Insurance has been slow to embrace digital changes due to regulations, existing policies, and limited capital for newcomers. However, there is a positive trend emerging.
According to Statista, many companies in Europe (59%) and North America (55%) have already begun implementing their digital transformation plans, signaling a growing recognition of the importance of digital transformation in the insurance sector.
Let's take a step back and define -
Digital Transformation in Insurance means using innovative solutions and data-driven insights to optimize insurer operations, automate agent workflows, tailor customer offerings, and provide seamless services to the policyholders.
The ultimate goal is to adapt to the ever-evolving needs and expectations of policyholders, creating a customer-centric and agile environment.
In this blog, we are going to discuss:
- The Plus Factors of Digitization in Insurance
- Challenges in the Insurance Landscape
- Key Trends in Insurance
- Rise of Insurtech
- How Gyde Makes Digital (& AI) Transformation Work in Insurance
The Plus Factors of Digitization in Insurance
A. More Opportunities for Personalization
Gone are the days of insurance being a dull and distant sector. With the rise of digital technology and data analytics, insurers now have the power to connect with their customers truly.
You are no longer unaware of your customers’ important life events – when a policyholder decides to sell their home, insurers can offer personalized solutions. Imagine sending tailored insurance options for a new home, auto, or life insurance plan to ease your customer’s mortgage burden.
And your customers won't have to wait long to get their queries addressed as a smart AI-powered chatbot is available 24/7 – that means better customer satisfaction and superior business growth.
To sum it up, digital transformation in insurance gives you the opportunity to create customer-centric, personalized solutions and stay ahead of the curve.
B. More Savings on Claims Journey
The conventional claims process typically involves the following:
- reporting the loss,
- handling the claim,
- evaluating the damages, and
- finalizing the settlement.
Unfortunately, this process often suffered from drawbacks like lengthy processing times of around 20 days and a lack of transparency, resulting in reduced customer satisfaction, increased costs, and limited scalability.
With the digitally evolving landscape, significant improvements have been made. For instance, reporting a loss can now be completed swiftly within a mere three minutes through online platforms.
Additionally, introducing detection facilities enables insurers to identify high-severity claims automatically directed to the appropriate process, making claim handling much simpler.
Moreover, real-time processing and rapid cash settlement procedures have reduced settlement times to two hours.
In short, by accomplishing more in less time, these advancements save valuable resources such as time, energy, and money, allowing insurers to focus on other important tasks.
C. More Innovation on Products
Established insurers, enjoying a dominant market position, often lack the drive to innovate or take risks due to limited competition and a secure foothold.
On the other hand, insurance startups struggle to challenge established players as they grapple with the need for substantial capital to mitigate risks, impeding their ability to make bold moves or significant investments.
While applying digital transformation in insurance, established insurers can enhance efficiency and customer experience by supporting online claims reporting, AI-driven automated underwriting, and user-friendly mobile apps.
Simultaneously, startups can seize untapped markets by leveraging digital technology to create new insurance products that cater to emerging customer needs.
For instance, consider the case of Airbnb, where homeowners became hosts and ventured into the hospitality industry. Customers here sought coverage for risks related to property damage, liability, and other issues that might arise when sharing assets or providing services.
D. More Security on Risks
Digital transformation in insurance brings forth new risks, but it also paves the way for secure solutions by leveraging the power of data. Despite the apparent contradiction, the transition to digital systems enables us to address risks effectively.
These risks encompass cyber threats, fraud, data breaches, operational inefficiencies, business disruptions, reputational damage, and non-compliance with regulations.
Companies must embrace innovation, invest in cyber risk understanding, and forge collaborations with experts to thrive in this digital landscape. By developing robust risk measurement frameworks, they can establish successful lines of business in this domain.
Furthermore, insurance firms employ backup and recovery systems, redundant infrastructure, and contingency plans for critical processes. They also utilize data privacy and compliance tools to ensure adherence to regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. These tools facilitate secure data handling, consent management, and automated compliance monitoring.
To sum up, digital transformation in insurance introduces risks, but with the right strategies and technologies in place, we can overcome them and achieve greater security.
Challenges in the Insurance Landscape
A. Changing customer journeys
Shifting from established, traditional processes to digital customer journeys requires change management efforts – ensuring smooth adoption and acceptance among your employees, agents, and customers.
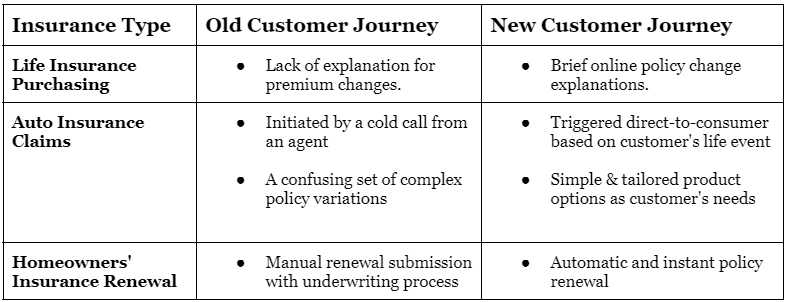
No doubt, the new customer journey is more efficient, but the real challenge lies in learning and using these new digital processes, as they can be a bit tricky to grasp at first. This can lead to reluctance from your employees. But don't worry, there are strategies to help you overcome this resistance to change.
B. Legacy systems and infrastructure
Aside from improving customer journeys, there is another challenge you will face - IT infrastructure and legacy systems.
IT infrastructure is the broader concept that encompasses all the technology and resources needed for an organization's IT operations. At the same time, legacy systems are a subset of that infrastructure, referring specifically to older and outdated components or software that may need to be upgraded or replaced.
To address these challenges, companies often prioritize enhancing their IT infrastructure. This entails adopting modern technology, such as cloud-based systems, implementing automated testing, and leveraging reusable software components.
Additionally, they need a flexible layer that seamlessly connects customer-facing applications to their core systems.
C. Regulatory and compliance considerations
Cybercrime is a growing problem, and businesses and consumers face increasing risks. The amount of money lost to cybercrime has almost quadrupled in just a few years, going from $112 billion in 2012 to over $400 billion in 2015.
This is a significant concern, especially for industries like insurance and banking, which have strict regulations to ensure security and protect customers.
Insurers must navigate a complex landscape of privacy and data protection regulations when transitioning to digital customer journeys. They must ensure compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
You can use robust cybersecurity and risk management measures to protect customer data and prevent cyber threats. Meanwhile, many companies in the insurance industry recognize that automation can be a cost-effective and efficient way to address compliance issues.
The only tip here is to proceed with caution.
7 Key Trends in Insurance
1. IoT
The IoT, which refers to the interconnected network of devices and sensors, offers great potential for insurance companies. By using these connected sensors, insurers can give a superior level of monitoring that enables you to make more informed decisions and provide better services to the customers.
As a matter of fact, the number of internet-connected devices in the IoT is rapidly increasing. In 2008, there were 12.4 billion such devices, and by 2025, it is estimated that there will be more than 50 billion.
These devices, equipped with sensors connected to various objects or even worn by people, can collect vast amounts of real-time data. This data can be analyzed and responded to without human intervention, transforming how companies operate in many industries, including insurance.
For insurers, the IoT presents opportunities and threats to their business models. It offers new ways to interact with customers and gather valuable data. However, to succeed, insurers need to forge partnerships, scale their operations, and embrace the potential of the IoT quickly.
2. Blockchain
Imagine a shared, public ledger that records transactions and is open for everyone to see but cannot be controlled by any central authority. This is what blockchain is. It has been described as a "machine for building trust" by The Economist newspaper.
Here's how blockchain works: When a transaction occurs, such as selling a ticket, a new data block describing the transaction is added to a chain. But this addition can only happen after all the relevant participants agree on the validity of the action. For example, before a ticket is sold, there must be a consensus that the seller is the rightful owner.
Features of Blockchain in Insurance -
- It is decentralized, replicated on multiple nodes, ensuring no single point of failure.
- Data stored in the blockchain is immutable, making it difficult for hackers to tamper with.
- Encryption with digital signatures authenticates participants and their actions, ensuring secure identification and data registration.
Blockchain eliminates the need for customers to provide personal data for verification repeatedly. Once the data is verified, customers can grant access using a private key. This ensures privacy and prevents sharing with third parties without permission.
3. Advance Analytics
By employing advanced analytics throughout the value chain, insurers can prevent high-cost cases, identify market micro-segments, and provide interactive and personalized underwriting.
Insurers are increasingly using advanced analytics to make better decisions. For example, some auto insurers use credit scores to assess risk more accurately. They have discovered that people who pay their bills on time are safer drivers. Similarly, life insurers are leveraging social networks and geographical data to reduce fraud by up to 25 percent.
In what ways does Advanced Analytics help?
- Predict fraud,
- Control claims costs,
- Identify total loss cases,
- Optimize handling costs,
- Predict litigation, and
- Estimate the severity of bodily injury cases.
4. Artificial intelligence (AI) and Machine learning (ML)
Machine learning allows algorithms to learn from data and adapt to new situations without explicit programming. It's like teaching the algorithm through experiences and giving it a strategy to learn independently.
In the current scenario of digital transformation in insurance, AI/ML solutions have emerged at top, compelling insurers to do more than just predictions and outcome forecasting.
Insurers can use it for classification, such as identifying images, making connections between data, and even generating new information. For example, machine learning algorithms can fill in missing data or generate the next frame in a video sequence.
A great example of AI in insurance is Lemonade, a New York-based start-up. They use an AI-powered conversational chatbot to recreate the experience of texting or messaging with an agent. This chatbot delivers personalized sales recommendations and instantly issues policies. It provides customers with a seamless and tailored experience, making insurance more accessible and convenient.
5. Robotic process automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software to perform tasks in a process just like a human would. It’s like a robot that excels at repetitive tasks quickly, accurately, and tirelessly so that humans can focus on activities requiring emotional intelligence, reasoning, judgment, and customer interaction.
RPA is transforming the way processes are handled for digital transformation in insurance. Imagine a scenario where 500 premium advice notes need to be processed. In the past, it would take two days to complete this task. However, with RPA, it now only takes 30 minutes.
Here's how it works: Various brokers write business for clients, and their information needs to be gathered into a central repository. RPA manages the process, transferring the premium advice notes from the brokers to the repository.
Automation through RPA is a cost-effective and efficient solution for insurers, especially in highly regulated industries like insurance and banking. Compliance with regulations becomes easier and faster with automation.
Additionally, RPA enhances customer service by empowering staff to handle more complex inquiries while the software handles routine customer requests.
6. Strategic IT Modernization
Insurance companies are adopting a bimodal approach that combines "digital IT" and "foundational IT" to meet customer demands and achieve operational excellence.
In digital IT, traditional sequential software development is being replaced by agile methods. This allows teams to work in sprints, quickly delivering innovative features and products in response to customer needs. By embracing agility, insurers can keep pace with market changes and release new offerings more efficiently.
However, insurers must address their core platforms to transform their operations truly. Many incumbents still rely on outdated systems written in languages like COBOL or PL/I, which lack the speed and flexibility required for digital business.
A digital operating model is essential for success in this modernization journey. It revolves around agile ways of working and collaborating internally and externally with partners and vendors.
Upgrading IT capabilities is a comprehensive process encompassing architecture, applications, infrastructure, processes, and operating models. It requires long-term commitment and significant investment, potentially taking up to five years to fully implement.
7. Cultural Change
According to McKinsey research, the biggest challenge in pursuing digital transformation in insurance is cultural or behavioral change.
Fair enough, culture takes time to root and doesn’t happen overnight. But how can you go about it?
- Collaboration - Traditional hierarchical structures can hinder innovation and slow down development. By forming small, cross-functional teams and adopting an agile approach, insurers can accelerate their pace and reduce development time. This allows for faster decision-making and more efficient responses to customer needs.
- Customer-centricity - Insurers should prioritize the customer's perspective instead of solely focusing on business goals or competitor strategies. Considering how decisions create value for the customer becomes a fundamental part of the decision-making process. By shifting the focus to the customer, insurers can improve their products and services to meet customer expectations better.
- Adopt an Entrepreneurial mindset - Achieving cultural change often requires starting fresh and thinking like a start-up. It means breaking free from old rules and traditional ways of doing things. Embracing innovation and exploring new technologies like cloud computing can enable insurers to move quickly and adapt to the rapidly changing digital landscape.
Rise of Insurtech
The rise of InsurTech has been fast and, in many ways, inevitable.
Digital-first insurers and aggregators entered the market without legacy systems, manual workflows, or deeply entrenched processes. That freedom allowed them to adopt technology early, scale quickly, and grow revenue faster than traditional insurers.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this shift. As customers moved online and agents worked remotely, digital insurance platforms met demand with frictionless onboarding, faster policy issuance, and aggressive digital distribution.
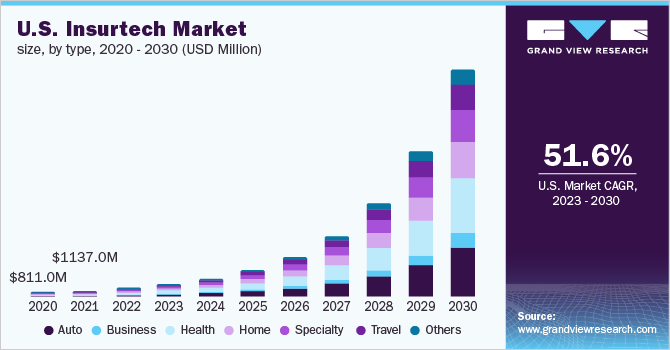
Convenience became the baseline expectation.
Investor confidence followed. Venture capital poured into InsurTech, with billions invested in a single year, signaling belief not just in digital insurance, but in insurance built natively for modern workflows.
But this success also exposed a new gap.
As InsurTech matured, scale introduced complexity. Compliance requirements tightened. Risk models grew more nuanced. Human judgment, exceptions, and regulatory nuance began to matter as much as speed.
What separated leaders from the rest was no longer who was digital but who could operationalize intelligence specific to their business, their data, and their regulatory reality.
Pivot your way ahead
Digital transformation in insurance is an execution question. As systems grow more intelligent, the margin for human inconsistency shrinks.
The insurers who succeed won’t be the ones who adopt the most tools but the ones
who ensure every tool is used correctly, consistently, and confidently.
Transformation doesn’t fail because teams resist change. It fails when change isn’t designed for how work actually happens.
That’s the gap modern insurers must close.
How Gyde Makes Digital (& AI) Transformation Work in Insurance
Digital transformation in insurance rarely fails at intent. It fails when AI systems meet workflows, regulatory pressure, and human judgment.
Gyde focuses on that execution layer. Here's how:
Identity & Onboarding: Reducing Risk From the First Interaction
Customer onboarding is one of the highest-risk moments in insurance. Manual document checks, fragmented sanctions screening, and inconsistent risk assessments slow down growth and increase compliance exposure.
Gyde’s KYC/AML Verification Agent embeds AI directly into onboarding workflows. It verifies identity documents, cross-checks global sanctions and PEP databases, and produces audit-ready decisions in minutes without forcing teams to change how they work.
Underwriting & Risk Decisions: Speed Without Sacrificing Rigor
Underwriters are expected to move faster while handling more data and tighter scrutiny. Traditional AI tools either oversimplify risk or overwhelm users with outputs they can’t trust.
Gyde’s Loan Underwriting Co-Pilot supports underwriters with structured analysis, clear risk signals, and explainable recommendations. Human judgment stays in control, while decisions become faster, more consistent, and easier to defend.
Customer Communication: Preventing Compliance Issues Before They Happen
Even after decisions are made, compliance risk remains high. Customer emails and disclosures are often written under pressure and reviewed too late.
Gyde’s Brand-Safe Email Agent reviews outbound communication in real time, flagging risky language, missing disclosures, and tone violations before messages are sent, preventing issues instead of reacting to them.
Bottomline:
Across onboarding, underwriting, and communication, Gyde applies one principle: intelligence only creates value when it is embedded into actual workflows and governed from day one.
That’s how Gyde helps insurers move from isolated AI pilots to production-ready systems they can trust.
Book a 20-min demo to see how it can apply to your enterprise needs!
FAQs
What is meant by “business-specific intelligence” in insurance?
Business-specific intelligence refers to AI systems that are trained and constrained by a company’s own data, policies, workflows, and risk tolerance. In insurance, this means AI that understands underwriting logic, claims processes, regulatory constraints, and human judgment rather than relying on generic assumptions or public data alone.
Why is generic AI risky for regulated industries like insurance?
Generic AI systems are trained on broad data and lack awareness of industry-specific rules, policies, and compliance obligations. In insurance, this creates risk because decisions must align with regulatory frameworks, internal underwriting rules, and documented processes. When AI operates without this context, it can generate outputs that are technically correct but operationally or legally invalid.
When should an insurance company consider investing in enterprise AI systems?
Insurance companies should consider enterprise AI systems when:
- AI pilots are failing to scale
- Compliance and audit risk is increasing
- Data quality issues are impacting outcomes
- Manual decision-making is slowing growth
- Existing systems cannot adapt fast enough
At this stage, the problem is lack of operational intelligence (which indeed could be solved by use of enterprise-grade AI agents).
What is the impact of digitalization on the insurance industry?
The impact of digitalization on the insurance industry includes enhanced customer experience, improved operational efficiency, advanced data analytics, product innovation and customization, enhanced risk management, and increased collaboration and partnerships.
What is the term used to describe IoT in the insurance industry?
The term used to describe the uses of IoT (Internet of Things) in the insurance industry is "IoT insurance" or "insurance telematics." It involves using connected devices, such as sensors and trackers, to collect real-time data about insured assets or individuals. Insurance companies then utilize this data to assess risks, personalize insurance offerings, determine premiums, and enhance the overall insurance experience.
For example, in auto insurance, IoT devices installed in vehicles can monitor driving behavior, including speed, acceleration, braking, and location. This data enables insurers to provide usage-based insurance policies, where premiums are determined based on actual driving habits rather than general assumptions.

