Learning agility is the MOST-DESIRED skill among corporates. Yet, L&D and HR leaders find it difficult to instill it in their teams.
The rationale behind this challenge is hidden in the current landscape, where employees are bombarded with an excess of information from diverse sources—be it online courses, in-person workshops, or endless documentation.
A fair question arises – How can we expect our already-busy employees to soak up this wealth of knowledge without feeling lost and unmotivated?
Think about athletes. They invest substantial time in practice, forging muscle memory for peak performance.
In a parallel fashion, learning agility is about integrating adaptability, decision-making, and problem-solving as a part of training initiatives. So that employees can better deal with difficult situations and information overload.
In this blog, we'll explore the concept of learning agility and share some practical tips for implementing, improving, and measuring it at your workplace.
Let's dive in!
What is Learning Agility in the Workplace?
Learning Agility is an individual’s ability to be flexible, curious, and quick while addressing new challenges and ambiguous work situations. Embedding it into your organization's framework requires time, resources, and, most of all, patience.
L&D teams looking to foster this intangible skill into the learning culture might have to deviate from the original plan and incorporate new practices into employee training.
At its core, learning agility begins with oneself. It involves creating space for both learning and unlearning. In simpler terms, for learning to be effective, it's essential to apply theoretical knowledge practically, ensuring that the learning process is not just memorization but a pathway to new possibilities.
Core Components of Learning Agility
Your employees will have to develop flexibility competency where they can set goals in any unfamiliar situations where they may not know what to do. In such moments, they have two choices: waiting for a solution to emerge or taking the initiative to find a solution on their own.
Our focus is on the latter option because that's what learning agility is all about. To grasp this concept, let's break it down into four core components:
Mental Agility (Quick Thinking Skills)
- This component assesses learners' ability to generate innovative solutions when facing challenges swiftly.
- For instance, consider Jenny, the new project manager with mental agility. Confronted with stakeholders requesting additional features beyond the initial project scope, she can make a series of sound decisions to recalibrate her timeline.
- Leveraging self-awareness and reflection, Jenny identifies necessary changes and support to maintain progress. She can learn, unlearn, and relearn to change in response to new information.
Change Agility (Adapting to Change)
- Employees showcasing change agility, like Jenny, thrive on curiosity and experimentation. Despite facing a surge of last-minute tasks, they remain resilient and open to changes.
- For both managers and frontline representatives, possessing the ability to adapt to change is crucial because they're the ones who deal directly with customers and clients.
- By using different diverse change management tools and techniques, they can confidently deal with challenges and make things more organized and efficient, even when everything seems chaotic
People Agility (Getting Along with Others)
- Considering Jenny's handling of communicating changes to her team showcases her exceptional people agility. Dealing with diverse individuals and potential resistance to change, she opts for open communication, listens to concerns, and makes herself available for addressing issues.
- People agility involves strong interpersonal skills, including collaborating effectively.
- Individuals with this quality are open to feedback, learn from others' experiences, and work well with various people.
Results Agility (Achieving Goals in Any Situation)
- By the end, Jenny does a great job overcoming challenges, successfully incorporating additional features that elevate the project's value and functionality.
- This achievement showcases her results agility— an ability to succeed despite challenges.
- The project's success is gauged through stakeholder satisfaction, adherence to the timeline and budget, user engagement, deliverable quality, team productivity, positive market response, and return on investment (ROI).
How does learning agility differ from traditional learning approaches?
- Employees acquire relevant skills on the job.
- Organizations implementing this approach recognize the value of informal and experiential learning rather than monotonous learning.
- It combines a holistic set of cognitive, interpersonal, and emotional skills.
- It’s a lifelong habit that trainers need to include in their training initiatives rather than a one-time event or presentation.
Why does Learning Agility matter?
Because:
- Your team becomes more adept at handling new and unfamiliar situations.
- They don’t resist change and also actively participate in company initiatives.
- With new-found flexibility and resilience, they bounce back quickly from setbacks and challenges.
- Their productivity levels peak when they apply new knowledge and skills to their roles.
- Organizations can experience an overall performance boost by gaining confidence, taking calculated risks, and infusing creativity into their tasks.
- The focus on learning agility helps organizations turn team members into leadership roles as they progress in their careers.
The ultimate benefit will be seeing your organization grow and sustain for longer.
Learning Agility Examples
Here are various instances showcasing the importance of learning agility as a skill in your workforce:
New Technology Adoption
Amidst numerous tech applications, cultivating learning agility empowers employees to grasp new tools swiftly. To support this, leadership can provide in-app assistance like tooltips and guides. This approach ensures employees quickly familiarize themselves with the new tools, becoming agile learners on the job.
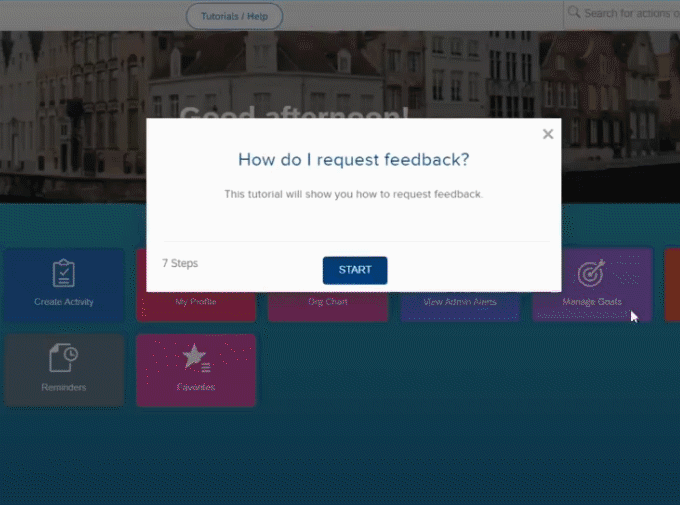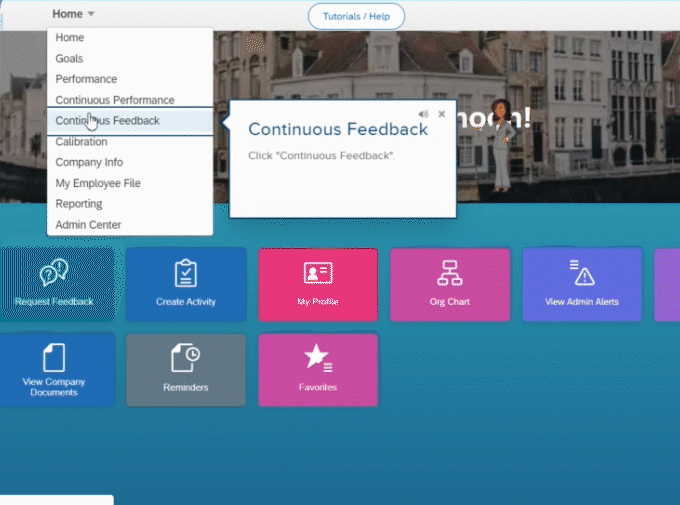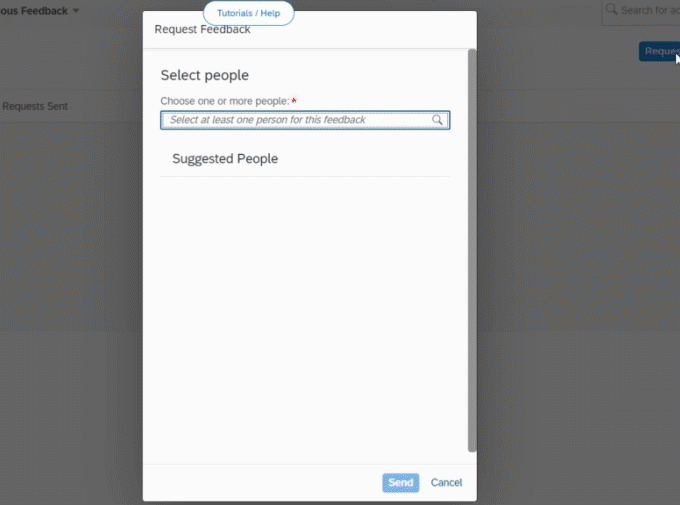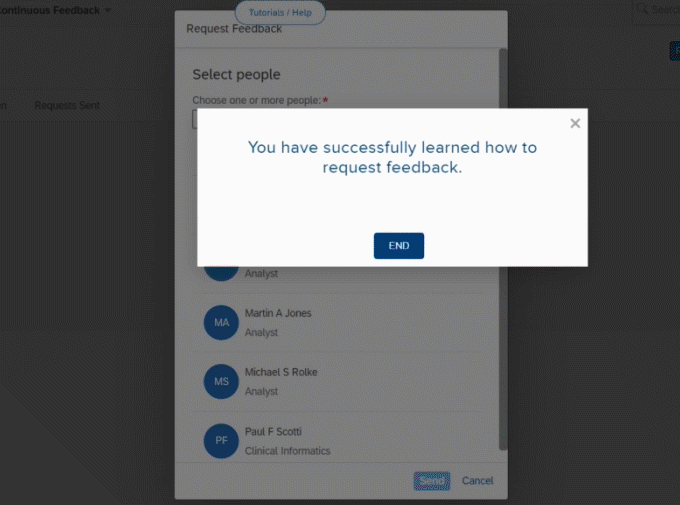
With instructional guides, as illustrated in the above image, employees can absorb new information seamlessly as they navigate through their work tasks.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Understanding and appreciating colleagues' perspectives from diverse departments makes learning more appealing and agile for employees, leading to continuous expansion of their skill sets.
This sense of cross-functional collaboration, facilitated by contemporary tools such as Google Workspace or Slack, closes communication gaps and promotes efficient collaboration towards shared objectives.
Leadership Development
Leadership isn't an inherent trait; it's cultivated through experiences. To naturally foster more individuals into leadership roles, harnessing learning agility can have long-term benefits for your organization.
For L&D heads, this can mean encouraging individuals to seek feedback actively, reflect on their experiences, and promptly adapt their leadership styles to meet the evolving needs of their teams and the organization.
Crisis Management
In the face of a sudden market shift, the ability of employees to swiftly gather pertinent information, analyze it, and mitigate the impact becomes crucial for an organization.
This involves a skillful filtering process where they retain essential information, discarding what doesn't contribute to their understanding. Such quick response mechanisms are vital for effectively addressing unforeseen challenges.
Customer Service Improvement
To boost customer service, representatives must effectively handle multiple tasks, including attending to customers and managing data. Familiarity with tools becomes invaluable in such scenarios, enabling reps to adapt their approaches on the fly.
To make them self-dependent in solving customer queries, you can include in-app knowledge bases(illustrated above), resulting in more effective interactions and heightened customer satisfaction.
Practical Tips to Measure Workplace Learning Agility
1. Use Skill Taxonomy to Identify Gaps
It's easy to say, "hire people who can adapt," but the details on "how" are often overlooked. With skill taxonomy—a powerful tool that leaders and managers can use to streamline the recruitment and training process systematically.
This involves a comprehensive compilation of both hard and soft skills, spanning from interpersonal communication to specialized competencies tailored to various organizational roles.
As a matter of fact, almost 89% of L&D professionals emphasize the significance of tracking skills data. This helps to actively improve current employees' skills, ensuring they're ready for the changing demands of work in the future.
2. Take Learning Agility Assessments
Initiate a structured approach to assess learning agility by incorporating the IBM Learning Agility Assessment for your employees. Using psychometric tests, this tool objectively measures cognitive abilities, attitudes, personality, and knowledge, comprehensively evaluating their learning competency.
This way, you can create a culture of self-assessment among employees to enhance awareness of their learning strengths and identify areas for improvement. Harness the power of AI-driven coaching and feedback tools to provide real-time support and guidance.
This dynamic feedback loop accelerates skill development and swiftly addresses skill gaps, fostering a culture of agility and continuous improvement within your workforce.
3. Measure with the Right Performance Metrics
Effectively gauging learning agility hinges on the thoughtful definition of tangible and intangible metrics.
Tangible metrics, being quantifiable, encompass aspects like enhanced task efficiency, project completion rates, and decreased error rates. In contrast, intangible metrics, challenging to express numerically, encapsulate attributes such as heightened problem-solving capacities, creativity, and adaptability.
Outlined below are key performance metrics tailored to assess learning agility:
- Cross-functional collaboration (demonstrating a capacity to absorb insights from varied perspectives)
- Learning Speed in Task Execution (showcasing adaptability and swift learning)
- Problem-solving capabilities (underscoring their ability to navigate complex problem scenarios)
- Willingness to Take Innovative Risks(reflecting an openness to learning through experimentation)
- Mistake-Resilience(highlighting the resilience and a commitment to continuous improvement)
Practical Tips to Improve Workplace Learning Agility
1. Define Clear Objectives and Prioritize
Clearly, articulate learning objectives aligned with organizational goals. For example, if your goal is to improve the customer service experience given by your reps, the learning objectives should focus on specific skills or knowledge related to customer interactions.
Once all objectives are outlined, approach each identified need systematically. Prioritization becomes a key factor at this stage, and seeking guidance from your superiors can be invaluable in setting these priorities.
2. Craft Personalized Learning Maps for Employees
In the era of information, precision in delivering knowledge to employees is vital. Personalization is the key here. Offer learning resources in various formats tailored to individual needs. Take the time to understand how your team likes to learn and then design training plans accordingly. You can also add short, focused learning modules that cater to busy schedules and support just-in-time learning needs.
For instance, in implementing a new CRM system, boost the chances of agile learning by developing role-specific help guides that come with built-in contextual experiences for users.
3. Explore Neuroplasticity for Agile Learning
Learn about neuroplasticity to create top-notch learning programs that make the most of how our brains work. Use proven techniques like spaced repetition, gamification, and hands-on experiences to boost the brain's ability to learn and adapt.
Also, encourage a growth mindset among your team, reminding them that skills can grow with practice and hard work. Encourage a culture where learning from mistakes is not only accepted but embraced. One-on-one meetings, addressing both positive and challenging aspects of projects, contribute to the continuous growth of agile learners within your organization.
4. Embrace Tech for Smarter Learning
According to a LinkedIn Learning Report, a big focus for managers in 2023 is role-specific digital upskilling and digital transformation.
To nail this, go for adaptive learning platforms. They adjust difficulty and suggest resources based on how well each person does. Moreover, integrating Gen-AI capabilities within the technological infrastructure expedites the process of learning material creation, saving you time when developing training programs.
Also, remember to pick the right tech. The tech you choose should have robust analytics features, giving you detailed info and showing if your team is quickly picking up the software skills you invest in.
Potential Challenges Implementing Learning Agility
Bringing learning agility to the workplace has its challenges. Let's take a closer look at what these challenges could be:
- Resistance to Change:
Employees may resist changes to traditional learning methods. There might be a reluctance to embrace new technologies or methodologies, especially if the existing approaches have existed for a long time.
The antidote – Clearly communicate the benefits of learning agility, addressing concerns, and showcasing success stories. Involve employees in decision-making and provide adequate training and support to ease the transition.
- Leadership Buy-In:
Without support from leadership, initiatives to enhance learning agility may lack direction and momentum. Leaders might not see the immediate value or may be resistant to investing resources in what they perceive as non-core activities.
The antidote – Advocate the strategic importance of learning agility for organizational competitiveness. Provide leaders with data and case studies demonstrating the positive impact of a learning-agile workforce. Engage leadership in the planning and decision-making process to secure their commitment.
- Technology Integration Issues:
Integrating new technologies into learning programs may face technical challenges, including compatibility issues, security concerns, and a learning curve for both employees and administrators.
The antidote – Conduct thorough technology assessments before implementation. Provide comprehensive training for users and administrators. Work closely with IT departments to ensure smooth integration and address security concerns. Pilot new technologies before full-scale implementation to identify and resolve potential issues.
- Lack of Resources:
Limited budget, time, and manpower can hinder the development and implementation of effective learning agility programs. This may result in suboptimal resources allocated to training initiatives.
The Antidote – Prioritize learning initiatives based on their impact on organizational goals. Explore cost-effective solutions and advocate for increased budget allocation by showcasing the long-term benefits of a more agile workforce.
- Time Constraints:
Employees may perceive learning activities as time-consuming, especially in fast-paced work environments with competing priorities and deadlines.
The Antidote – Integrate learning into daily workflows to minimize disruptions. Implement microlearning strategies, breaking down content into smaller, manageable modules. Emphasize the immediate benefits and long-term gains of investing time in learning agility.
Experience Agile Application Training & Onboarding with Gyde
Gyde is a smart digital adoption platform designed to easily integrate learning agility into adopting new application software. As a result, your employees will be engaged with the tech stack during training and onboarding, and you will see quick returns on your application investment.
Gyde simplifies in-app training through interactive step-by-step guides. It sits within your existing or new software applications, appearing discreetly in the screen corners with a help icon. Anytime your employees need instant assistance, Gyde will show them the way!
Plus, it's a no-code platform, so anyone who knows the application can create training materials with a simple drag-and-drop interface.
Here's how Gyde turns your workforce into agile learners:
- Provides interactive walkthroughs with audio-visual cues, enabling employees to navigate any application at an accelerated pace.
- Gives access to a repository of help articles containing self-help information, addressing common queries that typically require additional IT support.
- Includes a 'what’s new' section, informing users about new updates within an application effortlessly.
- Offers backend analytics to identify how many users have engaged with resources and pinpoint dropoff points for quick modifications.
- Ensures multilingual support by converting all help content into various languages. This eliminates the need to create resources from scratch, allowing employees to learn in their native language.
Take advantage of a free demo with one of Gyde's learning experts to make your organization's learning strategies more agile and adaptive!
FAQs
What is the difference between learning agility and learning ability?
Learning Agility is quick adaptation, transfer of skills, and proactive learning from experiences. Meanwhile, Learning Ability is the general capacity to acquire new knowledge and skills.
What are the characteristics of an agile employee?
- Adaptability: Easily adjusts to change.
- Proactive Learning: Actively seeks learning opportunities.
- Open-Mindedness: Values diverse perspectives.
- Resilience: Bounces back from setbacks.
- Collaboration: Works effectively in diverse teams.
- Initiative: Takes the lead in proposing solutions.
- Effective Communication: Clear communication tailored to the audience.
- Customer-Centric Focus: Prioritizes understanding and meeting customer needs.
How can you implement learning agility within a large workforce?
By incorporating a Digital Adoption Platform into the implementation strategy, organizations can provide a more intuitive and user-friendly learning experience, promoting digital literacy and learning agility across a large workforce.
Conduct a thorough assessment of current skill sets, identify learning needs, and understand the organizational context. Integrate the DAP with the learning management system (LMS) for a seamless learning experience. Leverage the DAP to guide employees through the use of new technologies, ensuring a smoother adoption process.

