For C-level executives, every new technology investment is a high-stakes decision. In many ways, it feels like flipping a coin…
Heads – Increased efficiency, higher adoption rates, maximized ROI, seamless workflows, and a more innovative work environment.
Tails – Resistance to change, low adoption, underutilized features, long learning curves, and failure to achieve expected ROI.
However, in real world, new technology implementation isn’t as black and white as a coin flip. It takes careful planning, the right resources, and a solid strategy. It’s not just luck that decides success. It’s how well you prepare for it.
In this blog, we break down what goes into the strategy phase, the risks to watch out for, and the best practices (for before, during, and after implementation) to help you get it right.
Here’s all that we’re going to cover in this blog:
- New Software Implementation vs. New Technology Implementation
- Know Your ‘Why’ Behind Implementing New Technology
- How Companies Are Prioritizing New Technology Investments
- Risks of Implementing New Technology
- 7 Steps To Implement New Technology In The Workplace
- 7 Best Practices To Implement New Technologies
New Software Implementation vs. New Technology Implementation
Ever noticed how people say "implementing technology" and "implementing software" like they mean the same thing? But there’s actually a difference.
- Technology is the big umbrella. It includes everything from AI and automation to entire IT systems.
- Implementing technology means introducing new tools, devices, or systems (like rolling out AI automation or setting up cybersecurity frameworks) that has the power to change how your employees work.
- For example, if a company moves from traditional data storage to cloud-based servers, that’s a technology implementation.
Whereas,
- Software is just one part of technology.
- Implementing software means setting up specific programs or applications that run on existing technology.
- It could mean setting up a CRM like Salesforce, adopting a new project management tool like Asana, or integrating an HR management system.
A simple way to remember it? All software implementations are technology implementations, but not all technology implementations are just about software.
This blog will focus on new technology implementation and its transformative potential.
Know Your ‘Why’ Behind Implementing New Technology
New tech sounds exciting. But is it actually helping you? Or just burning cash?
Here are 4 questions to make sure your investment makes sense.
1. Competitive Edge: Are You Doing This to Stay Ahead?
Technology should set you apart from the competition. Not just help you keep up.
Example: Amazon’s one-click checkout. While others had clunky carts, Amazon made buying online easy, differentiating them from the market e-commerce competitors.
How do you know if this is the case: Ask – if we removed this technology, how would our position change? If the loss would significantly impact customer experience or competitiveness, it's a key differentiator.
2. Security First: Are You Prioritizing Operational Safety?
If protecting sensitive data is your goal, cybersecurity tech is non-negotiable.
Example: Banks don’t gamble with security. Multi-factor authentication, AI-driven fraud detection, end-to-end encryption are all a part of it. In fact, JPMorgan spends millions to stay ahead of hackers.
How do you know if this is the case: Start by evaluating your security framework. If the organization has existing vulnerabilities (like weak access controls, lack of encryption, or prior security incidents) implementing the cybersecurity technology becomes essential.
3. WFH Situation: Are You Trying To Adapt to the Hybrid Work Model?
Remote teams thrive when tech eliminates friction.
Example: Microsoft & Slack doubled down on Teams & Huddles. Why? To make remote work feel as seamless as in-office collaboration.
How do you know if this is the case: Organizations can assess this by evaluating whether the technology enables remote and in-office teams to work efficiently without disruptions. Key indicators include improved communication, access to resources, and workflow integration across devices and locations.
4. Maximize Potential: Are You Looking To Automate Mundane Tasks and Boost Efficiency?
If a task is repetitive, a machine should be doing it.
Example: Salesforce Einstein & HubSpot AI handle lead scoring, follow-ups, and data entry, so your sales and marketing teams can actually close deals.
How do you know if this is the case: Start by identifying bottlenecks (like manual data entry, follow-ups, scheduling, or routine reporting) that slow down productivity. If automation is working as intended, employees should be spending more time on strategic work rather than admin-heavy tasks.
Bottom line: If your tech isn’t solving a real problem, it’s just an expensive distraction. Choose wisely.
How Companies Are Prioritizing New Technology Investments in 2025
Companies don’t invest in technology without a purpose. There’s a pattern. A strategy. And if you want to see what’s driving it, check out this chart from Tech.co’s The Impact of Technology on the Workplace Report.
This chart offers some insight into how companies are prioritizing new technologies:
Priority 1: Automation & Security
AI and cybersecurity are leading the charge here. Companies are using them to automate repetitive tasks and safeguard business operations. Because efficiency and security aren’t optional.
Priority 2: Better Connectivity
From 5G to online collaboration tools, companies are investing in tech that makes remote work feel seamless. Better communication isn’t just a perk; it’s what creates innovation.
Priority 3: Emerging Technologies
Blockchain, VR/AR, and RPA hold massive potential, but they’re still in the early adoption phase. Businesses see the opportunity but are waiting for better integration before going all in.
This ranking isn’t random. It reflects a clear strategy: tackle immediate needs. Efficiency, Security, and Connectivity are the three ranked priorities for businesses before they dive into high-risk, high-reward innovations.
Risks of Implementing New Technology
Let’s explore some challenges that come with rolling out a shiny new piece of tech.
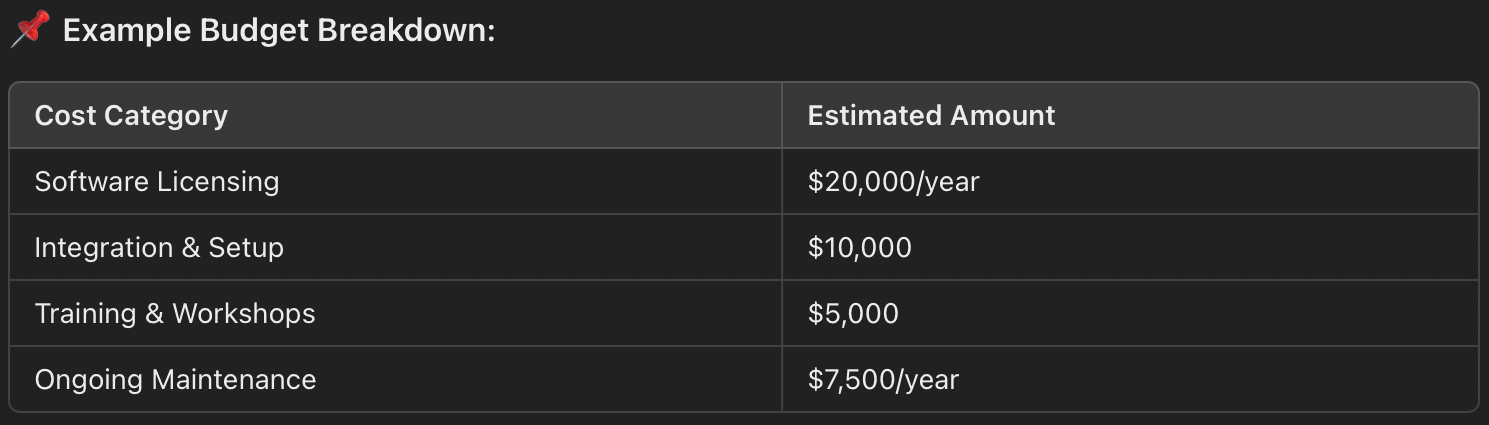
1. Financial Risks
New technology isn’t cheap, and hidden costs like integration, training, & customization constantly add up. Think of investing in a new CRM to automate sales call, only to see poor KPIs. Plus, over-relying on a vendor can be risky. If they stop updates or go out of business, you’re left looking for solutions.
2. Operational Disruption
When implementing new technology, disruptions cannot be avoided. Let's say, you introduce a new warehouse management system. Getting warehouse managers and frontline employees to adopt it can temporarily slow down order processing.
If downtime isn’t planned for, operations can become chaotic, leading to overwhelmed employees and frustrated customers.
3. Employee Pushback
New tech rolls in. People push back. It’s human nature. If you don’t tackle it early, that resistance spreads–fast. For example, an accounting firm rolls out cloud-based bookkeeping. Employees who are used to old system, push back. And then, adoption drops, efficiency takes a hit, and the whole transition starts to fall apart.
Suggested Read: Strategies to tackle resistance to change
4. Data Security and Privacy
New technology often brings new vulnerabilities. For example, a company might implement a cloud storage solution without checking its compliance with GDPR or HIPAA. A data breach could mean exposing sensitive customer info. This leads to hefty fines and irreparable damage to the company’s reputation.
5. Training and Skill Gaps
Even the best tech is useless without skilled users. For example, if a retail chain rolls out AI-driven inventory management software but sees no improvement because store managers aren’t trained to use basic features or interpret the analytics. In some cases, companies may need to hire expensive specialists, further straining budgets.
6. Integration Challenges
New tech often struggles to play nice with existing systems. For example, a company adopting a new HR software might experience data migration issues, causing employee records to get jumbled or lost. Compatibility issues can disrupt workflows, causing more problems than solutions.
7. Innovation Risks
Early adoption of new technology can feel inspiring but it can risky. A real-world example is Google Glass. Many businesses invested in it, anticipating a revolution in workplace collaboration and field operations.
However, the product didn’t mature as expected, support died out, & the technology became outdated, leaving organizations with an expensive gadget that couldn’t deliver.
In Short: By understanding the risks and following the steps and best practices below, you can avoid wasting money on yet another shiny object.
7 Steps To Implement New Technology in Your Organization
Following are the steps to help you implement new technology from start to end.
Skip a step, and you risk confusion, resistance, or worst case—wasting time and budget on a tool no one uses. By following these seven steps, you’ll not only implement new technology but also make sure employees fully adopt it.
We’ll break them down into three key phases:
BEFORE IMPLEMENTATION
1. Spot the Need for Change
Scroll up to this section if you've missed it: Know Your ‘Why’ Behind Implementing New Technology. Before starting with any new digital initiative, your foundation, your 'WHY' should be strong.
Here's how you start to identify the kind of technology you need:
🔹Start with a Technology Audit: Map out all existing technologies—software, hardware, and network infrastructure. Know how different teams to use these tools daily. Are they helping them, or are they holding them back? Such conversations will show inefficiencies, redundancies, and missing links.
🔹Listen to Pain Points: Ask your employees about the technical or operational issues they face.
- Which tasks take the longest? What would make them faster?
- Where do approvals get stuck? How can we make it easier?
- What specific limitations do you face? Are there workarounds or better tools?
- What kinds of errors occur most? How do they impact your work?
Remember: Ignored problems only get worse. A minor inefficiency today can lead to missed revenue targets, decreased productivity & higher employee frustration.
Listen proactively, identify patterns, and explore solutions with them, for them!
2. Create a Plan
At this stage, enthusiasm is high. Teams are eager to execute their ideas, but execution needs structure.
This is the time to translate the identified problem into a problem statement and build a compelling business case to secure leadership buy-in.
Here’s how to set up a strong implementation plan:
🔹Set specific, measurable, and achievable goals that align with business priorities. Identify the core problem and define success metrics to track progress. For example, instead of saying, "Improve customer service," a clearer goal would be: "Reduce response time from 24 to 6 hours using automated chatbots."
🔹 Set realistic timelines. Break the implementation into phases. Consider key steps like planning (2–4 weeks), approval (2–6 weeks), execution (4–12 weeks), training (4+ weeks), and ongoing optimization. Think of potential roadblocks that can arise for your organization.
🔹Next, assemble a dedicated implementation team with key change agents who will be part of the implementation process. For small businesses, a lean team of 2–3 may be enough, while larger enterprises need a cross-functional team spanning IT, department heads, & end-users.
🔹Appoint a project manager. This person will oversee the project, manage roadblocks, and make sure deadlines don’t slip.
With a clear roadmap, the right people, and strong leadership alignment, you will be one step towards success.
3. Choose the Right Technology, Software, or Equipment
When implementing new technology, the conversation doesn’t start with, “Let’s adopt AI” or “Let’s get automation.” It works in reverse.
Organizations first identify the challenges they need to solve, then explore the best technology to address them. This approach varies across industries. What works in healthcare may not suit manufacturing, and a solution for banking may not fit IT.
So how do you select the right technology and convince leadership to invest in it?
🔹Start by evaluating vendors with a critical eye. Don’t settle for surface-level promises. Demand proof. Assess capabilities, scalability, storage, usability, and cost. Test before you commit. Avail free trials, if available.
🔹 Identify costs for technology, implementation, training, & maintenance to find out financial feasibility. Present a cost-benefit analysis to leadership, showing how the investment improves efficiency & reduces errors. Their inputs are a must.
Let's say a banking firm invests in cybersecurity tech by choosing a fraud detection software. It may seem expensive, but if it reduces fraudulent transactions by even 10%, it proves its worth.
🔹Set up sandbox environments to run real-world simulations. Make sure that the software performs exactly as promised. A sandbox provides an isolated testing ground, allowing your team to validate functionality, detect issues, and get hands-on training.
In short: Align technology with business needs, not trends (and most importantly back all related decisions by data, feasibility, & long-term impact)
DURING IMPLEMENTATION
4. Personalize the Platform Experience
With the right technology selected, the real deal starts. This stage needs the organization and vendor to collaborate to create better experience for the end-users.
To achieve this, here are a few key steps to take:
🔹Adjust UI/UX for better adoption. Simplify navigation and layout to match users' technical proficiency. Customize themes, branding, and interface elements to reflect company identity.
For example, customer support. A CRM system should allow CS reps to access relevant customer histories in one click, avoiding cluttered screens.
🔹Configure features to match business needs. Remove unnecessary functionalities that could overwhelm users and simplify the interface. Enable only the relevant modules for each department (e.g., in an ERP system, HR might need payroll management, while finance requires budgeting tools).
🔹Integration with existing tools should be easy. Make sure data exchange with other platforms your business already uses is possible. Set up APIs, connectors, or middleware solutions to enable real-time communication.
🔹Localize and make the technology platform multilingual (and it's a must, if you have global workforce). Adapt the language, date formats, currency, and region-specific workflows to match user preferences. Include localized customer support or chatbot responses in multiple languages.
🔹Customize dashboards based on user roles. C-level executives, managers, and frontline employees should have different views. Restrict access to sensitive data to prevent unauthorized changes.
In short: A system that isn’t intuitive from day one is a wasted investment. Prioritize ease of use, efficiency, and long-term success.
5. Roll Out and Onboard End-Users
With the new system designed and tested, it’s time to go live. But not all at once.
A strategic, phased introduction is the only way to make sure smooth implementation and prevent operational disruptions.
🔹Start with a controlled launch. Roll out the technology to a select group before expanding. For example, a manufacturing plant with 100+ machines could start with IoT sensors by XYZ vendor on 10 machines, track the impact over 3 months, & tweak settings before deploying across the entire facility.
🔹Showcase small wins to secure support. For an enterprise rolling out a new AI-powered sales automation tool, a sales director sees faster pipeline movement and improved prospect response rates. He shares this success with executives, leading to additional budget approval for full-scale implementation.
🔹Forward-think the tech adoption. Conduct orientation sessions (whether in-person or virtual) to familiarize users with the new tool. Make initial technical training mandatory to prevent confusion, boost efficiency, and ensure employees confidently embrace the technology.
Your hard work has led to this moment. Don’t let small setbacks derail progress. Have your tech implementation team on standby to resolve initial issues, answer questions, and eliminate friction.
AFTER IMPLEMENTATION
6. Make Training Stick for Real
A few weeks into your new technology implementation, you will either see a boost in productivity or a drop. If productivity dips, it likely means your training programs have poor retention.
Training cannot be just about handing out manuals or hosting a one-time session. It needs to be engaging, continuous, and designed for how people actually learn and work.
To ensure smooth adoption:
🔹Use training methods that align with both people and processes while reducing resistance to change. In industries that rely on technology-driven equipment, software documentation should be digital, easily accessible, and role-based. Employees should be able to find what they need instantly without unnecessary friction. Investing in training and development software at this stage can help structure onboarding and provide a consistent learning experience.
🔹Offer multiple training formats to suit different user preferences. Some employees may prefer reading a how-to article, while others learn better through videos or interactive guides. Training should be flexible enough to meet them where they are.
🔹For software-related training, consider AI-driven DAPs (Digital adoption platforms) like Gyde. These platforms provide step-by-step walkthroughs and contextual help articles, embedding training directly into the software.
What makes Gyde a top choice among DAPs for training? Its ease of use is a major factor. Here are some key features that set it apart:
- Audio-visual walkthroughs: Within the newly rolled tech software, you can have visual cues with audio instructions guiding employees from first to last step.
- Multilingual Help: All walkthroughs and help articles can be converted to the user's preferred language for a personalized experience.

- Assist Mode: For experienced users who only need occasional support, Gyde shows only the necessary steps.
- New Feature Announcements: Keep users informed of software updates and process changes through the ‘What’s New’ section, making sure they engage actively with new updates.
- AI Content Creation: Training admins can simply capture workflow, and it automatically generates multiple training formats, from videos to contextual guides.
Now, the last step – keep improving! Monitor post-launch performance and tweak your tech (or related training) to make it even better.
7. Optimize & Track Impact
Training is just the beginning. Optimization is where true efficiency and adoption take shape. Once the technology is live, the focus must shift to evaluation.
Organizations must track:
- User and stakeholder feedback to identify usability gaps and adoption challenges.
- Performance against pre-defined KPIs to ensure expected outcomes are being met.
- Areas for improvement that require immediate action to optimize efficiency.
Pro Tip: Gather direct user feedback. Data tells you what is happening; user feedback tells you why. Collect input, address concerns, and refine training accordingly.
In case of software implementation, if you're using a Digital Adoption Platform (DAP) like Gyde, you gain real-time analytics on walkthrough engagement, help article usage, and process views. Here's how it helps you:
- Track Feature Adoption: If new features are meant to improve efficiency, monitor how often users engage with guides and walkthroughs to measure their effectiveness.
- Pinpoint Drop-Offs: If employees frequently abandon workflows at specific steps, use drop-off analytics to detect the friction points and fix them immediately.
Need a template to help you get all these steps in one excel sheet?
This L&D Leader's New Tech Implementation Playbook - Template by Gyde has got your back! Peek into the ‘Note’ section for tips on how to use it, then cruise through the playbook filled with checklists and action plans to guide your every move!
7 Best Practices for Implementing New Technology
When experiencing technological change, we recommend keeping these best practices in mind:
1. Align Technology with Business Goals
Technology should never be implemented in isolation. Your technological investments must directly support your organization's strategic objectives. Think of your business goals as a North Star, with technology initiatives carefully orbiting around this central purpose.
To align technology with business goals, consider these powerful frameworks:
- Strategic Alignment Model (Henderson and Venkatraman)
This model bridges the critical gap between business strategy and technological implementation. The key question to ask is: How can technology transform our business objectives into tangible results?
For instance:
→If your goal is improving customer service, technology might enable solutions like AI-powered chatbots or simplify workflow automation
→When seeking operational efficiency, technology could introduce robotic process automation or advanced data analytics platforms
- Balanced Scorecard Approach
This compact method makes sure technology investments create value across multiple business dimensions:
→Financial Perspective: Cost reduction, revenue generation
→Customer Perspective: Improved satisfaction, service quality
→Internal Process Perspective: Workflow optimization, productivity enhancement
→Learning and Growth Perspective: Employee skill development, innovation capacity
By mapping technological initiatives against these dimensions, you create a holistic strategy that transforms tech from a cost center into a strategic enabler.
2. Collaborate Across Teams
Having a shared vision is key to any successful collaboration. IT and business teams should work together to set clear goals and KPIs that everyone can track.
For Example: If the goal is to increase sales, the business team might want to improve lead conversion rates, while the IT team focuses on optimizing the tools that support this. Create a joint metric that both teams are working towards, such as increasing lead conversion by 20% through better data quality and automation.
Another thing is don’t let communication become a one-off event. Regular check-ins with key decision-makers help keep alignment remains on track. These can look like:
- Assessing progress: Is the technology meeting business expectations? Are there any roadblocks that need addressing?
- Reaffirming buy-in: Keeping stakeholders engaged make sure they stay excited about the project and motivated to invest resources when necessary.
- Course correction: Sometimes, technology isn’t hitting the mark, and regular check-ins make it easier to pivot and re-align.
It’s also important to create a culture of continuous communication, not just at the start of the project but throughout its lifecycle. Regular cross-team meetings, shared project management platforms (like Asana or Jira), and open channels (Slack, Teams) can keep everyone in sync.
For instance, if your team is implementing a new HR software system, HR, IT, and operations should regularly check in on user feedback. Is the new system helping simplifying employee management processes? Are there bugs or issues IT needs to address? These kinds of real-time conversations prevent major issues down the road.
Alignment doesn’t happen in silos. IT and business teams need to work hand-in-hand.
3. Employee Training Should Be Your Top Priority
We can't stress this enough – no matter what kind, employee training and support are fundamental to any software or technology implementation. If your team doesn't know how to use the new tools, the whole purpose of bringing in that tech will fall flat.
We've already covered most of this in the steps above, but let’s take a moment to explore the best ways to train your employees. Here are a few proven methods that work really well:
- On-the-Job Training: Employees learn while working, gaining practical skills in real-time.
- Microlearning: Training is broken into bite-sized lessons, making learning easier and less overwhelming.
- Gamification: Adds fun and competition to training, keeping employees engaged and motivated.
- eLearning: Online courses and modules that employees can complete at their own pace.
- Social Learning: Encourages peer-to-peer knowledge sharing through discussions, forums, and group activities.
Next, let's talk tools that can make employee training and support more effective:
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): These platforms offer structured courses, often with certifications and badges to track progress. Only downside is that employees have to leave their workflow to access them.
- Knowledge Base Platforms (KB): A go-to hub for documentation, guides, and resources. It keeps everything organized, but like an LMS, it’s external, meaning employees have to switch contexts to find what they need.
- Digital Adoption Platforms (DAPs): Unlike LMS and KB platforms, DAPs provide real-time, in-app support with walkthroughs, videos, and contextual help right within the software employees are using. This makes it internal, right in the flow of work.
Pairing the right training methods with the right tools makes tech implementation and more importantly, adoption—a whole lot easier.
4. Use Change Management Frameworks
Various frameworks can simplify technology implementation, and the McKinsey 7S Model is a proven one. For example, when integrating Gen AI into your operations, this model will look something like this:
🔹Strategy
Clearly define Gen AI objectives and make sure they align with the broader organizational goals. For example, if a company aims to enhance customer support, its Gen AI strategy could focus on implementing AI-driven chatbots to handle basic inquiries. This would free up human agents for more complex issues.
🔹Structure
Adapt your organizational design to support Gen AI integration:
- Create new roles as needed
- Redesign reporting lines to facilitate smooth communication
- Establish cross-functional teams for collaboration
🔹Systems
Assess and refine:
- IT infrastructure to support Gen AI
- Workflows to incorporate Gen AI tools like ChatGPT or Gemini
- Check data governance protocols to ensure accuracy and compliance
🔹Shared Values
Create a culture of innovation:
- Address any technological apprehensions
- Promote ethical Gen AI adoption and responsible usage
🔹Skills
Identify skill gaps and plan for development:
- Conduct a thorough skills gap analysis
- Provide targeted training, including both technical and soft skills
🔹Style
Lead by example:
- Demonstrate strong leadership commitment to Gen AI adoption
- Encourage data-driven decision-making across the organization
- Embrace an iterative approach to technology integration
🔹Staff
Manage the workforce transition effectively:
- Communicate openly about changes and their impact
- Offer reskilling opportunities for employees who are prepared for new roles
This framework aligns all elements (from leadership and workforce to processes and values) making the change smoother and more sustainable.
Note for Readers:
While the McKinsey 7S Model offers a great approach to implementing new technologies, it’s also helpful to explore other change management frameworks. Models like the ADKAR Model, Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model and others also can help.
5. Make Learning In The Flow of Work
The thing is, when employees have to dedicate separate time for software training, it doesn’t lead to retention. Why? Because the real learning happens when they’re actually using the technology. If they don’t apply it right away, they forget.
The solution? Employees should get the help they need, exactly when they need it without leaving their tasks. And that’s where a DAP like Gyde help.
With an in-app resource center (aka the Gyde widget), employees can access help articles, walkthroughs, SOPs, modules, and more—all in one place.
Here’s why it works:
✔ Employees don’t waste time hunting for answers in different tabs or manuals. Support is right there, inside the tool.
✔ A sales rep sees walkthroughs tailored to their daily tasks, while a manager gets insights relevant to their role. No one gets irrelevant content.
✔ With Gen AI, it becomes easy and fast for training admins to create walkthroughs, help articles and process videos in minutes.
So, instead of having to set aside separate time for training, learning becomes a seamless part of the daily workflow.
6. Keep an Eye on Metrics
Define clear KPIs that show whether your technology is hitting the mark. For example:
- Have Clear KPIs:
Before implementing new technology, sit down with all relevant stakeholders (IT, business, operations, and leadership) to define what success looks like. Without clearly defined Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), you’re left measuring arbitrary data that may not align with your strategic goals.
- Combine Quantitative and Qualitative Data:
While numbers like ROI and adoption rates provide hard data, don’t overlook the importance of qualitative metrics like user feedback, employee sentiment, and customer satisfaction. Combining both quantitative and qualitative metrics gives you a well-rounded view of how the technology is performing.
- Establish Benchmarks:
Metrics only matter when they are compared to something. Benchmarks help you set a success standard and track progress for employee's past performance or industry norms.
For Example: If your previous CRM system had an adoption rate of 60%, a new system should aim for at least 80% adoption within the first 6 months to indicate success.
- Use Analytics Tools:
Use built-in reporting features to simplify tracking and gain real-time insights. Dashboards and reports can save time and provide instant insights into how the technology is being adopted and its effectiveness.
7. Make Feedback the Backbone of Implementation Strategy
- Figuring out how to get feedback from the people who are using it – your end-users.
- When it comes to integration issues or any other challenges users may face, gathering feedback through surveys, assessments, or even informal check-ins to understand what’s working and what’s not.
- For software implementation, tools like Gyde simplify feedback collection with an AI-powered instant feedback mechanism built right in.
- After an employee completes a walkthrough, they’re prompted with a few quick questions within the app. These questions help training admins assess how well the employee understood the process.
- This kind of process-related feedback is incredibly useful when it comes to tweaking or updating training content to make sure it’s truly relevant for users.
So, instead of waiting for issues to pile up, you’re proactively improving the training experience in real-time.
Over To You
We’ve covered a lot about tech implementation, but here’s the key takeaway: intentionality is everything. The ‘why’ behind your tech adoption should be crystal clear.
As you must have guessed from the steps to implement new technology, it is only half the battle. True adoption happens when users actually engage with the tool and integrate it into their daily workflows.
That’s where smart and intuitive solutions like Gyde come in. With in-app guidance through step-by-step walkthroughs and how-to articles, Gyde helps end-users navigate new technology easily.
Enterprises like Verizon, Fidelity, and Bajaj trust Gyde to simplify technology adoption. If you want your implementation to be more than just a rollout, but a true transformation, it’s time to enable your users with the right support.
FAQs
What are the types of technology implementation?
The main types of technology implementation are:
- Hardware Implementation: Installing and configuring physical devices and infrastructure.
- Software Implementation: Deploying and integrating software applications and systems.
- Cloud Implementation: Moving systems and services to cloud-based environments.
- Network Implementation: Setting up and optimizing network systems and connections.
- Automation Implementation: Integrating automated systems to fasten work processes.
What is the latest new technology?
Generative AI (Gen AI) is a cutting-edge technology that uses machine learning models to create content, such as text, images, and videos, based on input data.
Gen AI is revolutionizing industries like content creation, customer service, and design by automating tasks and enhancing creativity. The global generative AI market is expected to reach $118.6 billion by 2030, growing at a 34.6% CAGR from 2023. Tools like ChatGPT and DALL·E showcase Gen AI's potential in natural language processing and image generation.
As for the latest new technology, Quantum Computing is gaining traction. It promises to solve complex problems faster than traditional computers, with companies like IBM and Google leading the development. The quantum computing market is projected to grow to $1.7 billion by 2026.
How to introduce new technology to customers?
To introduce new technology to customers:
- Focus on how the technology solves customer pain points or improves their experience.
- Provide clear, real-world examples or use cases that show its impact.
- Make sure customers understand how to use it through tutorials, guides, or customer support.
- Share success stories from early adopters to build trust.
- Offer a trial or pilot to allow customers to experience the technology with minimal risk.


