Microlearning has been a popular approach in training circles for a while now, raising all kinds of questions:
- Is it just a video?
- Can it be a text?
- Is 5 minutes really the cut-off?
- How do you create it without losing your mind?
And then... there are the brave souls (like you) tasked with building microlearning programs, who, naturally, turn to Reddit, hunting for advice :)
At first glance, microlearning might seem like a “must-have training method” in a trainer’s toolkit. But implementing it needs more than a one-size-fits-all approach.
To see its true potential, L&D leaders/training managers need to research, test, and make sure the approach aligns with employee needs and organisational goals.
We’ve done the groundwork! In this blog, we’ve discussed everything you need to know to make microlearning work for your workplace.
[Don’t get overwhelmed by the length—jump to any section that interests you]
- What is NOT Microlearning?
- What is Microlearning?
- History & Evolution of Microlearning
- Learning Theories Behind Microlearning
- Types of Microlearning
- Benefits of Microlearning
- Real-life Examples of Microlearning
- How to Implement Microlearning
- Strategies to Measure Microlearning
- 3 Best Microlearning Platforms
- Gen AI’s Impact on Microlearning
- How Digital Adoption Platforms Redefine Microlearning for Applications
The Fundamentals
What is NOT Microlearning?
Given the myths about microlearning, we thought it’d be best to clear the air and start with the discussion of what microlearning is not.
Sometimes, what it isn’t tells you just as much as what it is!
#1 It’s not an ALL-IN-ONE Training Solution
Microlearning isn’t here to replace entire training programs, like instructor-led training, e-learning sessions or assessments. It’s meant to complement, not compete with, other methods of employee training.
#2 It’s not NEW
Though microlearning seems trendy, the idea has been around for a long time. For instance, old-school flashcards used to memorize vocabulary or math problems—are early forms of microlearning.
It’s just that the method has evolved a bit since then (check: History & Evolution of Microlearning to see how!).
#3 It’s not only for GEN Z
Microlearning isn’t just for a specific generation. It can be made for anyone tired of long training sessions—may they be in their 20s or 50s. Whether you’re upskilling employees or onboarding new hires, microlearning meets everyone’s needs.
#4 It’s not for complex topics
That’s just not true! In fact, if your employees need to improve knowledge retention rates for complex concepts without feeling overwhelmed, breaking such topics into smaller, repeated sessions can help big time!
#5 It’s not only limited to one format
Forget the TikTok stereotype—microlearning can be videos, infographics, podcasts, quizzes, or even interactive scenarios. For example, an employee might learn how to use new software through a series of short videos, take a quick quiz, or read how-to articles.
What is Microlearning?
Microlearning is a way to train employees by breaking down complex topics into small, easy-to-digest nuggets. It is delivered over time within flexible schedules, helping employees understand and remember the material better.
That’s the definition of microlearning—but it’s also so much more! Microlearning is:
- A complete unit of instruction (a focused lesson on one specific topic or skill).
- An activity that thoroughly engages employees (no passive watching, only active involvement).
- Designed to get a specific outcome (it’s goal-oriented & drives measurable results).
- Based on brain science (read: the learning theories behind microlearning).
- Accessible within the flow of work (learn on the job, right when it’s needed).
Quick FYI: You might wonder how ‘short’ microlearning is — Well, there’s no strict rule! It can range from 3 minutes to an hour, depending on the learning need & context.
After all, it’s not so easy to pin one exact definition of microlearning. But you could always take the gist of what it is (and what it’s not), and you’ll know if your program is on the right track!
History and Evolution
The concept of microlearning can be traced back to the early 20th century, though it wasn’t called that until later. Early pioneers in this field include:
- John Dewey (Focused on learning through real-life experiences and short, hands-on lessons)
- B.F. Skinner (Developed the idea of reinforcing learning with small, step-by-step actions)
- Edgar Dale (Created the Cone of Experience, which showed that learning is most effective when it’s interactive and practical)
Fast forward to today, microlearning looks very different from its early days, all hail to rapid technological progress. Let’s look at the key changes:
- With the widespread use of smartphones, tablets, and laptops, employees can access training materials anytime, anywhere. Whether you’re at your desk or on the go, you can quickly dive into training whenever it fits your schedule.
- Microlearning platforms now personalize content (with AI) to help learners with exactly what they need to improve their work performance.
- Such platforms also have advanced analytics that reveal areas where employees struggle, enabling the creation of targeted content to address those gaps.
- Digital dashboards within some of these platforms can also have game-based elements, such as badges, points, and leaderboards, that add an interactive and motivational aspect to microlearning.
- Modern microlearning tools can connect easily with HR and training platforms – making it easy to track progress, measure results, and align training with business goals.
Learning Theories Behind Microlearning
Microlearning is not just a trend—it’s rooted in solid brain science (how one learns). In his book, Short & Sweet Microlearning, Karl Kapp explores four learning theories that explain why microlearning works so well:
Behaviorism
Behaviorism says learning happens through rewards, repetition, and the association of actions with outcomes. It suggests that learners are more likely to repeat a behaviour if they are shown positive results.
To apply behaviourism in microlearning, instant feedback and gamification are powerful tools. For example, after a learner completes a module, they could take a short quiz. If they answer correctly(action), they earn a badge or point(outcome).
Cognitivism
Cognitivism suggests that our brain processes information by first paying attention, then encoding and storing it in short-term and long-term memory, followed by consolidation and retrieval.
Microlearning aligns with cognitivism naturally as it breaks content into manageable chunks, reducing cognitive overload, and helping recall information through repetition.
Constructivism
Constructivism suggests that learners build new knowledge by connecting it to what they already know. It promotes active engagement and problem-solving.
Microlearning can incorporate this theory by including interactive elements like role-playing scenarios and case studies. These activities encourage learners to apply new concepts in a context they understand.
Connectivism
Connectivism is a modern learning theory that suggests learning happens best when learners connect with other peers & share knowledge, especially with the help of digital tools & technology.
Microlearning works well with connectivism because it encourages learners to use social tools and collaborative platforms. For instance, learners could access microlearning modules through mobile apps or engage in discussions within an online community.
Endnote: Each theory provides a unique perspective on how we learn and offers guidance for designing impactful microlearning content.
Types of Microlearning
When we talk about types of microlearning, we refer to the different formats or end-products that can be created:
1. Video-Based Microlearning
Concise videos (2–5 minutes) that explain a concept or show a task. For example, explainer videos, animated tutorials, or video walkthroughs.
2. Interactive Quizzes and Assessments
Test knowledge or reapply to learn engagingly. For example, scenario-based questions or flashcards with immediate feedback.
3. Infographics and Visual Aids
Provide quick, digestible insights through visuals. For example, charts, graphs, or step-by-step guides for complex topics.
4. Audio-Based Microlearning
Podcasts or audio snippets learners can listen to on the go. For example, Leadership tips or sales strategies delivered in 3–5 minute clips.
5. Text-Based Microlearning
Bite-sized text content like checklists, FAQs, or micro-articles. For example, “Top 5 tips to improve productivity” or step-by-step task instructions.
6. Gamified Modules
Engage learners through challenges, badges, or rewards. For example, a game that teaches customer service skills by simulating real-world scenarios.
7. Mobile Apps
Deliver microlearning through push notifications, mini-lessons, or reminders. For example, daily soft skill tips on workplace apps
8. Social Learning Nuggets
Peer-to-peer knowledge sharing through forums, chat groups or social media posts. For example, a shared tip on Slack group for troubleshooting a technical issue.
9. Just-in-Time (JIT) Learning
On-demand learning content accessible at the moment of need. For example, quick how-to guides embedded within applications.
10. Email and Chat Nuggets
Deliver microlearning content via daily or weekly emails or chatbots. For example, a “Tip of the Day” email or chatbot-based training.
FUN FACT: We were pretty surprised in our research to find out that microlearning can actually take the form of memes—and there are even courses teaching you how to create them!
Quick Takeaway: Each type of microlearning can be personalized to the learner’s preferences, time availability, and learning objectives.
Benefits of Microlearning
Now that we’ve micro-learned about microlearning, it’s high time we talk about the benefits—what happens if you get it right? Spoiler alert: it’s all good news.
1. Your employees can now learn anytime, anywhere.
2. Interactive quizzes & games make learning feel less like training & more like playing.
3. Microlearning delivers exactly what your employees need, right when they need it.
4. With microlearning, your training content is easy-to-update
5. Short, targeted lessons are like sticky notes for the employee’s brain!
6. Microlearning saves time and money while keeping development costs manageable.
In Short...
Microlearning isn’t just impactful—it’s elephant-sized impactful. Your employees will soak up training faster, apply it better, and deliver the business results you care about.
Real-life Applications of Microlearning
Case Study 1: At Home
→Overview: Home décor retailer
→Challenge: Traditional training methods (handbooks) were outdated.
→Focus Areas: Onboarding, safety, customer service, compliance, and leadership.
→Solution: Implemented a digital micro-learning tool with gamified content.
→Results:
- 3,000+ employees across 100 stores received bite-sized daily training.
- Platform adapted to focus on areas needing improvement.
- 90% reduction in onboarding time.
- 36% decrease in safety incidents.
- Company-wide training completed in weeks.
Case Study 2: Bajaj Finance
→Overview: Non-Banking Financial Company
→Challenge: Data errors in loan applications on the Salesforce platform, causing files to go on hold and delaying business.
→Focus Areas: Field sales agents & reps
→Solution: Implemented Gyde, an AI-powered Digital Adoption Platform (DAP) for in-app on-the-job training on Salesforce.
Gyde helped training and onboarding for Bajaj's field agents with these features:
- In-app walkthroughs for step-by-step guidance within the app interface, using visual callouts & audio instructions to help users follow processes
Field validation for highlighting critical steps in real-time, so that the agents can input correct data and fewer loan files would go on hold
Multilingual support for allowing agents to translate walkthroughs and help content into their preferred language on the go!
→Results:
- Loan file holds dropped from 18% to 9.7%.
- Better CRM adoption.
- Productivity skyrocketed—all within just three months.
Case Study 3: InterContinental Hotels Group (IHG)
→Overview: Hospitality
→Challenge: Training needed to keep up with the fast-paced customer service demands across 5,000+ hotels.
→Focus Areas: Frontline employees (reps, customer service agents) across hotels worldwide.
→Solution: Switched from long classroom sessions to mobile-friendly microlearning modules.
→Results:
- In just two days, reps in five countries completed over 5,500 lessons.
- Onboarding time was reduced from five weeks to two.
- Knowledge test scores improved significantly.
These companies show how microlearning can deliver fast results—whether it’s through gamified training, on-the-job support, or bite-sized lessons on the go.
The Implementation Guide
How to Implement Microlearning
ANOTHER FUN FACT: 5-minute microlearning piece ≠ 5 minutes of work
Here’s the deal: Implementing microlearning takes its own sweet time. But don’t worry—once you understand the principles, align with your business goals, and really dig into what your learners need, you’ll have a great head start!
Take it step by step, and remember: the effort you put in now will pay off with smarter, happier learners later. Trust us, they’ll thank you (well, maybe silently).
Step 1: Define Clear Learning Objectives
Let’s get one thing straight—vague goals like "Improve leadership skills" don’t cut it. Be laser-focused.
Deconstruct broad goals:
- Instead of "Improve leadership skills," break it down:
⏵ Develop active listening techniques during team meetings.
⏵ Implement SMART goal frameworks in performance reviews.
⏵ Provide constructive feedback that drives action.
Next, let's know who you're creating these microlearning sessions for!
Step 2: Analyze Your Audience's Needs
To create great microlearning programs, you need first to create content that resonates. It’s not just about what you want your learners to train on—it’s about how they want to learn.
Use techniques like the below to know your audience:
1. Behavioral Mapping:
- Work patterns: Are they desk-bound or always on the go?
- Tech comfort levels: Are they digital natives or still warming up to new tools?
- Learning preferences: Do they prefer video, infographics, or interactive content?
- Time constraints: How much time do they realistically have for learning?
2. Technology Ecosystem Evaluation:
- Device usage: Do they prefer mobile, desktop, or both?
- Internet accessibility: Is offline learning important for them?
- Software compatibility: Can your platform fit into their existing tech stack?
3. Feedback Collection Methods:
- Anonymous surveys for quick responses.
- Online focus groups for deeper insights.
- One-on-one interviews for personalized feedback.
- Learning analytics to identify patterns and improvement areas.
Quick Tip: This is the perfect time to set your baselines (knowledge/revenue). [Read: Strategies to Measure Microlearning]
Step 3: Choose a Digital Platform
The right technology can make or break your microlearning initiative. Pick one that matches both your tech ecosystem and your learners’ preferences.
What to look for:
- Accessibility: Works on desktop, mobile, and offline.
- Gamification: Make learning fun with badges, points, or challenges.
- Progress tracking: Show learners their growth—it’s motivating.
- Engagement tools: Like in-app assessments.
Platform Type Comparisons:
- DAPs (Digital Adoption Platforms):
DAPs are excellent for microlearning in real-time software training. They provide in-app guidance in the form of step-by-step walkthroughs & help articles. DAPs like Gyde also have interactive quizzes within the app itself that assess learners’ knowledge. Plus they are mobile-accessible – enabling learning in the flow of work.
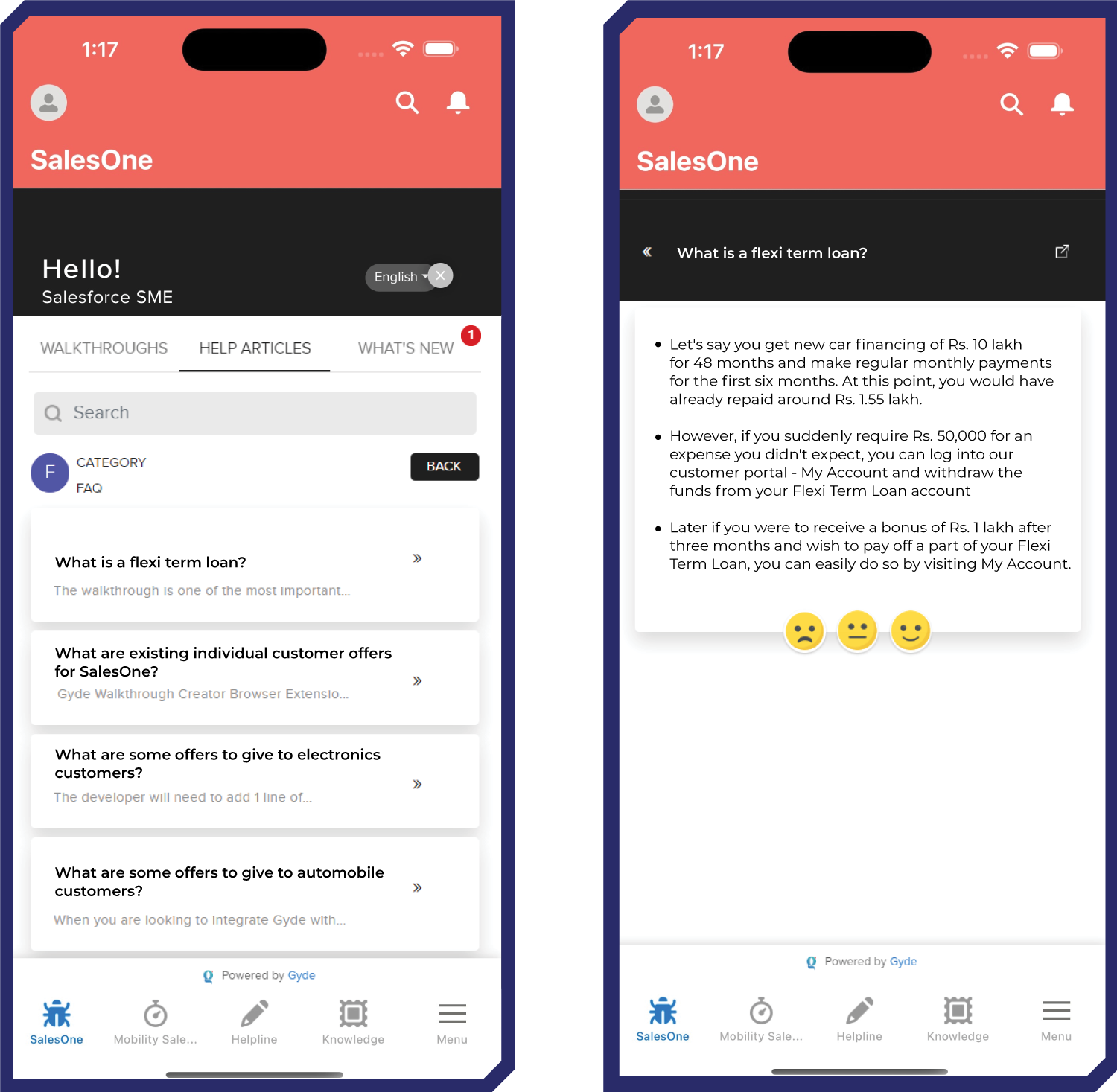
- LMS (Learning Management Systems):
LMS platforms are ideal for structured, compliance-driven learning that provide a centralized hub for eLearning courses. They offer good tracking and reporting features, making them perfect for formal training programs.
While they can deliver short course videos, they can be less flexible for microlearning's “in flow of work” requirement as learners might have to leave their work and look into the LMS platform for help.
- Mobile Learning Apps:
Mobile learning apps are perfect for delivering flexible, on-the-go microlearning content. They are especially beneficial for field sales force teams that are mobile-first or frequently on the move.
Curious about how to train your field sales team in the NBFC sector? Check out Gyde article for some serious niche tips!
[We have mentioned our top three picks below]
Step 4: Build a Storyboard
A storyboard helps you visualize the learner’s journey and make sure it is coherent. To create it, keep these three principles in mind:
- Cognitive Load Management: Avoid overloading learners with too much information at once.
- Progressive Knowledge Building: Start simple and layer complexity gradually.
- Contextual Learning: Show the ‘how to apply’ what learners have learned.
Example: For a CRM training series, start with modules like "CRM Basics," then move to "Using CRM for Lead Generation," and end with "Advanced Reporting Techniques."
Step 5: Design Bite-Sized Content
Create content that is laser-focused on one topic or task. Use the storyboard that you’ve created.
- Keep it short: Based on what your learners prefer, create microlearning in specific duration and stick to it.
- Multimedia approach: Mix videos, infographics, quizzes, and flashcards to cater to different learning styles.
- Interactive scenarios: Include role-playing or simulations for real-world applications.
For instance, you can create a 5-minute video showing "How to Handle Difficult Customers" followed by a quick interactive quiz.
Step 6: Run a Pilot
This step is crucial for enterprises that can’t afford to settle for "good-enough" microlearning, especially when it could potentially disrupt your organization.
Before rolling out to the entire workforce, conduct a pilot with a small group to evaluate your microlearning content. Look at these two distinct metrics:
Quantitative Metrics:
- Completion rates
- Assessment scores
- Time spent on learning
Qualitative Insights:
- Learners’ experience (e.g., ease of use, content clarity)
- Perceived effectiveness and relevance of the training
Pro Tip: Gather all that feedback, tweak what needs tweaking, and then launch the final version with confidence. You’ve got this!
Step 7: Publish and Update at Intervals
Once your content is ready, publish it on whichever digital tool you've chosen. But don’t forget—it’s a living, breathing program that needs regular updates. Here are a few things to keep in mind:
- Publish content with clear instructions given to users on how to access it.
- You can use emails, slack groups, or online community to do so.
- Track performance (Read: Strategies to Measure Microlearning)
- Regularly refresh content based on learner feedback, technology trends and updates & ongoing reassessment of skill gap.
- You can also have quarterly content audits.
We get it—your microlearning implementation process may involve more than seven steps, especially depending on the training topic. But these foundational steps will give you a solid head start.
Remember: Microlearning is more than just a training method—it’s a mindset. When you combine understanding learner psychology, the right platform, clear objectives, & engaging content, you’re not just training—you’re transforming the way learners grow.
Strategies to Measure Microlearning
At Navigate 2024, Cammy Wood, Director of Learning Engagement at GoDaddy, shared insightful strategies for measuring microlearning in her session, "Microlearning for Real-Time Problem Solving."
1. Establish Baselines for Measurement
Before diving into improvements, it’s important to understand where you’re starting from. That’s what baselines do for you – they give you a clear reference point to track growth. Here are three examples of baselines you can create:
- Knowledge Baseline:
Conduct pre-training surveys to assess learners’ initial comfort levels and familiarity with the topic. Ask questions like, “How confident are you in applying this concept?” or “Have you encountered this issue before?”
Later, compare these responses to a post-training survey to measure improvement.
- Utilization Baseline:
Track how often learners engage with microlearning resources. For instance, how many people accessed a particular module, how frequently they revisited it, or how long they spent on it.
- Revenue Baseline:
If your microlearning modules aim to boost performance in sales or customer service, measure the direct business impact. Look for metrics like increased revenue, faster deal closures, or higher customer satisfaction scores tied to trained behaviors.
2. Define Microlearning KPIs
Measuring the success of microlearning needs you to focus on engagement and outcomes. Cammy suggests looking at:
- Engagement Metrics:
How often are learners coming back? For example, “repeat learners” can be a sign of success. Imagine if employees frequently return to short videos you've created on phishing email identification or password hygiene. That's a sign that the content is practical, easy to internalize and resonate with their daily tasks. - Retention Metrics:
Are learners retaining information better? Use quick quizzes or on-the-job assessments to track knowledge retention after completing microlearning. - Kinetic Conversion:
This refers to learners’ ability to turn knowledge into action. Are they applying what they learned in their daily tasks? Observation, manager feedback, or performance reviews can help measure this.
3. Keep Behavioral Goals in Focus
For microlearning aimed at changing behaviors (e.g., improving teamwork, communication, or leadership), focus on closing gaps:
- Identify the specific behavior you’re addressing (e.g., responding empathetically to customers).
- Design scenarios or challenges within the microlearning modules to simulate and reinforce the desired behavior.
- Regularly evaluate whether learners are demonstrating the behavior on the job through feedback from peers or managers.
If you've already explored microlearning and are looking for ways to refine its impact, her tips will offer a clear direction!
Top 3 Microlearning Platforms
Here are our top three picks for microlearning platforms:
1. Gyde
Gyde is an AI-powered digital adoption platform that sits right into any enterprise application, providing real-time guidance with microlearning assets. We saw some of these (assets) in the Bajaj Finance case study, like audio-visual walkthroughs, field validation, and multilingual support, and how they used them to their advantage.
But that’s not all—Gyde has even more features to help both new and seasoned users learn the application without ever leaving their workflow!
Features:
- Help Articles
By offering self-service support in the form of contextual help articles, users can resolve common issues and questions independently, without needing to contact IT support or wait for assistance.
- Assist Mode
Provide advanced users with targeted, context-specific guidance when they need help. Microlearning assets begin from their current screen, so they don’t have to start from the beginning.
- Bite-sized Process Videos
Deliver concise, 1-2 minute instructional videos right within the app. These micro-videos are automatically generated with a click of a button from the walkthroughs you create.
- Analytics to Measure Engagement
Track learner engagement and identify where users drop off or struggle. These analytics are available at granular level. Use this data to refine and optimize your training resources.
Pricing:
- Gyde doesn’t believe in "one-size-fits-all" solutions – they understand that every business has unique needs.
- The Gyde team is there at every stage, from initial setup to ongoing optimization.
- They’ll provide a custom quote tailored to your enterprise, making sure you only pay for the features and services that truly support your learning goals.
Suitability for Organizational Needs:
- Ideal for organizations using multiple applications, as it integrates with any enterprise software.
- Particularly great for improving employee onboarding and training or providing performance support on complex tools like CRMs or ERPs.
2. TalentCards
TalentCards is a mobile-first microlearning platform designed for businesses to deliver bite-sized training content to their workforce. It focuses on creating and sharing visually engaging, card-based learning modules that can be accessed anytime, anywhere.
By prioritizing mobile access and simplicity, TalentCards aims to break down traditional barriers to learning, making sure even remote employees can stay informed and skilled.
Features:
- AI-Powered Course Creation
Just type in the topic you want to train on, and the AI-powered platform does the heavy lifting, generating course content for you in no time.
- Gamified Learning Experience
TalentCards turns learning into a game, where users compete for points and rankings. It’s a fun, engaging way to keep your team motivated and eager to learn.
- Smarter Learning with Spaced Repetition
It uses a spaced-repetition algorithm to make sure learners remember what they’re taught. The platform intelligently serves up cards that users struggle with more often.
Pricing:
TalentCards provides a free trial, with paid plans beginning at $50 per month. Custom quotes are also available upon request for your organization.
Suitability for Organizational Needs:
- Best suited for industries with mobile workforces, such as retail, logistics, and healthcare.
- Most used for compliance training, soft skills development, and product knowledge dissemination.
3. Axonify
Axonify is an AI-powered microlearning platform that delivers personalized, bite-sized training sessions, which integrate easily into employee's daily workflows. It also incorporates gamification and reinforcement techniques to make training measurable.
Managers and administrators get access to real-time insights into training progress, employee engagement, and knowledge levels.
Features:
- Adaptive Learning
It customizes content delivery based on each learner’s unique needs and job role, ensuring that employees receive the most relevant training at the right time.
- Spaced Repetition
Axonify revisits key topics at regular intervals to make sure long-term knowledge retention.
- Engagement Tools
Gamification and reward systems are built in to make learning more interactive and fun, increasing learner participation and motivation.
Pricing:
Pricing is custom and based on the organization’s size, industry, and specific requirements. Axonify provides a demo to help potential users understand the value proposition.
Suitability for Organizational Needs:
- Ideal for companies in industries like retail, banking, and telecommunications where consistent training and compliance are crucial.
- Particularly effective for frontline teams requiring quick, targeted knowledge updates.
Need more tool recommendations → Check out Gyde’s blog on the top 15 microlearning tools!
Gen AI's Impact on Microlearning
Let's talk about how AI is transforming microlearning in a way that's actually exciting!
Think about your employee’s typical work day. They're juggling tasks, trying to learn new skills, and often wishing they could get just the right piece of information at just the right moment.
Generative AI is making that wish come true!
Let us break this down in a way that'll make total sense:
- Learning Management Systems (LMS) are no longer just digital course portals. They now feature “suggestive AI,” which gives learners personalized recommendations based on what they’ve already learned within the system.
- Digital Adoption Platforms (DAPs) are becoming even smarter. DAPs use something like “mediator AI,” which understands users' needs in real time and provides assistance to help them complete tasks within applications.
- And then, there’s quick content generation! AI can create, elaborate, and paraphrase training materials, allowing administrators to continuously update and improve training programs.
To help you further, we’ve provided some practical prompts that can help you start your AI-powered microlearning right away (just copy-paste these):
1/Brainstorming Prompt
"Help me create a 5-minute learning module about [YOUR TOPIC] for [TARGET AUDIENCE]. Break down complex ideas, include real-world examples, and design quick check-in questions."
2/Evaluation Metrics Prompt
"Design a smart assessment framework that measures not just what someone learned, but how they'll apply it in their work. Include engagement metrics, skill retention rates, and potential performance improvements."
3/Storyboarding Prompt
"Craft a storytelling-based learning experience for [TOPIC] that makes complex information feel like an engaging narrative. Use visual cues, interactive elements, and a flow that keeps learners curious."
But this isn't just about new shiny technology. We need to make sure AI-generated content remains accurate, ethical and maintains that human touch.
How Digital Adoption Platforms Redefine Microlearning for Applications
Forrester’s 2023 survey tells us something we already kind of suspected: people don’t like change. In fact, 21% of decision-makers said resistance to change is their biggest digital transformation headache.
And let’s be honest when it comes to training on systems like ERP, CRM, POS or HRMS—the expensive investments—resistance often reaches new levels. Why? Because they’re new, complicated (and not always the most fun to learn.)
But microlearning alongside DAP can change that!
Unlike traditional training methods—such as instructor-led sessions, eLearning courses, and email troubleshooting guides—which are disconnected from the actual work environment, DAPs are fully integrated.
For instance, AI-powered DAP like Gyde offers in-app guidance through short walkthroughs, contextual help articles, bite-sized videos and in-app assessments. They’re built to be internal and accessible, right within the employee’s workflow, making learning seem like a natural occurrence.
For training administrators, Gyde simplifies content creation with its no-code walkthrough builder. They just have to click through the application process to create walkthroughs. From there, they can instantly convert walkthroughs into training videos or step-by-step guides.
Gyde aligns perfectly with the principles of microlearning. It bridges the gap between complex software systems and user proficiency, making sure that your teams are equipped to succeed.
FAQs
What are the cons of microlearning?
Without proper structure and sequencing, learners may struggle to see connections between individual lessons, leading to gaps in their understanding. Microlearning can also result in over-simplification, missing out on important details needed for mastery. For certain tasks that require hands-on experience or deeper cognitive skills, microlearning may not provide enough comprehensive training.
What is an example of micro training?
An example of micro training could be a 2-minute video tutorial on how to use a specific feature in a software application, such as creating a new lead in a CRM system. The video would quickly demonstrate the steps involved, focusing on a single task, and provide a brief recap or key tips at the end. This allows employees to learn exactly what they need, right when they need it, without interrupting their workflow or requiring a long, in-depth session.
What is another name for microlearning?
In the training and development domain, microlearning is often referred to by several other names that emphasize its focus on short, focused learning experiences. Some of the common alternatives include bite-sized learning, nano-learning, just-in-time learning, on-demand learning, micro-training, snackable learning, and performance support.

![How To Implement Microlearning in Training? [Guide for 2026]](/content/images/size/w2000/2026/02/Blog-10--1-.jpg)
