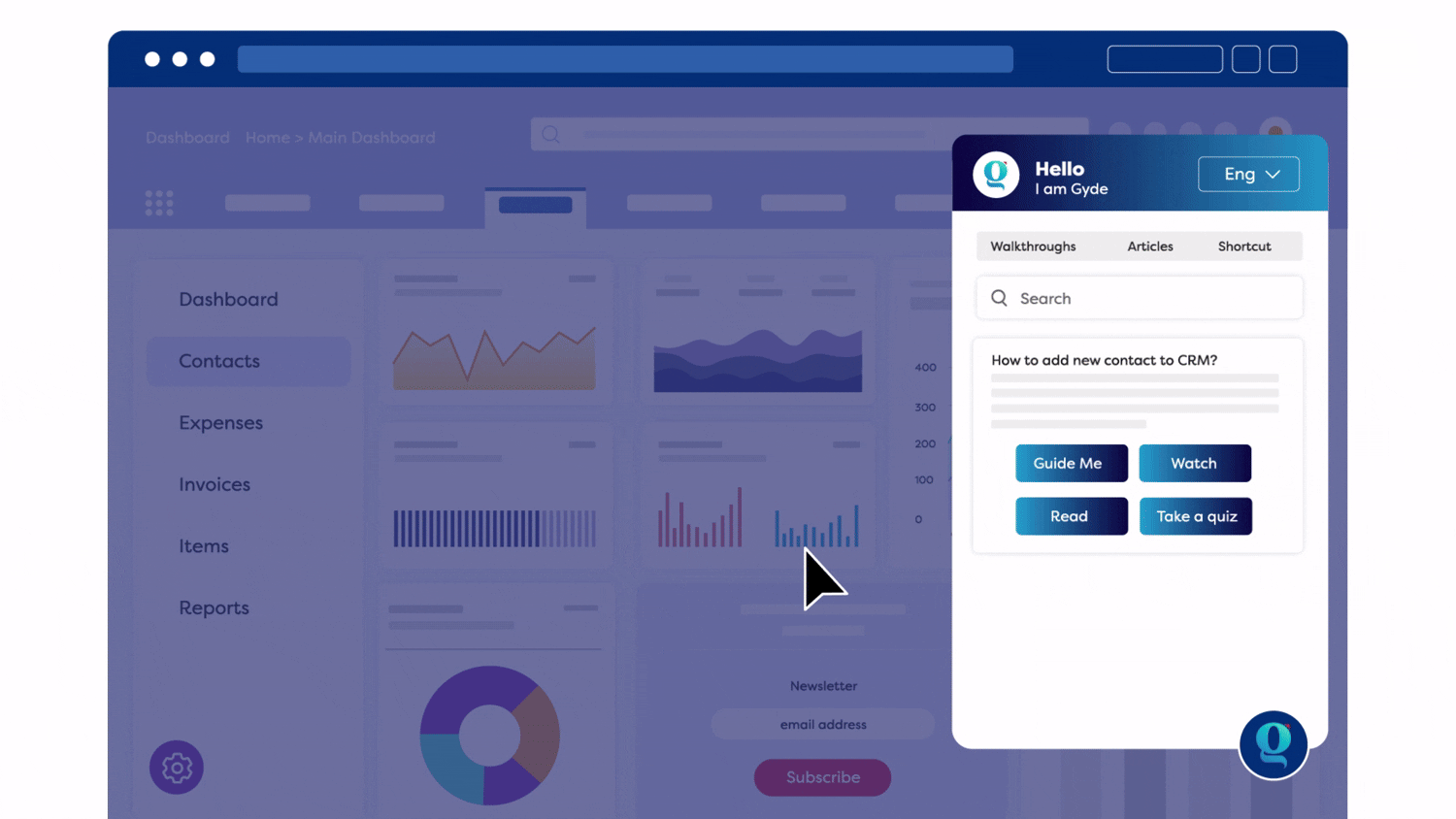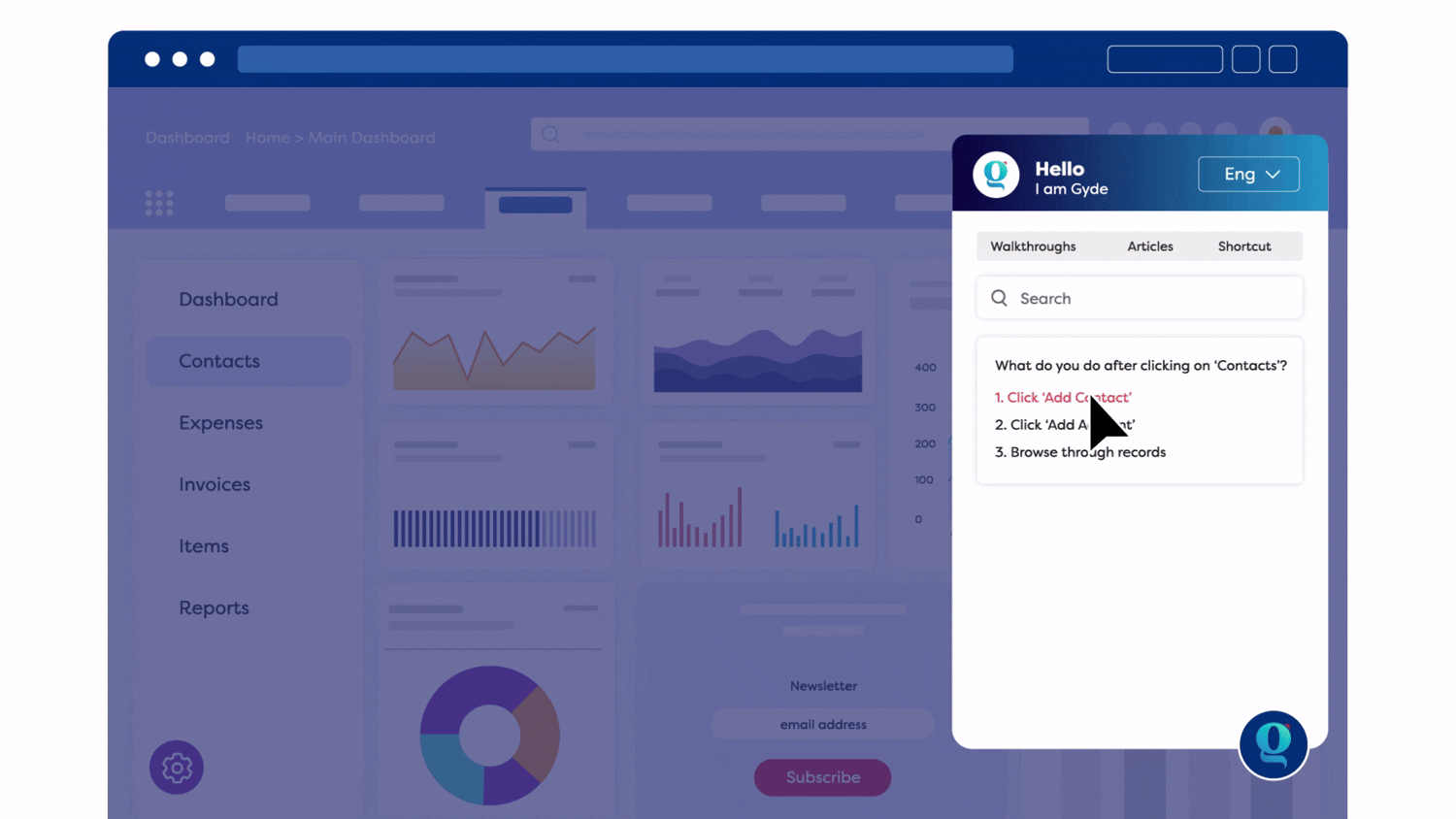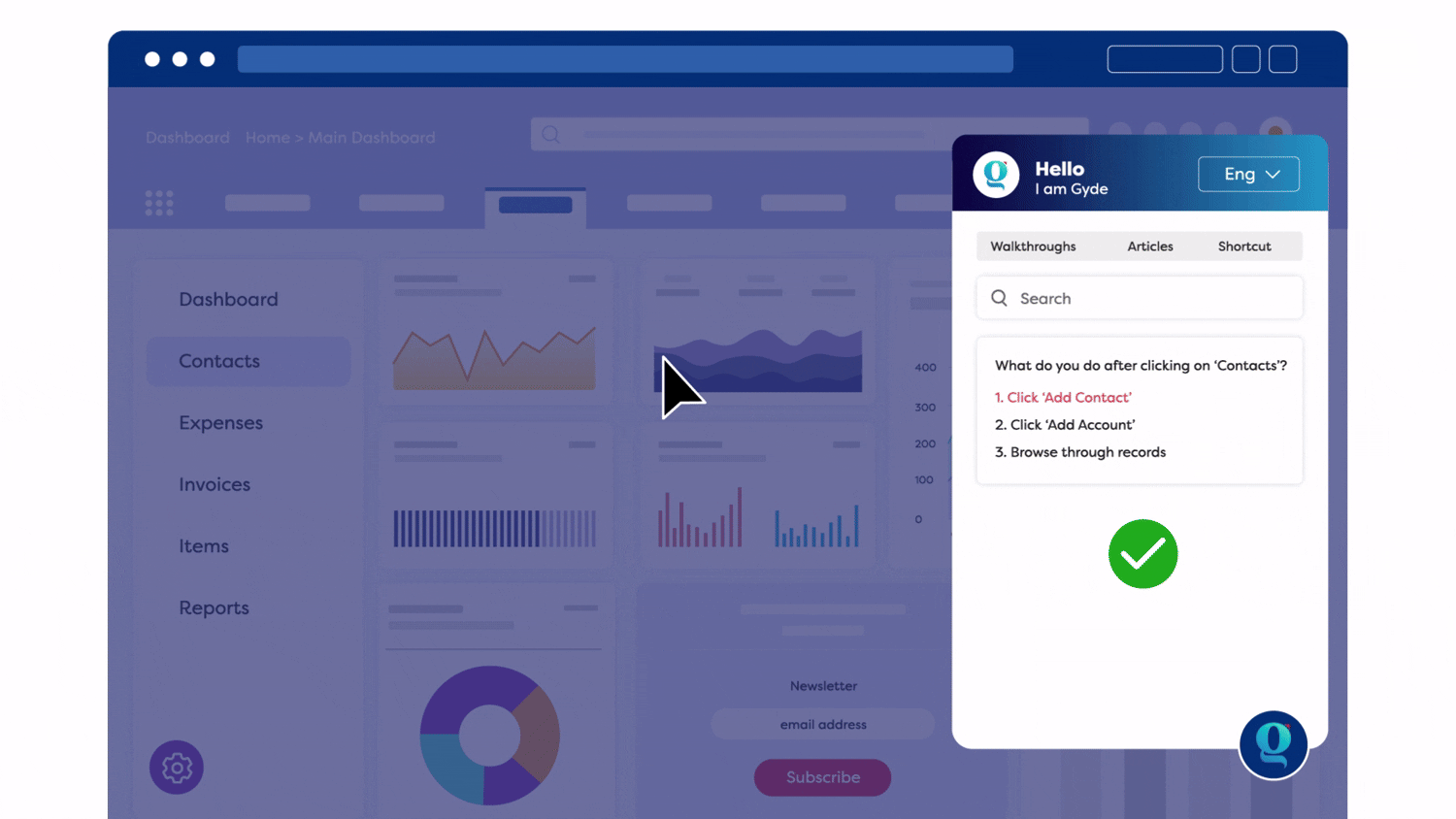
Bonus for Training Teams: Gyde’s AI-powered feature captures on-screen actions as you perform a task, automatically generating step-by-step walkthroughs, screenshots, videos, and clear titles with descriptions.
This means training materials that once took hours can now be created in minutes, keeping pace with rapid changes in healthcare systems & protocols.
What this means for your organization:
- Consistent execution of clinical and admin processes (less room for error or confusion)
- Better use of your healthcare software (no more costly underutilization)
- Fewer support requests to IT (staff can troubleshoot common issues independently)
To move forward in your Healthcare Transformation with adoption at the core, book a demo and learn how Gyde can make workflows easier, training more effective, and patient care better.
FAQs
How does AI improve patient care?
- AI improves patient care by enabling quicker and more precise diagnoses through the examination of medical images(like MRIs & X-rays), resulting in customized treatment plans based on the unique patient profile.
- AI can forecast possible health threats, allowing for proactive treatment, and offers virtual health support for better self-management.
- Plus, AI can simplify discovery and enhances hospital efficiency, freeing up healthcare professionals to spend more time on direct patient interaction and well-being, making for a more proactive and personalized healthcare experience.
What are examples of digital health tools?
Digital health technologies cover a broad range of technologies, such as:
- mobile health applications for wellness, chronic disease management, and telemedicine;
- wearable technology such as fitness trackers and continuous glucose monitors;
- telehealth platforms providing remote consultations and monitoring;
- electronic health records and patient portals for data access and management;
- health information exchange platforms for secure data sharing;
- digital therapeutics providing software-based therapies;
- artificial intelligence-based tools for diagnostics and personalized care,
All of these are focused on enhancing health outcomes, increasing access, and empowering individuals in taking control of their well-being.
How can small hospitals go digital?
Small hospitals can adopt digital transformation cost-effectively and strategically by prioritizing foundational technologies and a phased strategy.
- Starting with a cloud-based Electronic Health Record (EHR) system can automate patient data management, enhance communication, and minimize administrative hassles without the expense of large-scale infrastructure investments.
- Telemedicine applications can extend their network, providing virtual consultations and remote monitoring, which can be highly useful for follow-ups and patients in rural areas.
- Using mobile health (mHealth) applications for scheduling appointments, reminders for medication, and patient education can increase patient engagement.
- For administrative effectiveness, they can implement cloud-based practice management software for billing, insurance claims, and inventory management.
Remember, data security and regulatory compliance are essential throughout this process.

![Digital Transformation in Healthcare [Best Practices for 2026]](/content/images/size/w2000/2025/07/Digital-Transformation-in-Healthcare--Best-Practices-for-2025-.jpg)
