Training is a crucial catalyst for unlocking the full potential of employees in the workplace. And if you’re an L&D leader, you already know that the key to better training is getting employees genuinely interested in learning.
But truth of the matter is you can’t do that without choosing the right employee training method.
So, let’s take a look at different training methods, and while we’re at it, let’s address a common myth that’s still going strong in the learning community—but really needs to be put to rest.
Myth About Employee Training Method
Most companies (and trainers) will tell you that optimizing training means tailoring it to specific learning styles. You know, those styles that come up when employees fill out a training needs assessment (TNS).
These styles are typically grouped into four categories:
- Visual: Learning through images and visuals
- Auditory: Learning through listening and verbal explanations
- Kinesthetic: Learning through physical activities and hands-on experiences
- Reading/Writing: Learning through reading and writing activities
While this approach may seem intuitive, Research shows that focusing solely on these self-identified learning styles doesn’t necessarily improve learning outcomes. In fact, it can hinder them.
Imagine you’re training a group of 100 employees. Would it be effective to provide only visual aids for the 20 employees who claim to be “visual learners”? Probably not. The reality is, every employee benefits from a multimodal learning approach.
- Go the Multimodal Learning Way:
Individuals may or may not have a dominant style but can still gain from being exposed to a variety of learning methods. The key is offering a balanced mix of training methods that cater to different needs, ensuring all 100 employees get the most out of their learning experience.
In this blog, we’ll help you understand how to select the right training methods that create a well-rounded training plan!
We have researched the top 10 comprehensive employee training methods that help maximize your team’s productivity.
10 Types of Employee Training Methods
1. In-Flow Microlearning
Microlearning is one of the most effective employee training methods when the goal is speed, accuracy, and retention. But in enterprise environments, its real power emerges when learning happens inside the workflow.
Instead of relying on employees to remember what they learned in a course and apply it later, digital adoption platforms can deliver microlearning at the exact moment of action, guiding employees step by step as work happens.
Platforms like Gyde deploy domain-specific AI agents that act as in-the-flow training systems, embedded directly within business processes such as customer onboarding, compliance checks, or healthcare operations.
Pros:
- Learning happens in the flow of work
- Higher retention through real-world repetition
- Reduced dependency on refresher training and manuals
- Faster onboarding for complex, regulated workflows
Cons:
- Requires tight integration with enterprise systems
- Best suited for operational and software-driven roles
Pro Tip
For enterprises operating in regulated or software-heavy environments, the most effective microlearning strategy is contextual specific intelligence. AI agents embedded into workflows turn everyday tasks into continuous learning moments, making training both scalable and immediately useful.
Let's take an example:
In financial services, training employees on KYC/AML procedures is complex, constantly evolving, and error-prone when handled through static courses.
An AI-powered KYC/AML Verification Agent guides teams through the process in real time:
- Extracting and validating data from identity documents
- Cross-checking sanctions and PEP databases
- Explaining risk decisions and compliance outcomes as they occur
Here, microlearning happens during the verification process itself. Employees learn how decisions are made, what red flags matter, and how compliance logic works without pausing work or referring back to manuals.
2. Instructor-Led Training
Instructor-led training (ILT) is a traditional form of learning where a qualified instructor or trainer leads and facilitates the training session in a classroom or physical setting. ILT typically involves face-to-face interaction between the instructor and the learners, creating a direct and immediate learning experience.
This can be taken in various forms, including lectures, presentations, demonstrations, discussions, hands-on activities, group exercises, and assessments. The instructor guides the learning process, delivers content, provides explanations, answers questions, and engages learners through interactive activities.
Pros:
- Personalized instruction
- Immediate feedback
- Opportunity for group collaboration
Cons:
- Costlier affair
- Scheduling difficulties
3. E-learning
E-learning, also known as electronic learning, is an employee training method that delivers educational or training content using electronic devices and digital technologies. It involves using computers, the internet, and various multimedia tools to facilitate employee learning outside of a traditional classroom setting.
But its important to note that the effectiveness of e-learning depends on the quality of instructional design, interactive elements, multimedia components, learner engagement, and the availability of support systems.
There are two distinct types -
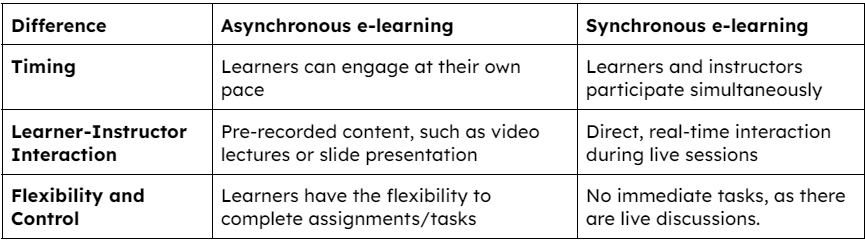
VILT(Virtual Instructor-Led Training) falls under the umbrella of synchronous e-learning, it specifically focuses on virtual instructor-led training sessions that simulate the traditional classroom experience in an online environment.
Pros:
- Flexibility and convenience for remote employees
- Ability to scale training across a large organization
- Cost-effective in the long run.
Cons:
- Feeling of isolation or disconnection from the learning experience
- Need for reliable technology and internet access
- Possibility of Distractions
4. Simulation employee training
Simulation training has proven highly effective in preparing people for real-world job conditions. By immersing individuals in realistic scenarios, they can gain practical experience in a safe and controlled environment.
The rise of the so-called "Metaverse" has sparked a new wave of interest in simulation training. It enables the incorporation of engaging gaming elements to increase motivation, attention, and overall employee learning outcomes. As a result, we can expect to see more investment in simulation training in the coming years as organizations seek to upskill their workforce in a fun, engaging, and effective way.
Simulation training can improve decision-making, collaboration, and change management skills. Research has shown that such training can significantly improve productivity and performance, with participants able to access the training tool on demand and engage in the deliberate practice of specific skills in a safe environment.
Pros:
- Realistic training experiences
- Interactive and engaging training
- Zero Risk
Cons:
- Lack of social interaction
- High Cost
5. On-the-Job Training
On-the-job training (OJT) is an employee training method with dynamic learning and skill development. It occurs while employees perform their actual job tasks. This approach involves immersive experiences, guidance, and mentoring provided by experienced colleagues or supervisors.
During OJT, employees actively engage in real work situations, working alongside experienced personnel to acquire knowledge and skills. They gradually assume more responsibility and independence as they gain proficiency. The training process may include demonstrations, job shadowing, practice sessions, and ongoing feedback and support.
Types of OJT methods commonly employed are:
- Coaching: This approach involves one-on-one interaction between a coach and an employee. It focuses on enhancing performance, providing personalized training, and helping employees achieve their goals.
- Apprenticeship/Shadowing: Apprenticeship pairs a new employee with an experienced one who serves as a guide and mentor. Through shadowing and hands-on experience, apprentices learn from their more seasoned counterparts.
- Mentoring: Mentoring establishes a reciprocal and collaborative relationship wherein a mentor supports the growth, learning, and career development of a mentee.
Pros:
- Personalized to the job and role
- Reduced training costs
- Improved employee morale
Cons:
- Inconsistency in training outcomes
- Time-consuming nature
6. Blended learning
Blended Learning or Hybrid Learning is an educational approach coined by Bonk and Graham in 2006 and solidified with the first Handbook of Blended Learning publication.
The models below differ in their approaches to structuring the training experience, the extent of online and in-person components, and the level of customization and flexibility provided to employees. Each model has its own advantages and can be chosen based on the specific needs and preferences of the organization and its employees.
The four models of blended learning are:
- Rotation Model: Employees will rotate between different learning stations, including online activities, individual instruction, and group work, for diverse learning experiences and skill development.
- Flex Model: Employees will complete most of their coursework online, with in-person discussions and activities with colleagues and trainers, providing flexibility, accessibility, and opportunities for collaboration.
- A la carte Model: Employees can customize their professional development by taking online courses in addition to traditional classroom instruction, offering flexibility, choice, and a structured learning environment.
- Enriched Virtual Model: Employees primarily learn online but have in-person meetings with trainers for personalized support, guidance, and assessment, striking a balance between independent online learning and face-to-face interactions.
Pros:
- Personalization leads to better engagement and outcomes.
- Students can access a wider range of resources and experts.
- Allows for personalized, self-paced learning
Cons:
- Technology Dependence
- Effective use of technology requires training and resources.
- Inequities in access to technology can widen achievement gaps.
7. Roleplaying
Role-playing training is a highly effective employee training method that simulates real-life interactions with a trainer or facilitator, allowing participants to practice and build confidence in their skills.
This active employee learning strategy involves performing realistic scenarios that help to identify and address problems.

Pros:
- Provides a safe and controlled environment
- Imparts confidence and improves communication
- Allows for immediate feedback and corrections
Cons:
- Time-consuming and require significant planning and preparation.
- May be uncomfortable for some employees
- May not accurately replicate real-life scenarios
8. Video Training
Videos are not just another training method, they're a versatile tool that can be incorporated into any employee training method, from on-demand training to microlearning.
With the ability to blend camera footage, animation, graphics, text, and audio, videos offer a dynamic and immersive learning experience unmatched by other e-learning formats.
To implement a successful video-based learning strategy, it's essential to keep content short, choose relevant topics, make it engaging and interactive, and optimize it for various devices.
Moreover, as more learners become mobile-first users, optimizing content for small screens is crucial to keep up with the mobile learning trend.
Pros:
- Versatile and adaptable to various training approaches.
- Offer dynamic and immersive learning experiences.
- Blend camera footage, animation, graphics, text, and audio.
Cons:
- Production can be time-consuming and costly.
- Poor video quality or production value may hinder engagement.
- Requires proper bandwidth and internet access for streaming.
- Potential for passive viewing without active engagement or application.
9. Case studies
Traditional lectures and presentations simply don't cut the chase. Case studies provide a hands-on approach to learning, allowing employees to engage with real-world scenarios and develop critical thinking skills. Plus, they're much more engaging than boring lectures and can lead to better retention of information.
But beware: not all case studies are created equal. They must be relevant to your organization's needs and goals and presented interactively and engagingly to be effective.
Refrain from regurgitating dry facts and figures; make sure your case studies tell a compelling story that will resonate with your employees and encourage them to think creatively and critically.
Incorporating case studies into your employee training program will help employees develop valuable skills and knowledge and create a more dynamic and engaging learning environment.
Pros:
- Provides practical application of knowledge and skills.
- Encourages active participation and engagement.
- Facilitates decision-making and analytical skills.
Cons:
- Requires careful selection and preparation of case materials.
- Needs skilled facilitators to guide discussions effectively.
- May require additional support materials or resources for thorough analysis.
10. Gamification
Our last employee training method is Gamification. It uses game design elements and mechanics in non-game contexts, such as employee training, to motivate and engage learners. The idea is to take what makes games so addictive and apply those principles to learning.
To add gamification to your corporate learning,
- Start by identifying the learning objectives
- Determining if gamification aligns with those goals
- Choose the appropriate game mechanics
- Track the performance of the game and make adjustments as needed.
When implemented thoughtfully and strategically, gamification can be a powerful tool in employee training.
Pros:
- Makes the learning experience more enjoyable and interactive.
- Encourages healthy competition and collaboration among employees.
- Provides immediate feedback and rewards for progress.
Cons:
- Requires careful alignment with learning objectives and content.
- The development of gamified content can be time-consuming and costly.
- Potential for an overemphasis on game elements, detracting from the learning itself.
Parting Thoughts
To determine the most suitable employee training method for your team, it is essential to consider various factors such as individual roles, organizational goals, industry requirements, and individual development areas. \
However, making sure that the training is engaging and avoids becoming dull and monotonous is equally important.
To avoid high costs, employees must be engaged in training in order to minimize disengagement. In fact, Gallup's research reveals that disengaged employees cost a staggering $7.8 trillion, which accounts for 11% of global GDP.
The solution - combine and customize different employee training methods to create a dynamic and engaging learning experience for your employees.
For example, for training service center employees, on-the-job training with role-playing can be highly effective as it allows them to practice their customer interaction skills while fulfilling their daily call quotas.
On the other hand, micro-learning and gamification can be an excellent choice for banking employees who need to learn new HRMS software. Breaking down complex processes into bite-sized walkthroughs and incorporating gamified elements like leaderboards can enhance their learning experience.
By prioritizing employee engagement and tailoring employee training methods to align with individual needs and organizational culture, businesses can cultivate a motivated and skilled workforce ready to tackle new challenges. Investing in your employees' development positively impacts your bottom line.
FAQs
What is the difference between training and learning?
Training is a structured process aimed at teaching specific skills or knowledge. On the other hand, learning is a broader, lifelong process encompassing understanding and capabilities through various means. While training provides a focused approach within a designated timeframe, learning can occur independently and spontaneously outside of formal training settings. Training is a subset of learning, and both are interconnected but serve distinct purposes in the educational process.
What is employee training meaning & importance?
Employee Training refers to equipping employees with specific skills and knowledge.
It involves structured learning opportunities like workshops and on-the-job training.
Importance:
- Improves employee performance and productivity.
- Increases job satisfaction and engagement.
- Contributes to employee retention and loyalty.
- Enhances overall organizational performance.
What are the five steps of training an employee?
- Needs Assessment: Identify the specific training needs of employees by assessing their current skills, knowledge, and performance gaps.
- Training Design: Develop a training plan and curriculum that aligns with the identified needs.
- Training Delivery: Conduct the actual training sessions, whether through workshops, e-learning modules, on-the-job training, or a combination of methods.
- Training Evaluation: Assess the effectiveness of the training program by gathering feedback .
- Training Reinforcement: Provide ongoing support and reinforcement to employees after the initial training.
What is the most popular method of training?
Multimodal training is becoming increasingly popular. It refers to an approach that combines various training methods and modalities to create a comprehensive learning experience. For example, a sales training program might include role-playing exercises, video demonstrations, and online quizzes to address different aspects of the sales process and accommodate a geographically dispersed sales force. It promotes active engagement and participation, fostering a dynamic and interactive learning environment.
What are the top five methods of training delivery?
Here are some of the most popular training delivery methods-
- On-the-job training
- Microlearning
- Video Training
- E-learning
- Roleplaying

