New tools new technology—every year, we see innovations designed to make work faster and easier.
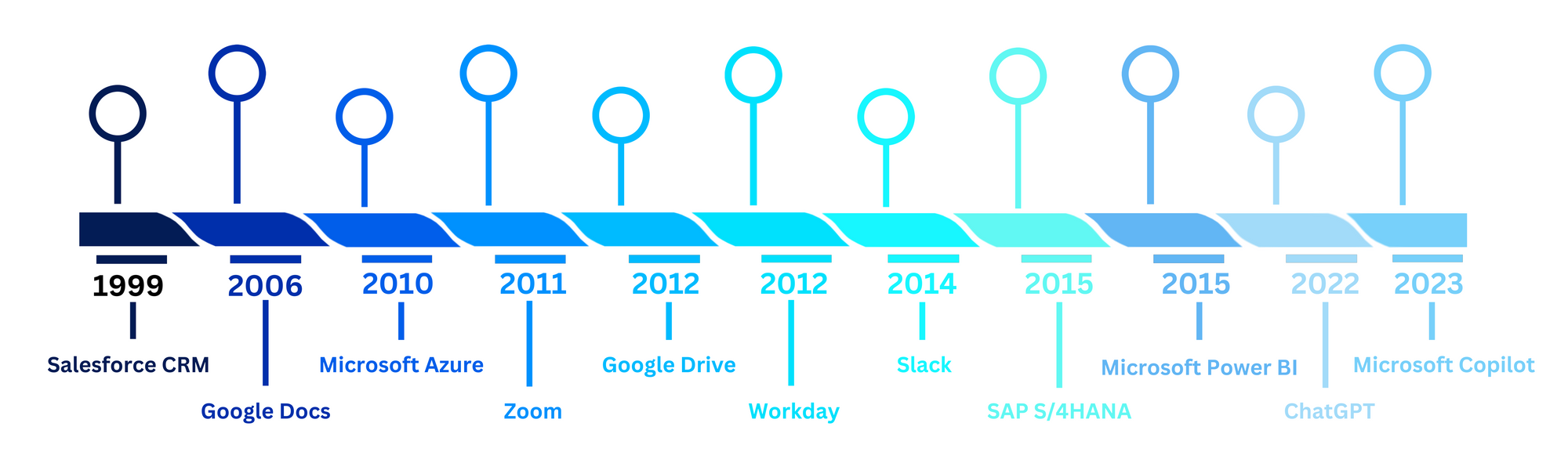
But here’s a stat that might make you question if that’s really happening:
91% of employees say they’re frustrated with their work software.
And it’s more than just employee inconvenience. It’s a retention risk – 71% of leaders admit that employees will leave if they don’t have access to the right tools, technology, or related technical knowledge to do their jobs well.
In other words, if companies don’t invest in training (that thoroughly covers the technical aspects), employees may struggle, grow frustrated, and eventually resign.

For training and development teams, the hard part isn’t running technical training sessions. It’s showing leadership why they matter. Because, leadership won’t invest unless they see tangible outcomes like higher efficiency or real business outcomes.
So, how do you create technical training that minimizes employee frustration and wins leadership support? In this guide, we’ll break down what technical training is, its types, when it’s needed, and the steps to develop a high-impact technical training program.
Summary of What's Covered:
- What is Technical Training?
- Why is Technical Training Important?
- Types of Technical Training Programs
- When is Technical Training Useful?
- How to Develop Great Technical Training
- Why use DAPs for Application-Related Technical Training?
I. What is Technical Training?
Technical training is all about helping employees learn the skills they need to use the tools, software, or equipment that are essential for their work
No matter the role—be it CRM usage, coding, cybersecurity, or machinery operation—technical training equips employees with essential hard skills.
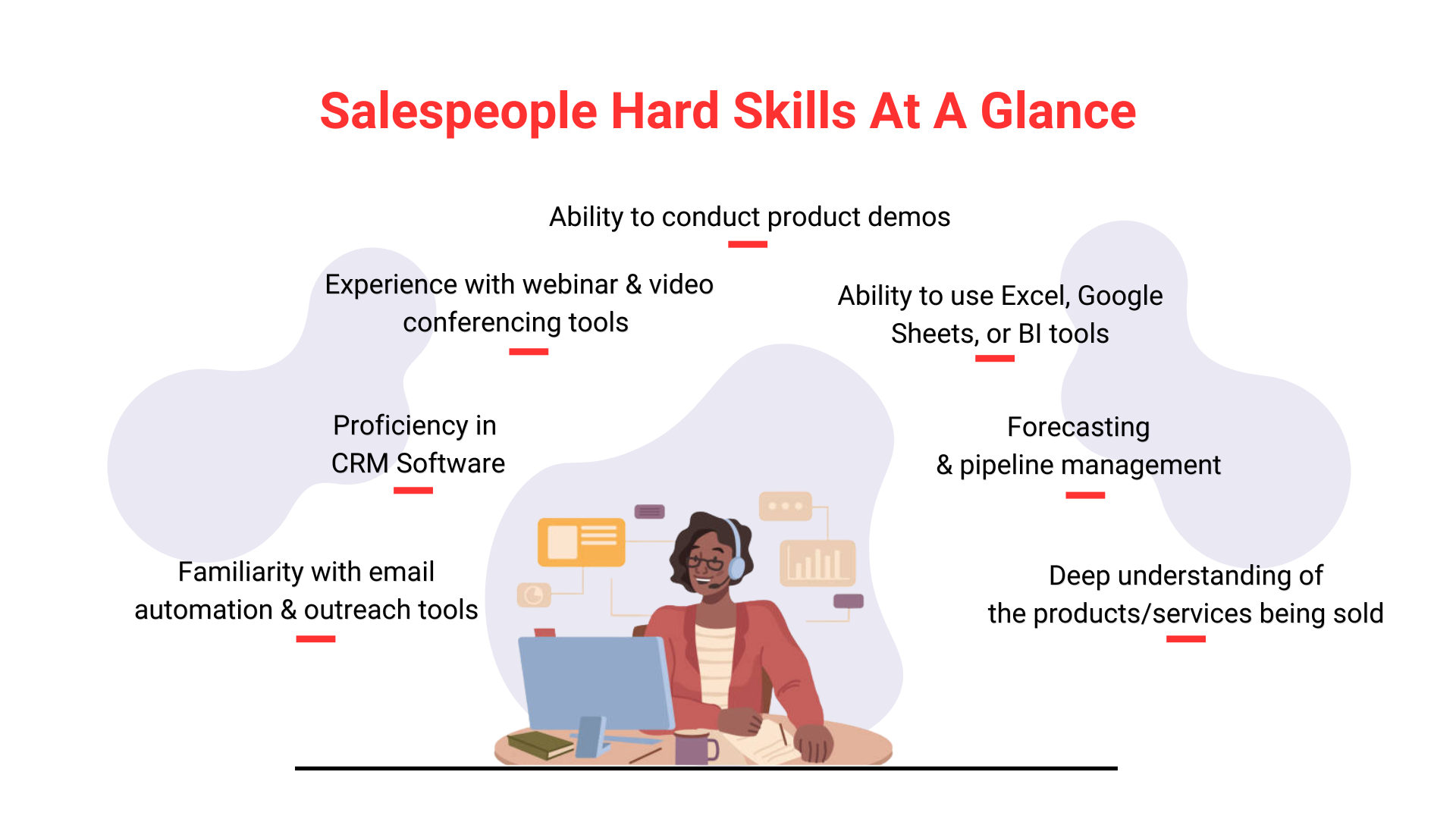
For example, the image below provides a quick glance at the critical hard skills that are an integral part of sales technical training.
Now, let’s explore how different industries integrate technical training into their workforce development.
Technical Training in Different Industry Sectors
Each sector's technical training is designed for employees to use industry-specific technologies — optimizing their performance & delivering high-quality service.
- In the finance sector, professionals are trained on software like QuickBooks, SAP, and Bloomberg terminals, which enable them to manage accounting, reporting, and complex financial analysis with precision.
- In retail, employees receive technical training on Point of Sale (POS) systems, enabling them to handle sales transactions, track inventory, and give better customer service.
- In banking, employees are trained on digital platforms that help in loan processing, account management, and other essential banking operations.
- In healthcare, technical training is given to clinical and administrative roles. It helps medical professionals use advanced medical devices, manage electronic health records(EHRs), and stay updated on specialized procedures.
II. Why is Technical Training Needed in the Workplace?
Training your employees in technical skills has some significant benefits for both the organization and its employees, such as:
- Keeps Skills Up to Date
Technical training keeps skills up-to-date, ensuring employees remain productive as technology and processes evolve. In fact, LinkedIn reports that 64% of L&D professionals today prioritize closing the skills gap that shows us the importance of continuous technical training in modern times.
- Boosts Productivity
Proper technical training prepares employees. It gives them a clear understanding of their tasks, enabling them to work more confidently. When employees have access to the right training resources, they are better qualified to troubleshoot issues independently, minimizing downtime and keeping the momentum going.
- Reduces Frustration
The increasing number of digital tasks can often lead to overwhelm, commonly known as "technostress." To mitigate this, employees need technical training that is clear, concise, and free from information overload. When training is focused and relevant, it empowers employees to easily adapt to new tools and systems, reducing resistance to change.
- Propels Constant Innovation
Technical training keeps your team up-to-date with the latest industry trends and technologies. This encourages a culture of innovation where employees feel empowered to suggest and implement new ideas. Picture your team with fresh ideas, ready to push your organization forward.
- Attracts Top Talent & Retains Employees
High-caliber talent looks for workplaces that offer continuous learning opportunities. By providing & showcasing your commitment to technical training programs, you attract skilled professionals to your organization. This not only helps in reducing costly turnover but also strengthens your employer's brand.
The Bottom Line:
By upskilling your workforce, you're not just developing their technical knowledge; you're building a future-proof organization that thrives on innovation and employee satisfaction. That's a win-win for both – the organization and its employees.
III. Types of Technical Training Programs
Different jobs, different tools, different training! Here’s how industries shape their technical learning paths to match their unique needs:
1. Academic Certifications
- Companies can incorporate formal certifications (offered by universities or industry associations) as part of their technical training.
- For example, AI framework courses from MIT or Harvard—these provide foundational knowledge & often include a certification process. This helps employees build credibility & allows employers to identify qualified candidates.
- Of course, these are typically pursued by employees independently, outside of their daily work.
2. LMS Courses and Online Learning Portals
- With the rise of digital learning, online platforms have become a popular way to gain technical skills.
- Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and edX offer training in software development, data science, machine learning, and more.
- Employees learn at their own convenience as such courses are accessible worldwide, eliminating geographical barriers. Plus, they are generally more cost-effective than traditional education.
3. Just-in-time Training and Shadowing
- Some technical skills are best learned by doing! These hands-on methods help employees gain practical experience in real time.
- Just-in-Time Training delivers learning exactly when employees need it—right at the point of need. This is especially useful in software technical training, where tools like Digital Adoption Platforms (DAPs) provide just-in-time guidance through in-app walkthroughs, help articles, and videos, making sure employees get real-time support without disrupting their workflow.
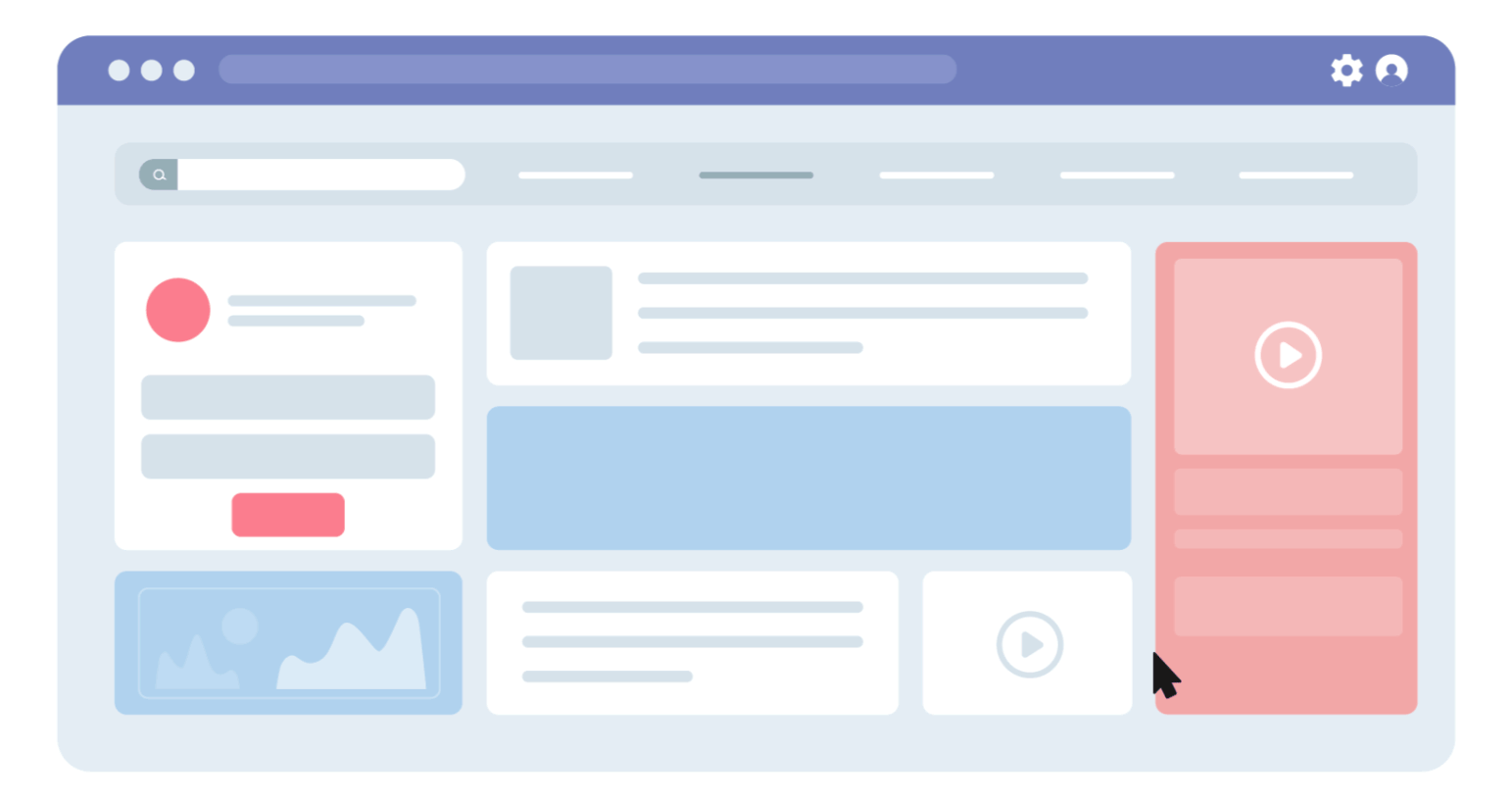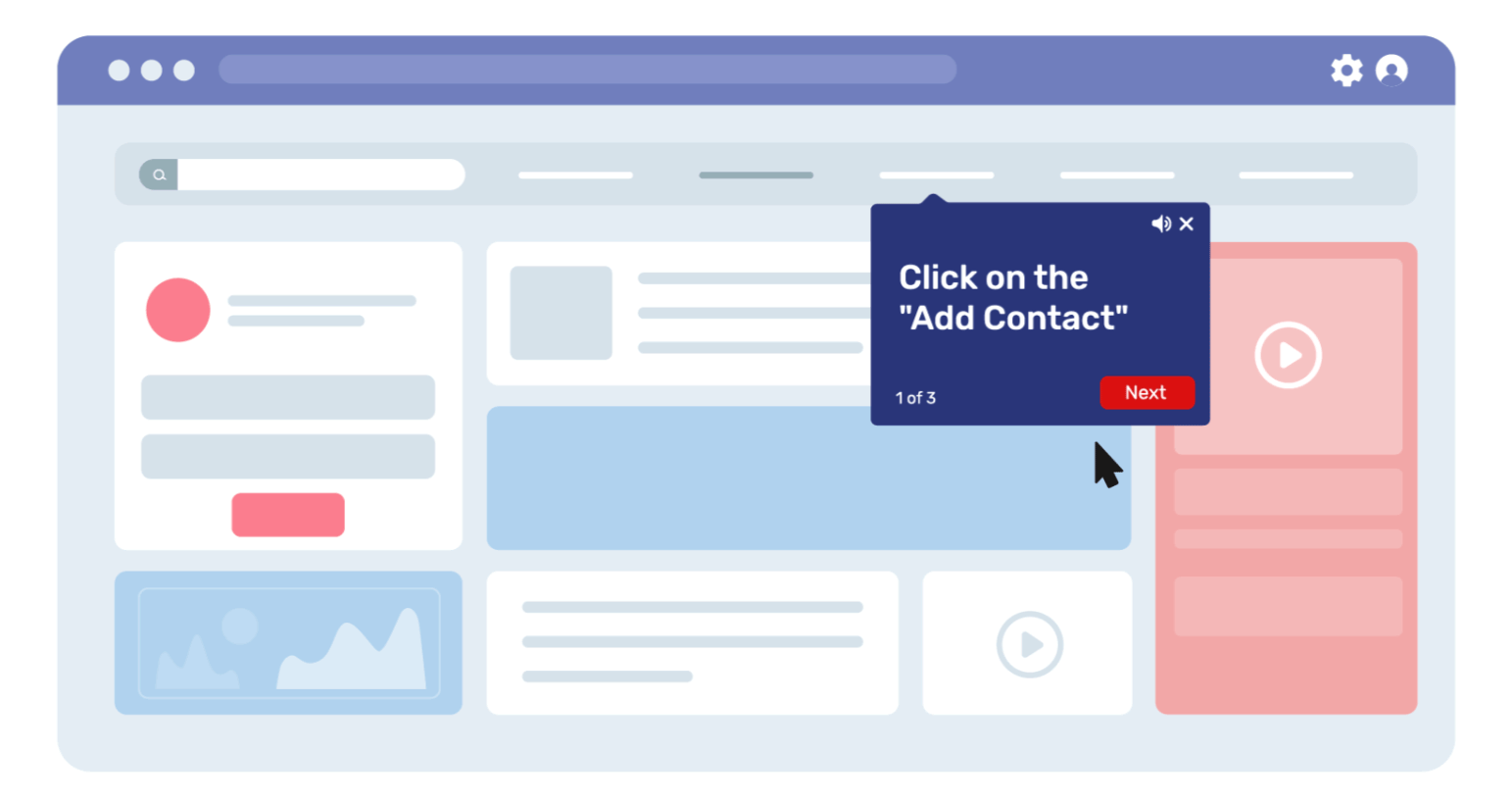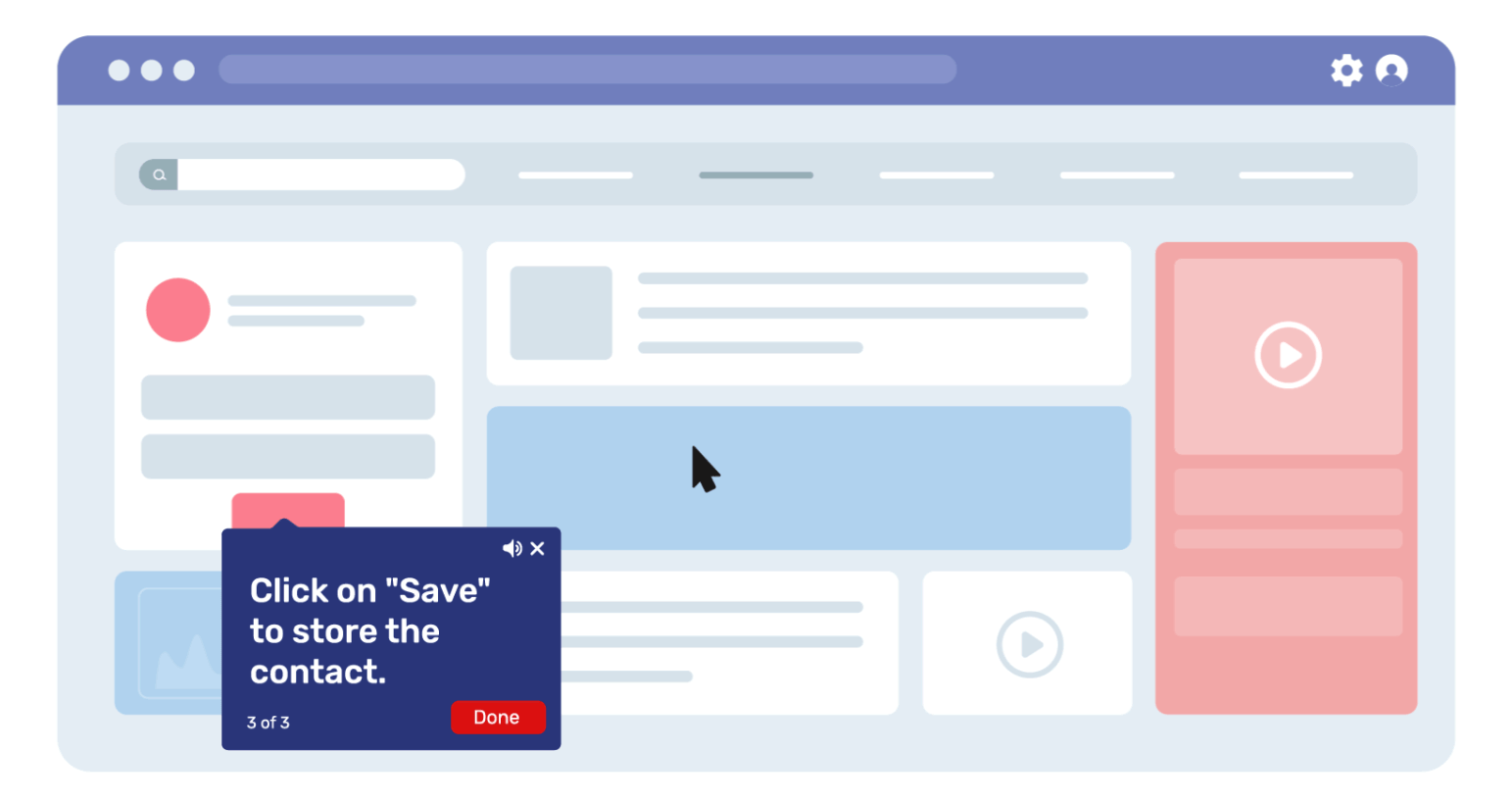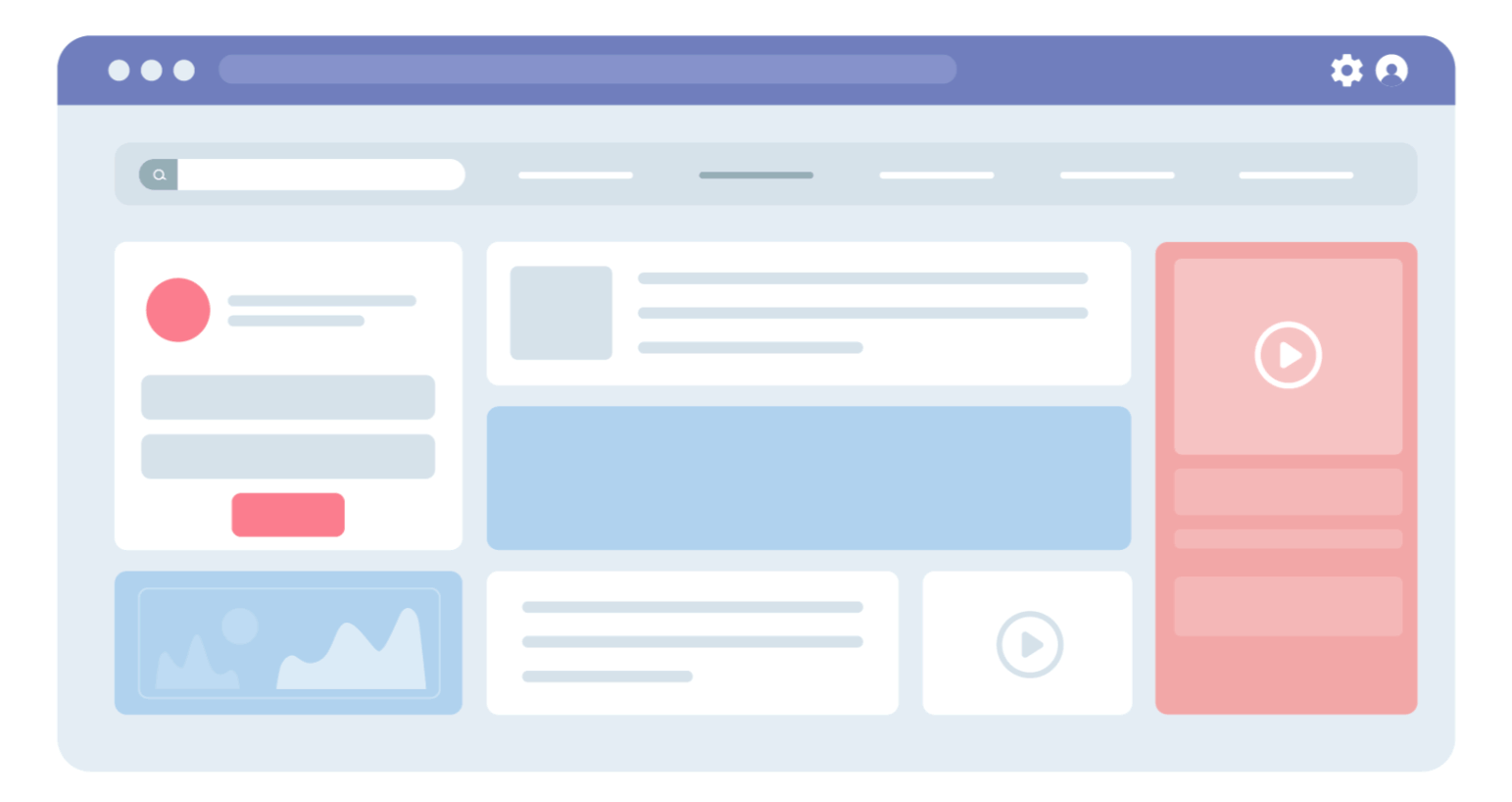
- Shadowing, on the other hand, allows employees to learn by observing experienced colleagues in action. By following a mentor through real work scenarios, employees pick up skills naturally.
- This is widely used in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and construction, where hands-on learning is crucial.
4. Simulations and Virtual Training
- Simulations and virtual environments are like on-the-job technical training—but without the real-world risks.
- They create safe spaces using technology, letting employees practice without worrying about costly mistakes. Perfect for high-risk fields like aviation, healthcare, and emergency response.
- Tech professionals can use AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud virtual sandboxes to practice cloud deployment, troubleshooting, and server management in real-world conditions.
- Surgeons and medical students use VR platforms like Touch Surgery to practice complex procedures before performing them on real patients.
5. Blended Learning
Blended learning combines multiple training methods to create a well-rounded technical learning experience for your team. Imagine you’re designing a year-long technical training plan for your marketing team:
- Months 1-2: Employees take structured courses through an LMS to build foundational skills in funnel strategies.
- Month 3: If they're struggling with the CRM, a Digital Adoption Platform(DAP) can provide in-app guidance and help them master the software.
- Later: If they need deeper SEO knowledge, offer an academic course or industry certification.
- Ongoing: Introduce new marketing trends through help articles or internal knowledge bases.
This blended learning mix keeps learning engaging, reinforces knowledge, and caters to different learning preferences.
IV. In What Situations Can Technical Training Be Useful?
1. Onboarding New Hires:
When new employees join a company, technical training helps them get up to speed with the tools, systems, and processes they’ll be using in their roles. It makes sure the transition to new role becomes easy and reduces the time it takes for them to become productive.
2. Skill Enhancement Programs:
When your employees are doing well but have even more potential, offering technical skills enhancement programs is a good idea. These programs can include specialized courses, workshops, or certifications in specific areas. For example, training employees on new AI advancements is becoming an important skill.
3. Advanced Training for Specialized Roles:
Advanced training is essential for high-level roles like Chief Information Officers (CIOs), Chief Technology Officers (CTOs), managers, and other leadership positions. These technical training programs help them sharpen their expertise and prepare for promotions or lateral moves within the company.
4. New Technology Adoption:
Employee resistance often arises when adopting a new technology or platform because it’s unfamiliar. However, with the right technical training, you can walk your employees through all the features, functionalities, and best practices. This helps them embrace and operate the new system accurately from the get-go.
5. Troubleshooting & Problem-Solving:
Remember the inevitable: technical glitches. They happen to the best of us, and when they do, it can grind everything to a halt. With on-the-job technical training, your team learns how to diagnose and resolve these issues quickly and independently. This frees IT resources, and keeps everything smooth.
V. How to Develop Great Technical Training
On the GydeBites L&D podcast, Cammy Wood, Global Learning Engagement Director at GoDaddy, shared her perspective on designing any training program. She says:
Creating training is simple when you focus on strategy and the various elements needed for an organization to adopt a learning mindset. At the same time, when you delve deeper, it becomes clear that it is a phased approach.
So, here are the key phases for designing a technical training program:
Phase 1/ Identify Training Needs in Technical Aspects
The first step is to pinpoint specific skill gaps in your organization. Here’s how:
- Conduct a Training Needs Analysis: Identify technical skill requirements for each role across departments.
- Assess Individual Skill Gaps: Use surveys, one-on-one interviews, manager feedback, and performance reviews.
- Observe Employees in Action: Monitor how they use software or equipment to spot areas needing support.
- Prioritize Training Needs: Differentiate between immediate (short-term) training and long-term skill development.
- Benchmark Against Industry Standards: Compare skills with industry best practices to identify key training areas.
By taking this multi-pronged approach, you'll makes sure your training program targets the right skills and delivers maximum impact.
Phase 2/ Develop SMART Training Objectives
With technical training needs identified, the next step is to set clear and measurable goals using the SMART framework:
- Specific: Define precise objectives that clearly state what trainees will achieve.
- Measurable: Determine how you will evaluate whether objectives have been met, such as through tests, performance evaluations, or project completions.
- Achievable: Set challenging yet attainable goals within the given resources and timeframe.
- Relevant: Ensure objectives align with the identified training needs and organizational goals.
- Time-bound: Establish a clear timeframe for achieving the objectives, which creates urgency and allows for tracking progress.

Creating SMART objectives makes sure your training program has a clear purpose and measurable success criteria.
Phase 3/ Embrace Technology for Enhanced Delivery
Today’s technical training uses technology-driven tools that simplify both training creation and delivery. Let’s explore a few:
1. Digital Adoption Platforms (DAPs)
We've already touched on DAPs in the context of just-in-time training, but they’re also a superior alternative to LMS for technical training on enterprise applications.
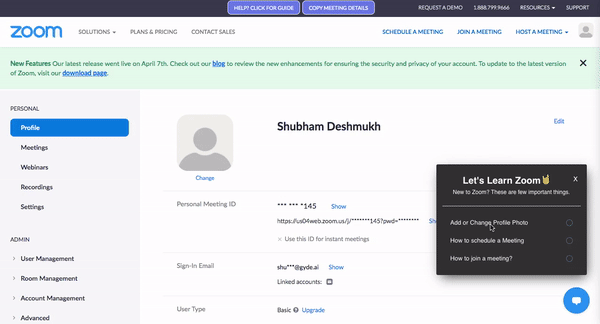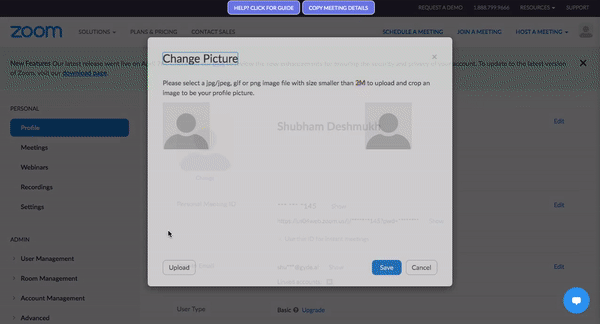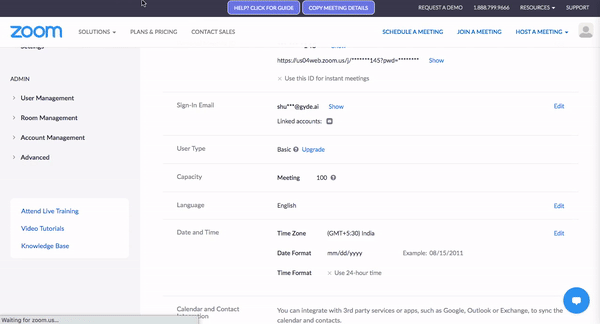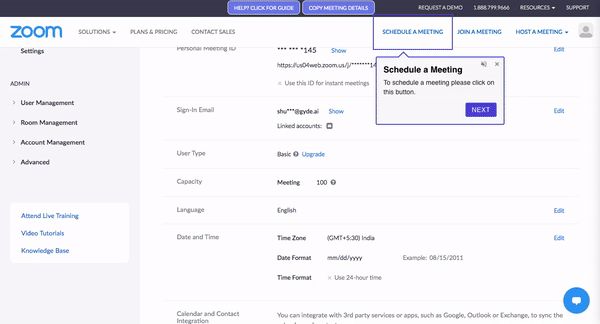
Take Gyde, for example. As an AI-powered DAP:
- It delivers contextual learning experiences through in-app walkthroughs, how-tos, and videos—right within the software interface.
- Its microlearning approach breaks down complex workflows, turning a 100-step process into manageable 20-step how-to guide.
- Plus, with its in-app assessments feature, users can quickly take a quiz on the process they just followed, reinforcing their process knowledge.
2. Learning Management Systems (LMS): An LMS serves as a centralized platform for employee training, enabling them to access courses, take assessments, earn certifications, and participate in discussion groups related to their learning topics. Key benefits include:
- Employees can access training anytime, anywhere.
- Track employee progress and measure training effectiveness with analytics.
- Automate course assignments, notifications, and compliance tracking.
(Check out the best LMS solutions)
Inclusion of Artificial Intelligence(AI):
- AI is being used across all training platforms today, simplifying how organizations create and deliver technical training.
- LMS platforms now come with AI-powered features that help trainers generate courses in minutes. With the rise of Generative AI, trainers can simply provide a brief on a topic, and AI instantly generates structured learning content.
- In Digital Adoption Platforms (DAPs) like Gyde, AI is integrated directly into the no-code walkthrough creator. Just open a software, click through a process on which you need to provide guidance, and AI auto-generates step-by-step instructions based on what’s on the screen. This saves a lot of time while creating technical training on applications.
Phase 4/ Create Easy-to-Understand Training Content
This phase may require significant effort, but it's crucial for creating impactful training. Although the content will vary based on technical needs, here are key principles to make sure it's great:
1. Replace traditional slide decks with diverse media formats such as:
- Use engaging video tutorials to demonstrate procedures and concepts visually.
- Allow trainees to practice skills in a simulated & hands-on environment.
- Apply game elements like challenges and progress bars to motivate employees to master the technical aspects of their job.
2. Focus on Clarity and Conciseness by:
- Breaking complex topics into manageable modules for easier understanding.
- Using clear, straightforward language and minimize technical jargon.
- Make comprehension better with visuals such as diagrams and screenshots.
3. Implement a quality assurance process with multiple checkpoints to make sure the content is:
- Accurate and up-to-date with current technical information.
- Aligned with the training objectives.
- Engaging and appropriate for the target audience.
By following these principles, you can develop training content that is not only informative but also engaging and easy for your employees to understand.
Phase 5/ Continuously Evaluate and Refine
Technical training is an ongoing process. To make sure your program adds real value, here are seven important factors to focus on when evaluating your technical training:
1. DAP Analytics for In-Workflow Learning: When using a Digital Adoption Platform (DAP), gain valuable insights into user behavior within the actual software application:
- Drop-off Points: Identify steps within step-by-step guides where users frequently abandon the process. This highlights areas requiring further clarification or simplification.
- Guide Popularity: Analyze which step-by-step guides are accessed most frequently. This can indicate areas where users struggle the most and need additional support.
- Software Usage Trends: Track weekly, monthly, and yearly usage trends for the software being trained on. This data can reveal areas where proficiency wanes over time, prompting refresher training or targeted interventions.
2. AI-powered Analysis: Explore the potential of AI to analyze large datasets from various sources (DAP data, LMS data, surveys, etc.). AI can identify trends, patterns, and knowledge gaps, providing actionable insights to optimize your training program.
3. Feedback Mechanisms: Gather valuable insights from participants and stakeholders through:
- Surveys: Conduct surveys to collect feedback on content clarity, instructor effectiveness, and overall program satisfaction.
- Focus Groups: Facilitate group discussions to delve deeper into participant experiences and identify areas for improvement.
3. Leverage LMS Data: If using LMS, use the detailed analytics provided by your LMS to track key metrics like:
- Learner Engagement: Measure time spent on modules, completion rates, and interaction levels.
- Knowledge Retention: Use quizzes, assessments, or post-training projects to gauge retention.
4. Performance Improvement: Track on-the-job application of skills through performance metrics or supervisor feedback.
Finally, Close the Loop:
Don't let feedback stay unheard. Share key findings with stakeholders and use them to refine future training initiatives. This will also build their trust in the upcoming technical training programs. This iterative process helps your program stay relevant and addresses evolving technical needs.
VI. Why use DAPs for Application-Based Technical Training?
Salesforce. SAP SuccessFactors. Workday. Whatever the platform, employees' technical proficiency directly impacts both their productivity and the application's return on investment.
To build this proficiency, organizations often rely on LMS courses, manuals, mentoring. But as a matter of fact, it’s external, time-consuming, and often forgotten when it’s actually needed.
However, with Digital Adoption Platforms (DAPs), training moves inside the software, happening in real-time, as employees work. No context switching. No long learning curves. Just instant, interactive guidance.
Take Gyde, for example. An AI-powered DAP that sits on top of any enterprise software and delivers your application end-users with:
- Audio-visual walkthroughs – To see exactly what to do, step by step.
- Context-sensitive help – To get the right guidance, at the right moment.
- Bite-sized videos – To watch recorded workflows for visual learners.
- In-app assessments – To check how well a process is understood.
As a result, businesses see:
- Less knowledge gaps – Every employee follows a standardized process.
- Full software utilization – No underused features. Higher Software ROI.
- Fewer IT/help desk tickets – Employees solve issues themselves.
What is an example of technical training?
Suppose a company switches to a new customer relationship management (CRM) system. This software keeps track of client interactions, but it can initially be a bit overwhelming. In this case, technical training would be a session (or maybe a series of sessions) designed to teach your team the new CRM. Employees will learn to enter new customer data, track sales opportunities, and generate reports. It would equip everyone with the skills they need to use this new tool and keep your client relationships running smoothly.
- What is the meaning of technical skills training?
Technical skills training focuses on the specific hard skills needed for a particular job. For example, a salesperson in financial services might need training on how to deliver a product demo for a new loan category. With the right training, they can present offerings more effectively, improve customer engagement, and boost productivity.
- What is the function of technical training?
Technical training bridges the gap between what employees know and need to know to excel in their roles. By providing instruction on specialized software, equipment, or procedures, it equips employees with the technical skills (like coding or data analysis) to work more efficiently and confidently.
This not only benefits employees with increased job satisfaction and career prospects but also benefits companies through a more competent workforce, improved problem-solving, reduced costs, and happier employees who are more likely to stick around.
- What is technical training in HR?
HR technical training equips HR professionals with the skills to use specialized HR information systems (HRIS) for managing data, analyzing trends, staying compliant, and leveraging recruitment tools and learning platforms. This tech-savviness allows HR to transform from administrative roles to strategic partners, using data to improve decision-making and the overall operations of the department.


