When organizations invest in training, the outcomes might look good on paper; "All training modules completed" or "50 hours logged on a topic".
But the reality is often quite different.
Studies on Ebbinghaus’ forgetting curve show that humans forget a substantial portion of new information within the first 24 hours. In short, your employees aren't retaining/remembering what they’ve learned in the times when they need it the most.
This lack of learning retention becomes the SILENT PRODUCTIVITY KILLER which quietly erodes the impact of your entire learning strategy.
Trust us...that’s not a problem you want to ignore and we get it.
That’s exactly why we put this blog together: to help you improve learning retention in your organization and see tangible gains in productivity, engagement, and business impact.
Here's what we've covered in this blog:
- What Does Learning Retention Mean For Employees?
- What Work Skills Do Employees Need to Retain Over Time?
- Why is Learning Retention So Important?
- Common Drivers of Learning Retention
- Common Barriers to Learning Retention in the Workplace
- How is AI Changing Learning Retention?
- Proven Strategies to Boost Learning Retention
- How To Measure Learning Retention?
- Learning Retention in Software Training Starts with a DAP
- FAQs
What Does Learning Retention Mean for Employees?
Learning retention refers to employees’ ability to absorb new information, store it in long-term memory, and recall it easily when needed. Simply put, it’s about making sure that what is learned actually sticks.
Humans are wired to forget. According to Hermann Ebbinghaus’ Forgetting Curve, within an hour of learning new information, people tend to forget up to 50% of it. Most of that knowledge sits in short-term memory and fades fast if not revisited or applied.
When employees retain what they’ve learned, it has direct impact on:
- Productivity (fewer mistakes, faster task completion),
- Confidence (less second-guessing or seeking constant help),
- Consistency (repeatable, high-quality outcomes),
- and Growth (building on past knowledge).
What Work Skills Do Employees Need to Retain Over Time?
Here’s a quick look at what employees need to learn and retain on the job for high performance:
- Role-Specific Knowledge: Like key processes and workflows, how to use tools and systems, product or service know-how
- Company Policies & Compliance: Security and data handling protocols, HR policies like attendance, leave, compliance rules, etc.
- Cultural Norms & Values: Normally how work gets done in the organization. Common communication etiquette & collaboration practices.
- Team Dynamics & Dependencies: Roles and responsibilities of teammates or who to contact for specific needs or approvals
- Customer or Client Expectations: What matters most to customers and standard protocols for delivering great service
- Soft Skills: When and how to use active listening, empathy, problem-solving, etc. and applying interpersonal skills in real scenarios
- Feedback & Lessons from Mistakes: Constructive feedback from managers or peers or what went wrong in past tasks and how to do better
Why is Learning Retention So Important?
You just saw how much an employee is expected to remember. Tools, processes, policies, product details, team dependencies... the list goes on. No wonder retention rates are low.
Now, put yourself in their shoes: how can anyone perform at their best if they’re constantly forgetting what they just learned?
The truth is, employees don’t need more information; they need smarter ways to retain and recall it. Without that extra hand (may it be contextual guidance, just-in-time help, or on-the-job reinforcement) they’re bound to struggle.
Retention isn’t something you think about later. From day one (onboarding or training) it should be part of the plan.
Here’s why:
1. Helps New Hires Stay Longer and Settle Faster
The first six months on the job are crucial as many employees decide whether to stay or leave during this period. When onboarding emphasizes retention, new hires experience a better transition & feel more prepared, which increases the likelihood that they’ll stick around longer.
2. Builds Skills and Confidence Over Time
With training designed to reinforce learning, employees can develop proficiency quickly. As skills become second nature, confidence grows, enabling employees to tackle challenges with greater ease & even explore new areas for growth.
3. Creates a Culture Where Learning Never Stops
Learning is a continuous process. When organizations encourage ongoing skill development, employees are eager to learn. They regularly seek out knowledge, whether through formal courses, peer learning, or self-paced modules.
Common Drivers of Learning Retention
If you want to understand why people actually remember what they learn, start with these 8 factors—they’re the ones that truly make learning stick:
1. Relevance to the Learner’s Role
People remember what feels useful. If the training connects to real tasks or challenges they face, retention goes up instantly.
2. Repetition & Reinforcement
Training effectiveness of one-time training is quite less. But spaced repetition, recap sessions, and follow-ups help move learning from short-term to long-term memory.
3. Application in the Flow of Work
When employees get to apply what they’ve learned soon after learning it, retention skyrockets. Practice cements memory.
4. Interactive, Engaging Formats
Quizzes, simulations, scenarios, even a bit of gamification keep the brain active and improve recall.
5. Personal Motivation
Internal drive matters. If someone wants to learn and sees the benefit, they’ll retain it better. Motivation fuels memory.
6. Supportive Environment
Managers who reinforce learning, peers who share tips, and a culture that values growth, it all makes retention easier and more natural.
7. Access to Just-in-Time Help
Performance support tools, in-app guidance, or bite-sized refreshers help employees recall info exactly when they need it.
8. Feedback & Reflection
Getting feedback on what was learned and reflecting on how it applies helps deepen understanding and lock in knowledge.
Common Barriers to Learning Retention in the Workplace
Even the most well-designed training programs can fall short if key barriers to retention aren’t recognized and addressed.
If you want to know why training doesn't stick, here are some of the biggest challenges organizations face in keeping knowledge alive and actionable:
Psychological Factors: Stress, Multitasking, and Motivation
- Workplace stress significantly hampers the brain’s ability to form and recall memories. Research shows stress can reduce retention by up to 40%.
- Add to this the reality that employees switch tasks roughly every three minutes, and it becomes clear why multitasking often leads to shallow learning.
- Motivation plays an equally critical role. Without clear relevance or a compelling reason to engage, learners quickly lose interest.
Work Environment Factors: Lack of Context and Poor Timing
- Learning that isn’t closely tied to an employee’s day-to-day tasks is easily forgotten. According to the well-established Forgetting Curve, up to 70% of new information can be lost within 24 hours without reinforcement.
- The timing of training matters to its training effectiveness. Traditional sessions are often delivered too early (in classrooms or workshops), long before employees actually need to apply what they’ve learned.
- This disconnect between learning and practical use drastically lowers retention.
Organizational Factors: Culture, Reinforcement, and One-Size-Fits-All Training
- A company culture that views training as a mere formality rather than an ongoing development process sets itself up for failure in employee retention.
- When continuous learning isn’t embedded into the organization’s DNA, employees rarely prioritize retaining and applying new skills.
- Another barrier is the lack of reinforcement. Without ongoing refreshers, follow-up practice, or real-world application, knowledge retention is weak.
- Furthermore, standardized training that ignores individual learning preferences leads to disengagement and poor retention outcomes.
How is AI Changing Learning Retention
Along with being tools that answer questions prompting, AI models are also becoming personal learning companions that actively reinforce what one learns over time.
Here's how models like ChatGPT, Gemini, Grok, and Claude are transforming retention for learners:
1. Adaptive Explanations Based on Weak Points
Every learner struggles differently. If someone keeps misunderstanding a concept, AI tools re-explain using analogies, simpler language, or step-by-step visuals. This personalization helps overcome cognitive blocks faster, making understanding more sticky.
2. Turning Passive Learning Into Active Recall
Instead of simply reading or watching content, learners can now talk to their knowledge. They can ask the AI to:
- Explain a concept in different ways
- Test them with quizzes or flashcards
- Let them teach the topic back to the AI
This kind of interactive retrieval practice is one of the strongest techniques for long-term retention.
3. Simulations and Roleplay for Better Recall
Models like Grok (known for its witty tone) and ChatGPT (great with roleplay) allow learners to practice through real-world scenarios:
“Act like an interviewer and grill me on SQL joins.”
“Play the role of a customer so I can practice pitching.”
Learning through simulation activates contextual memory, which is far stronger than rote memorization.
Proven Strategies to Boost Learning Retention
Understanding the drivers and barriers is step one.
Up next, we'll see practical strategies to turn that knowledge into long-term retention.
Strategy 1: Spaced repetition & reinforcement
Take a look at graph below.
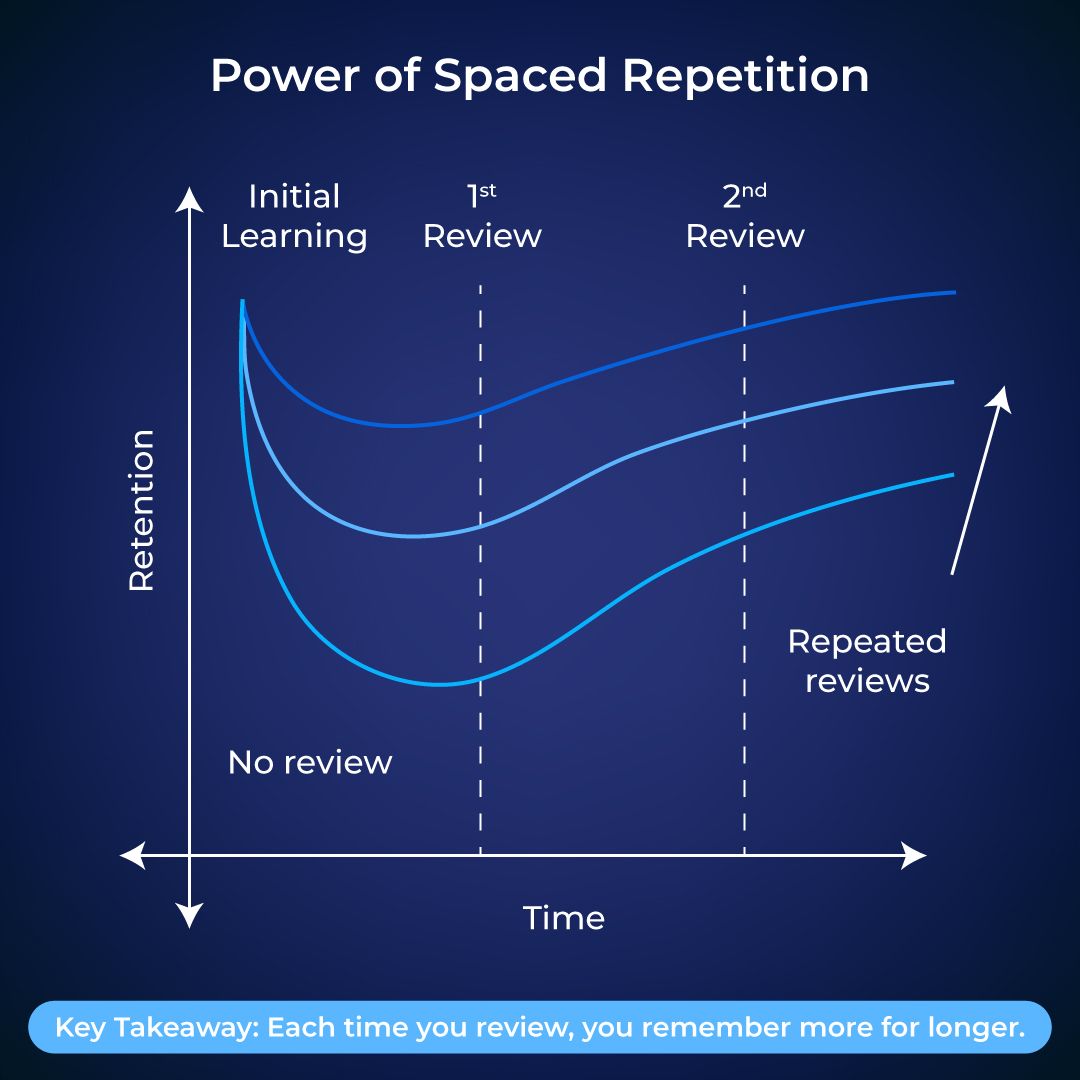
It shows us how learning retention improves when learners revisit knowledge over time. That dip you see in the first curve? That’s the forgetting curve in action. It shows how quickly we forget something if we don’t revisit it.
The format & timing can be different. Here's a quick example. Say your sales team just finished a session on objection handling. Instead of moving on, you could:
- Send out a short flashcard-style quiz the next morning.
- Share a “common objection of the week” scenario mid-week.
- Do a quick roleplay in next week’s team huddle.
Each repetition isn’t random; it’s spaced just enough to interrupt forgetting and reinforce the learning.
Strategy 2: Microlearning & Bite-sized content
Now, you might think spaced repetition and microlearning are the same thing but there’s a difference. Spaced repetition is when you reinforce learning. Microlearning is how you deliver it in the first place.
The beauty of microlearning is that each module is a complete unit of instruction.It doesn’t just drop a teaser or half an idea. It gives learners one clear takeaway from start to finish in under 10 minutes.
Suppose you’re rolling out a new CRM. Instead of a 2-hour training that covers every feature in one go, you break it down into microlearning video modules like:
- “How to Create a New Lead”
- “How to Track Lead Status”
- “How to Convert a Lead to Opportunity”
Each one has a goal. Learners don’t need to remember the whole system all at once. They learn what they need, when they need it.
Strategy 3: Multi-sensory learning
The human brain retains information better when it’s experienced through more than one sense. Training leaders can combining visuals, audio, movement, and interaction to make learning more engaging and build multiple neural pathways to the same information. This redundancy strengthens recall.
Such training could also be called blended learning.
Here’s what it looks like in action. Say you're training a team on a new customer service protocol:
- First, they watch a short explainer video (visual + audio).
- Then, they walk through the same flow in a click-through simulation (movement + interaction).
- After that, they get into small group discussions to reflect on tricky scenarios (social + reflection).
- Finally, they summarize their key takeaways in a short write-up (text + self-expression).
Same topic. Multiple sensory touchpoints.
For employees, this variety makes sure of knowledge retention. It isn’t limited to a single mode of understanding but is accessible through several “roads” in their brain, making it easier to remember and apply when it counts.
Strategy 4: Active learning & teaching others
We retain more when we actively engage with what we’re learning. That’s the core understanding of active learning. Learners retain better when they interact with it, question it, apply it, or explain it to others.
It’s a powerful strategy, but it’s not always one-size-fits-all.
For example, your team is getting used to a new CRM system. Instead of waiting until everyone’s an expert, you create space for small knowledge swaps, impacting overall knowledge retention. One person might share a tip that saved them clicks. Another might flag a common mistake and how to avoid it.
Over time, this turns into a culture of micro-mentoring. These low-pressure teaching moments don’t just help learners but they deepen the teacher’s understanding too.
Bottom line: if people can explain it, they understand it. And that’s the kind of retention that sticks.
Strategy 5: In-app learning paths
Employees today juggle multiple software applications daily. CRMs, HRMS, ERPs… the list goes on. Expecting them to remember how each one works after a single training session? Unrealistic.
That’s where in-app learning paths come in. These are contextual guides (such as walkthroughs, smart tooltips, or chat-based support) that appear inside the software. But what really makes them effective is personalization.
For example, say a new sales rep opens the CRM to add a lead. Instead of guessing, they’re shown a step-by-step overlay saying “Click here, enter this, select that.”
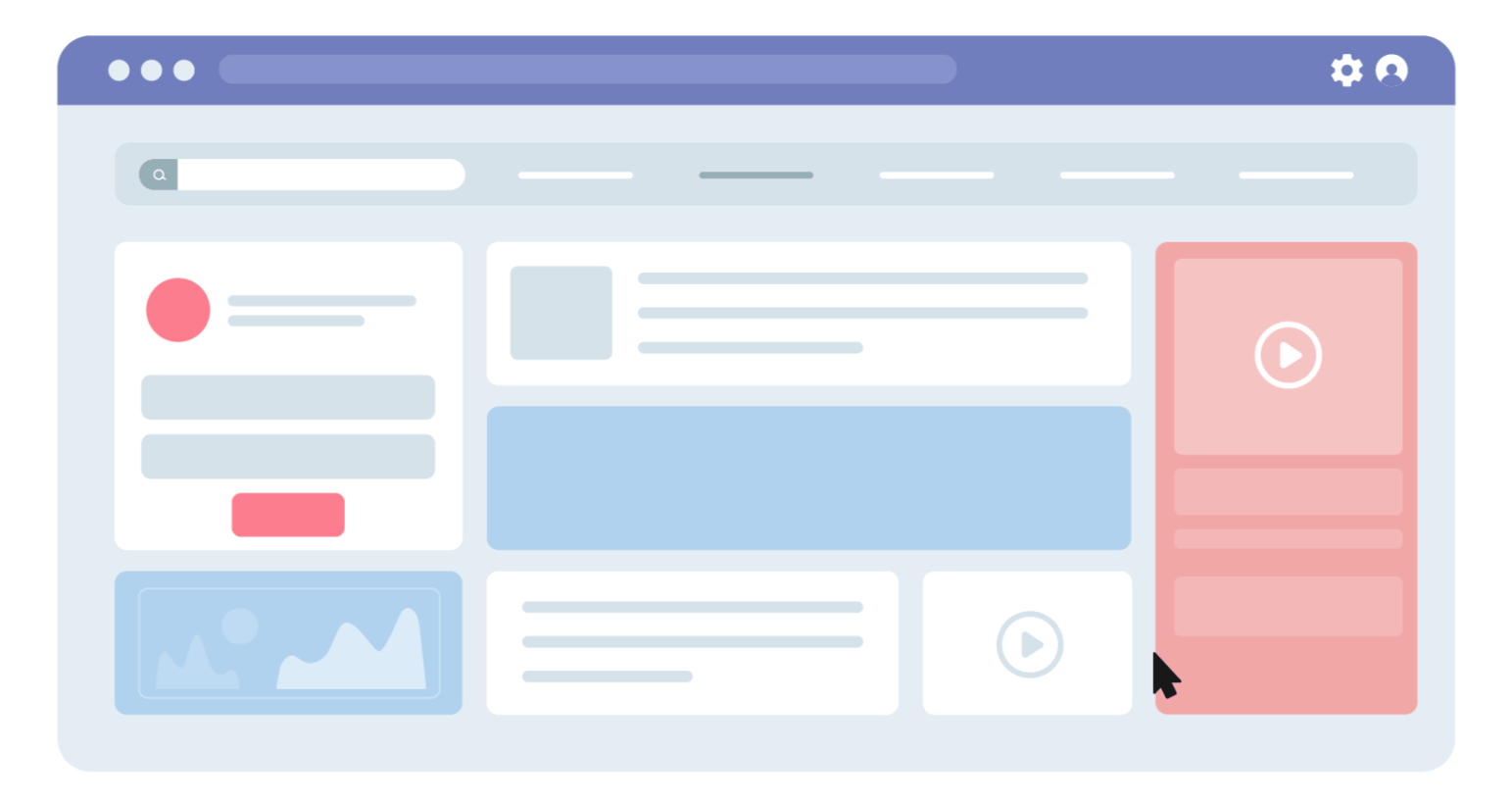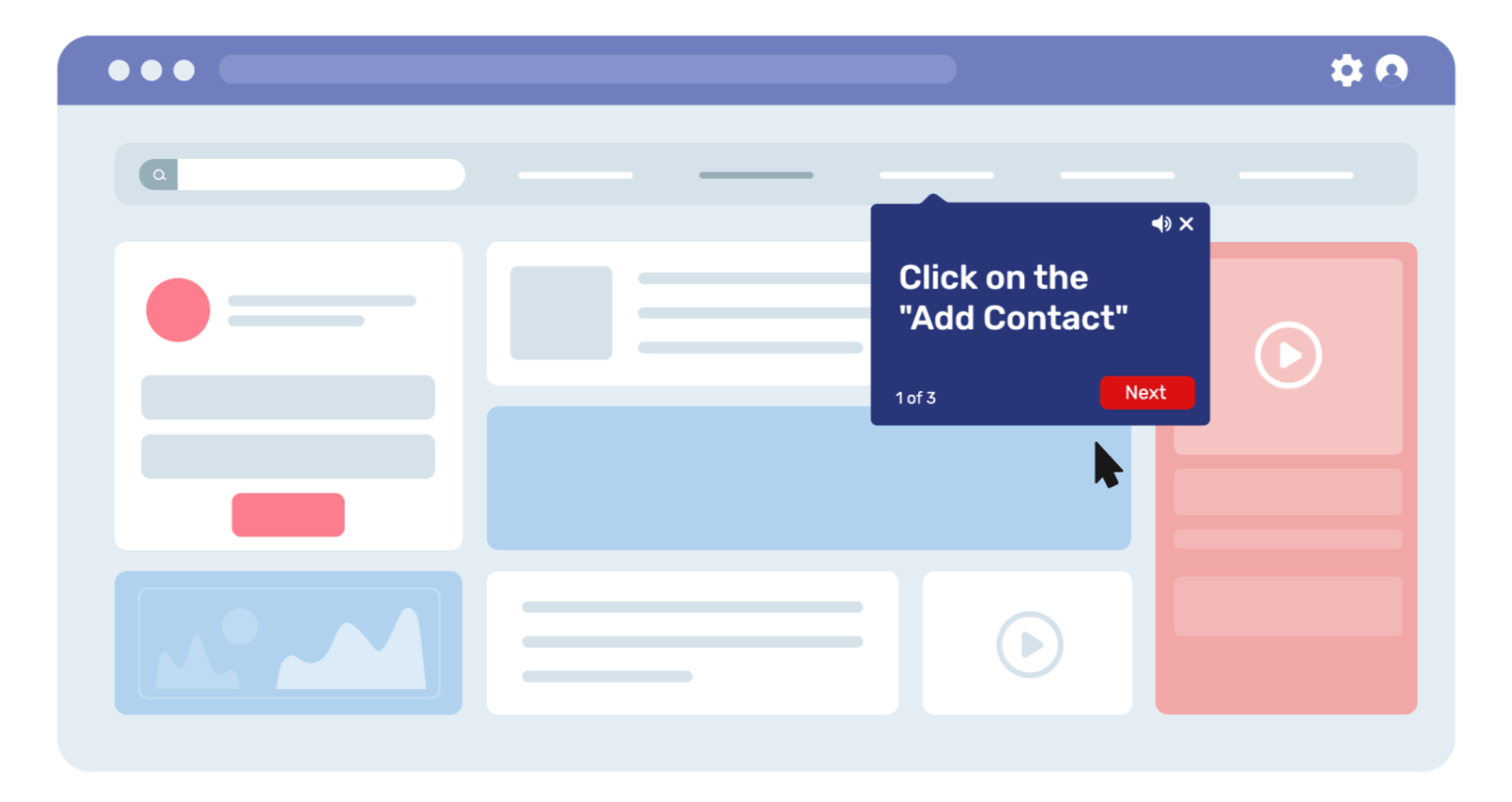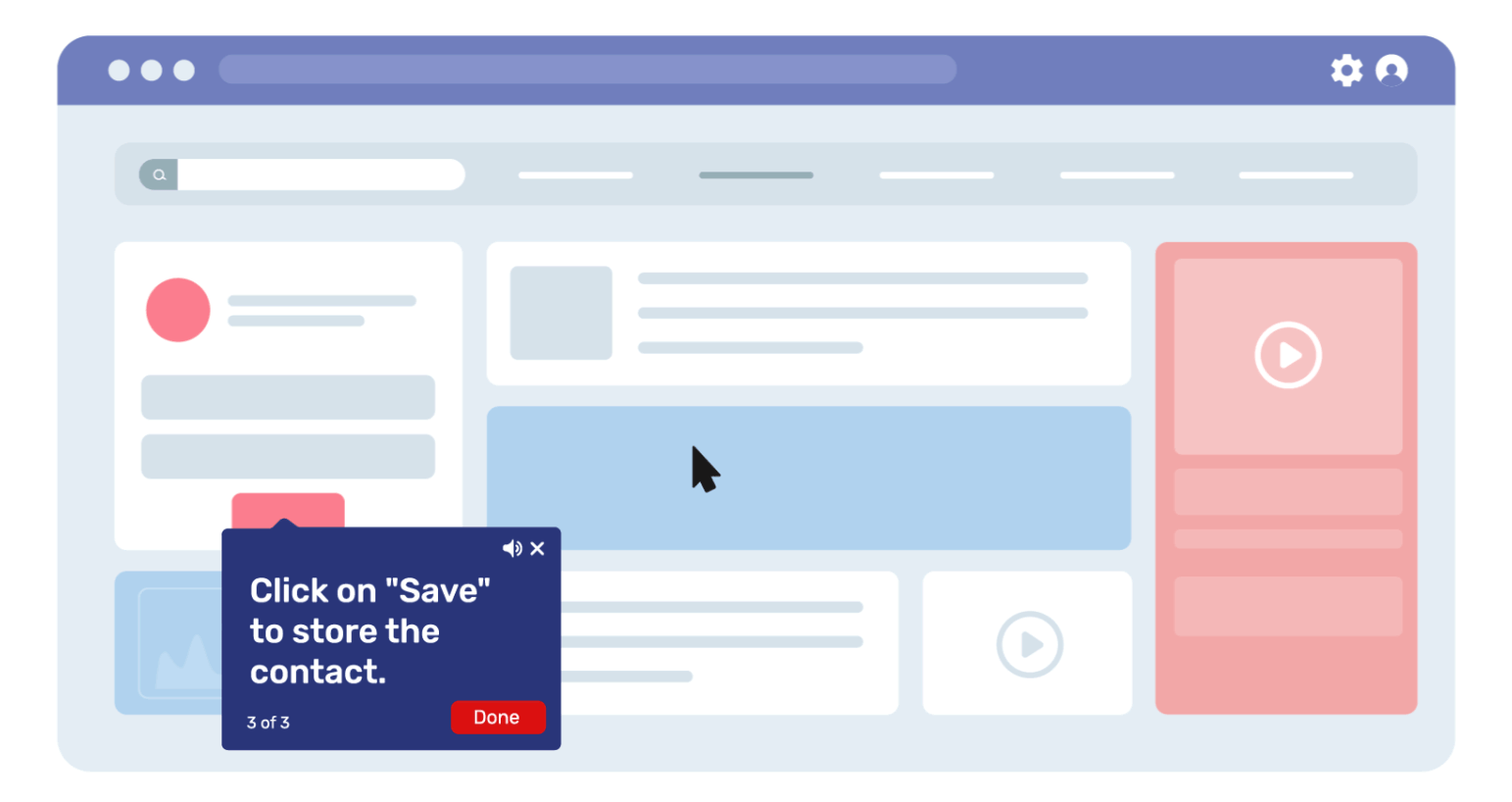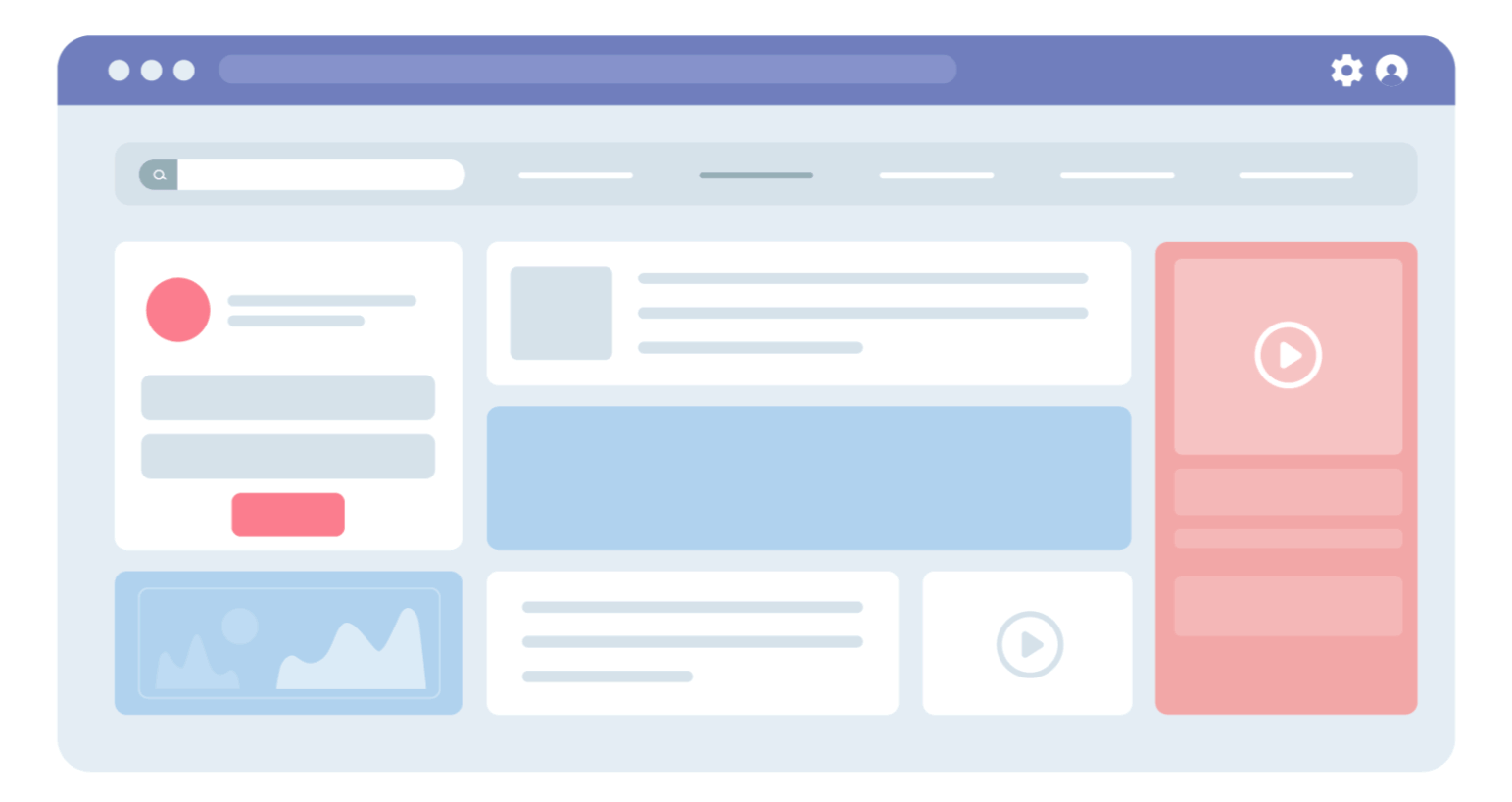
Meanwhile, a sales manager logging in sees on-screen callouts on customizing reports or tracking quarterly performance.
Same platform, different journeys, each tailored to the user’s role and context.
As a result, you'll see fewer mistakes, faster onboarding, and better retention, because employees are learning by doing, not by memorizing.
How To Measure Learning Retention
Often, when it comes to measuring learning retention, traditional training metrics give you a false sense of success:
- Quiz scores reflect short-term memory, not long-term recall
- Completion rates only prove people clicked ‘Next’ till the end
- Feedback surveys often measure satisfaction, not capability
Real learning retention shows up differently. You’ll know knowledge has truly stuck when you start seeing signs like:
- Fewer mistakes during task execution
- Less dependency on supervisors or documentation
- Knowledge retention happening independently even in new situations
- Reduced repeat questions and support queries
In the context of software training
Companies invest thousands of dollars rolling out CRMs, ERPs, POS systems, HR tools — all assuming that employees will naturally start using them the right way.
But how do you know if that’s actually happening?
Most platforms only show backend numbers: logins, clicks, time spent. Useful, but shallow. They don’t tell you:
- Did the employee remember the workflow?
- Can they complete tasks without guessing or asking for help?
- Do they follow the process the right way, every time?
Modern software training tools, such as DAPs, shift the question from “Did they attend the training?” to “Are they applying what they learned (consistently) inside the tool?”
Here's how:
- Track Usage of Support Content: See daily, weekly, monthly, and quarterly views. Monitor how walkthroughs, help articles, and videos are consumed. Identify drop-off points within a walkthrough or guide
- Spot Individual Learning Gaps: Find out which employees completed or skipped specific flows. Pinpoint who might need reinforcement or follow-up
- Reinforce with In-App Assessments: Let employees take quick quizzes after walkthroughs. Gauge immediate understanding and retention.
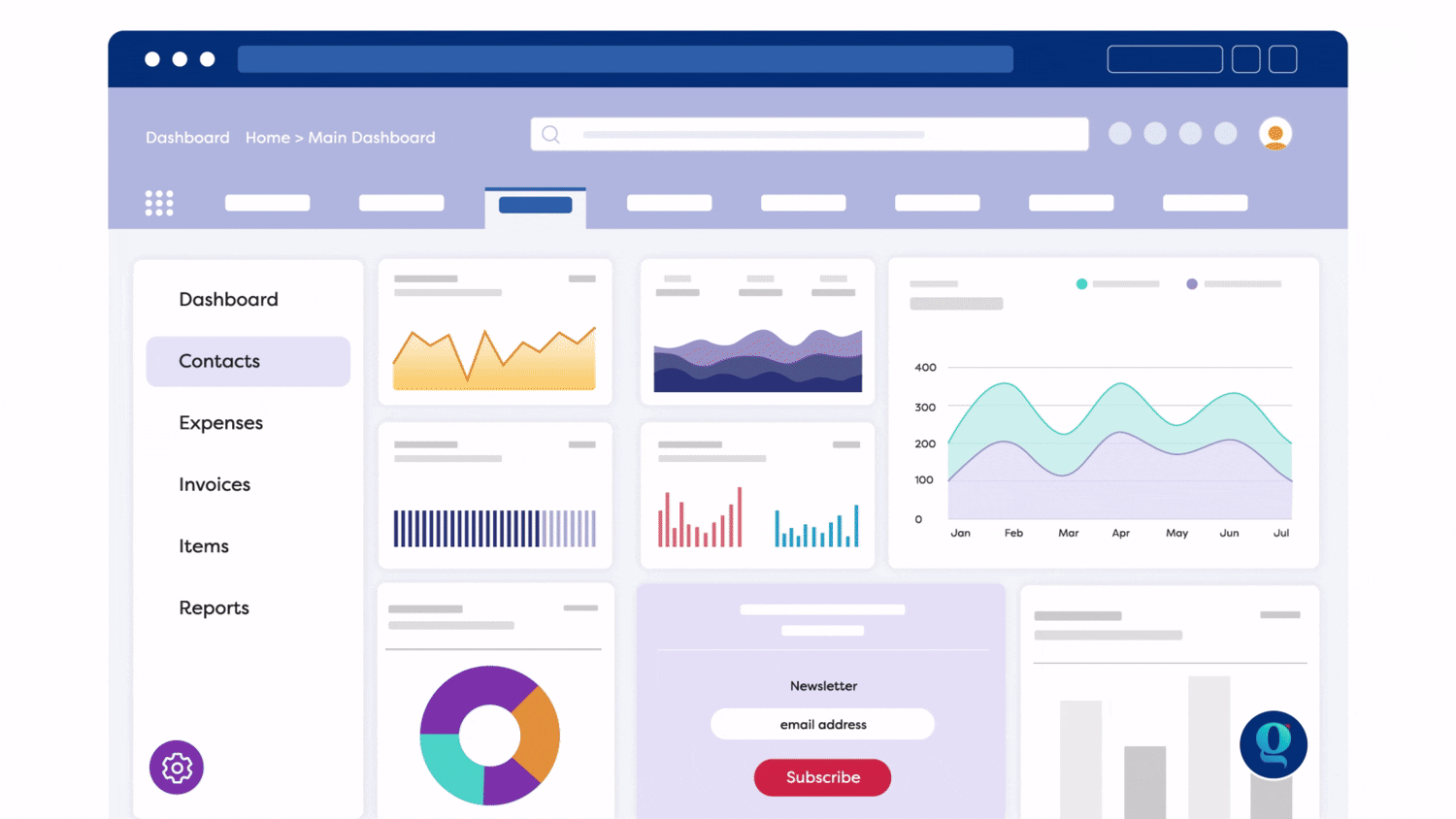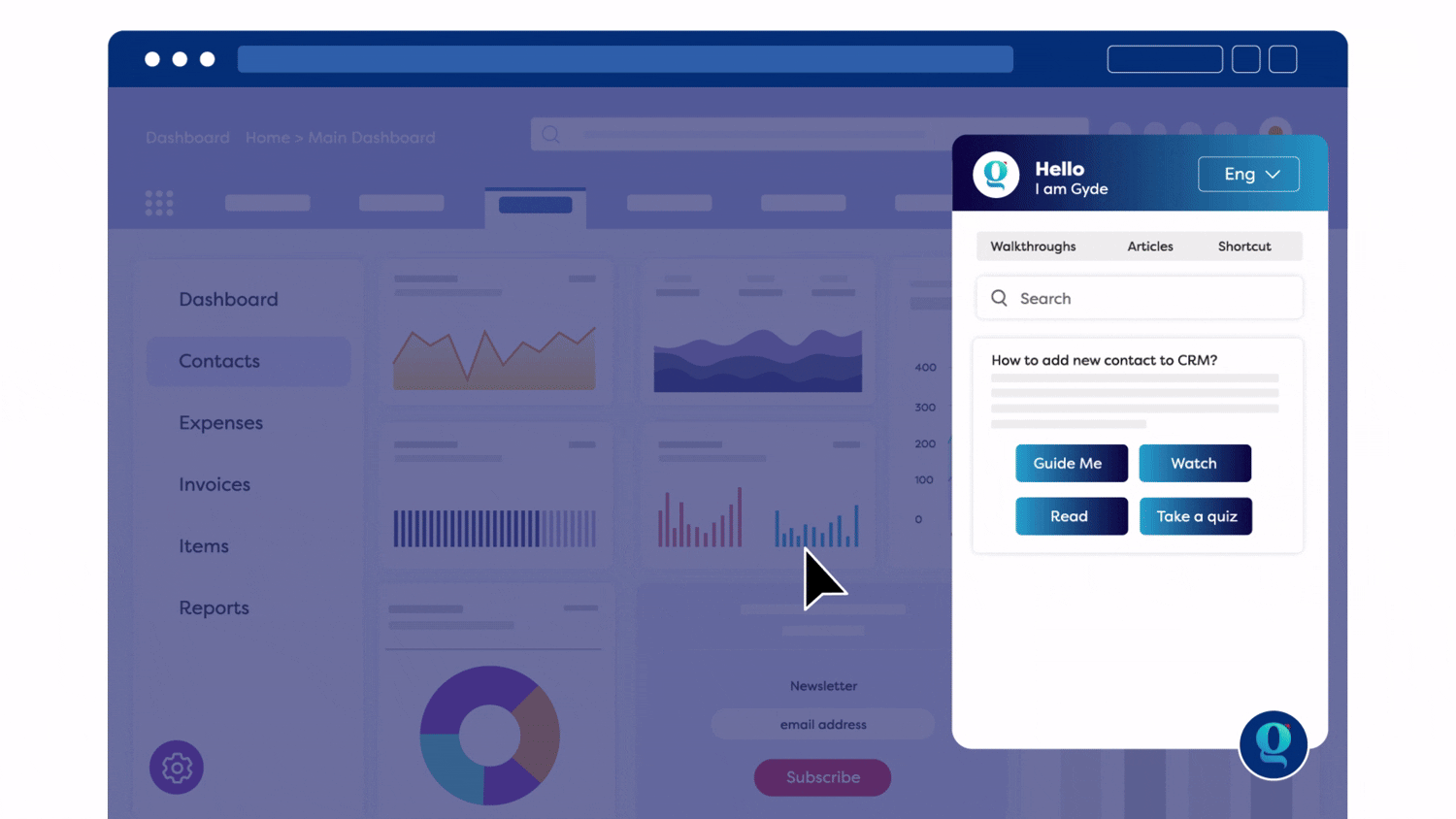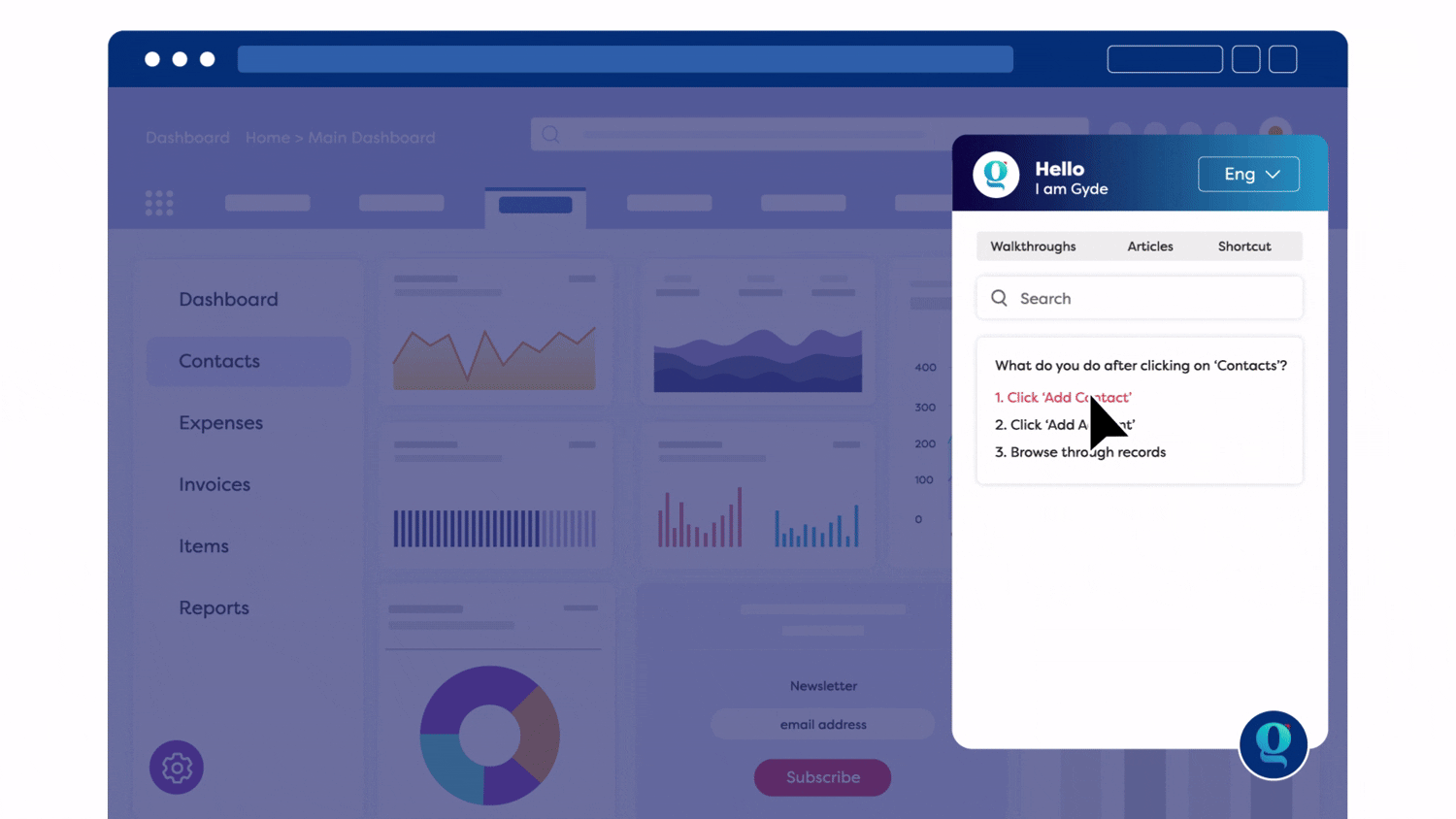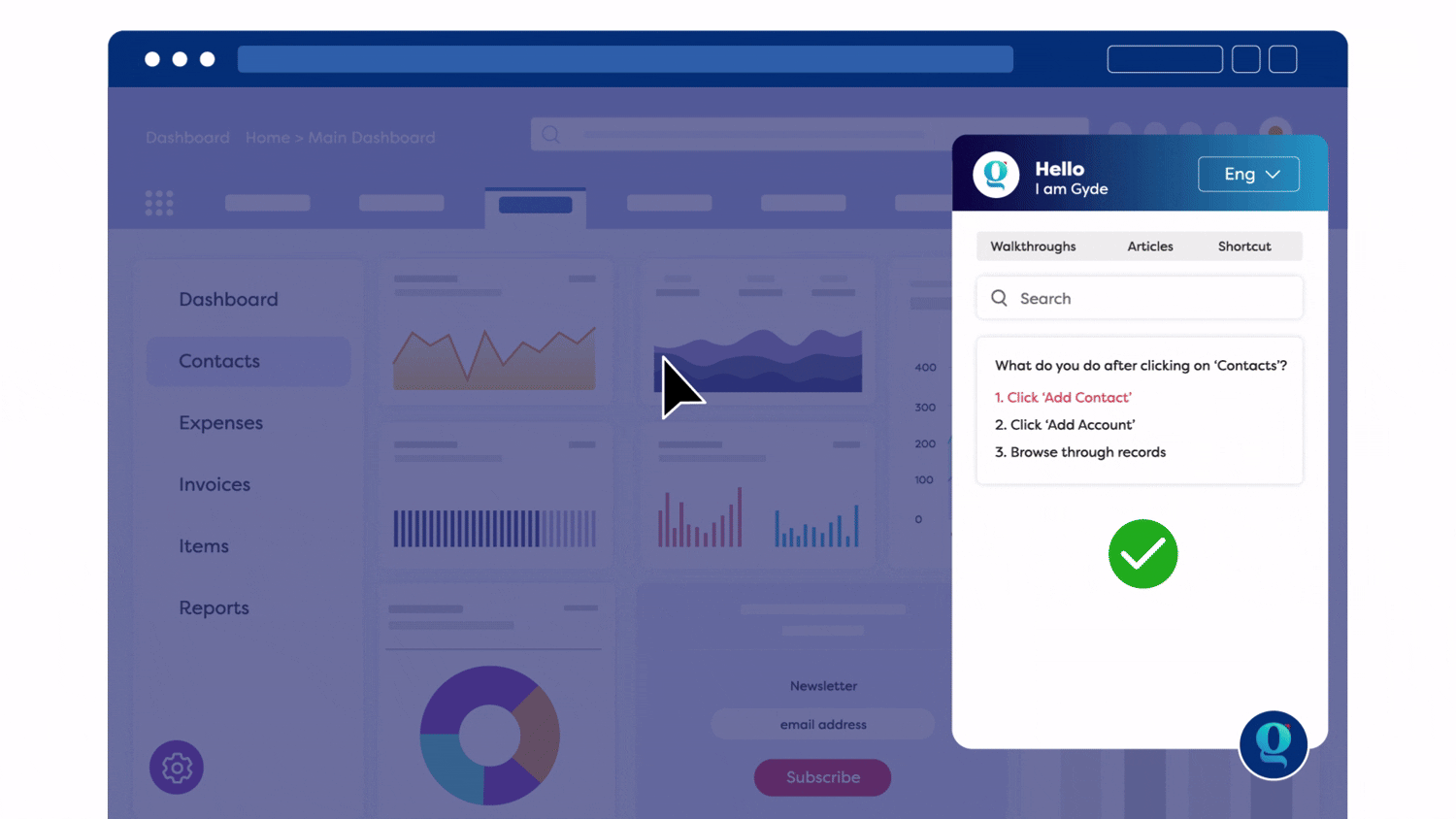
- Collect Instant Feedback: Emoji-based feedback on every walkthrough or article. Understand how helpful employees find the support content.
DAPs turn passive tracking into active learning insights, helping you see what’s sticking, what’s not, and who needs support.
Learning Retention in Software Training Starts with a DAP
There’s a simple filter every training program should pass from now on:
“Will they remember this when it matters?”
If the honest answer is no, something is broken (either the format, timing, or delivery mechanism). Because at the end of the day, retention is the real ROI.
Especially in software training, retention shouldn’t be an afterthought. You should treat it like a performance metric. And the easiest way to influence that metric is to shift to just-in-time support with Digital Adoption Platforms (DAPs).
DAPs like Gyde provide support in the formats users prefer (like audio-visual walkthroughs, help articles, videos) that appears subtly inside the application. Users can choose how they want help, which makes them proficient software users. Plus, all resources are easily translatable to any preferred language, so they remember better.
For training admins, built-in analytics show which guides are used most, where users drop off, and which processes need refinement. Gyde also leverages Gen AI to make walkthrough content creation intuitive and fast, capturing step titles and descriptions within processes as they happen.
Which means:
More how-to guides → more training support → more issues resolved → more confident users → higher productivity.
Because true learning retention within software application happens when users can perform tasks effortlessly at the moment it matters.
FAQs
How often should training content be repeated or refreshed?
- The frequency of repetition depends mainly on the complexity of the task.
- For most workplace learning, it’s ideal to reinforce the content within 24 to 72 hours after the initial training. This timing helps interrupt the forgetting curve and strengthens memory.
- From there, spacing out refreshers (first weekly, then monthly) helps solidify long-term retention without overwhelming the learner.
- The key is to repeat at intervals just before the knowledge begins to fade.
Can learning retention improve employee productivity?
Absolutely.
- When employees retain what they learn, they don’t waste time second-guessing steps, re-reading documentation, or asking for help. They complete tasks faster, with greater accuracy and confidence. That further means, fewer errors, less rework, and smoother workflows across teams.
- Retention also reduces dependency on support teams or peer assistance, freeing up time across the board. In short, strong learning retention turns training into real-time performance, directly boosting individual and team productivity.
How do walkthroughs support retention in software training?
- Walkthroughs simplify complex processes by guiding users step-by-step through tasks as they perform them.
- This real-time support helps reinforce actions immediately, making it easier for users to remember what to do the next time.
- Instead of relying on memory or flipping through manuals, employees learn by doing, strengthening retention through hands-on repetition.
- Over time, this builds confidence, reduces errors, and turns first-time learning into long-term mastery.

![What Is Learning Retention & How To Improve It [In 2026]](/content/images/size/w2000/2025/12/WhatsApp-Image-2025-12-31-at-10.55.51-AM.jpeg)
